Hemophilia: causes, signs, treatment
Manifestations of hemophilia have been described in the writings of physicians and medical historians of ancient times.In those distant centuries, doctors faced the problem of increased bleeding and death from it.But the cause of this disease was not clear, and treatment was also ineffective.
The official name and definition of this disease was received in the XIX century.
Table of contents: Etiology Causes of hemophilia development Scheme of transmission of hereditary traits Hemophilia types How hemophilia manifests.Complaints and symptoms How to suspect hemophilia in a newborn Confirmation of the diagnosis of hemophilia by laboratory data How to treat hemophilia and complications Preventative measuresEtiology
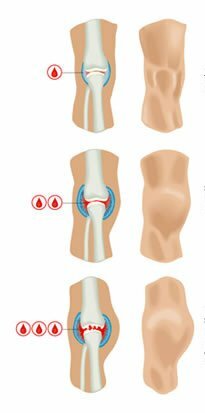 Hemophilia is a hereditary disease in which there is a violation of the process of coagulation( coagulation).As a result, the patient has bleeding in the joint cavity, muscle tissue, in all organs of the body.
Hemophilia is a hereditary disease in which there is a violation of the process of coagulation( coagulation).As a result, the patient has bleeding in the joint cavity, muscle tissue, in all organs of the body.
Hemophilia is a pathology in which there is increased bleeding.Medical classification refers this disease to a group of hemorrhagic diathesis, hereditary coagulopathies, conditions in which blood clotting is impaired.In severe cases, patients become disabled.
This disease often suffered from representatives of royal dynasties, causing hemophilia to be called a royal, or Victorian disease( in honor of Queen Victoria, the only female representative who was ill with this disease).
How to live with hemophilia?The answer to this question you will find by watching the video review:
Causes of hemophilia development
All information about a person is embedded in the chromosomes that are in the nucleus of the cell.Each feature that provides a resemblance to the parents is encoded by the chromosome site-the genome.
Pathological changes in genes( mutations) lead to a number of diseases.
The person has 23 pairs of chromosomes.The last pair is sex chromosomes, they are denoted by the letters X and Y. In women, this pair consists of two X chromosomes( XX), in men X and Y( XY).
The mutated gene responsible for the transmission of hemophilia by inheritance is embedded in the X chromosome.Does this mean that a sick child is born necessarily from a parent who is sick with this disease?No.Here it is necessary to understand the concept of "dominant" and "recessive" gene.
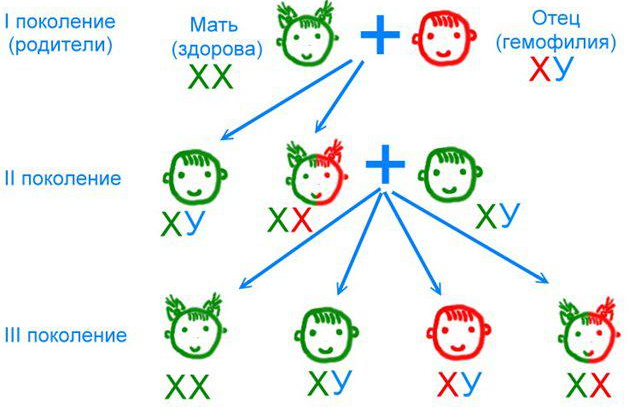
Scheme of transmission of hereditary traits
A born child receives two genes responsible for one particular trait, for example, for hair color.The first gene is from the mother, the second from the father.Genes are dominant( predominant), and recessive( secondary).If the child inherits two dominant genes from the mother and father, then this sign will manifest itself.If two are recessive, then too, it will manifest it.If from one parent the dominant is inherited, and from the second it is recessive, then the baby will show the sign of the dominant gene.
The gene that is the carrier of hemophilia is recessive.It is transmitted only from the X chromosome.Hence, in a female child, in order for this disease to arise, it is necessary to have in both X chromosomes recessive genes.If this happens, the child dies after the formation of his own hematopoietic system.This happens on the 4th week of pregnancy.If the sign of hemophilia is only in one X chromosome, and the second carries a healthy gene, then the disease does not manifest itself, since the dominant healthy gene will be suppressed by the recessive gene.Therefore, a woman can be a carrier of the disease, but does not suffer from it.
Hemophilia varieties
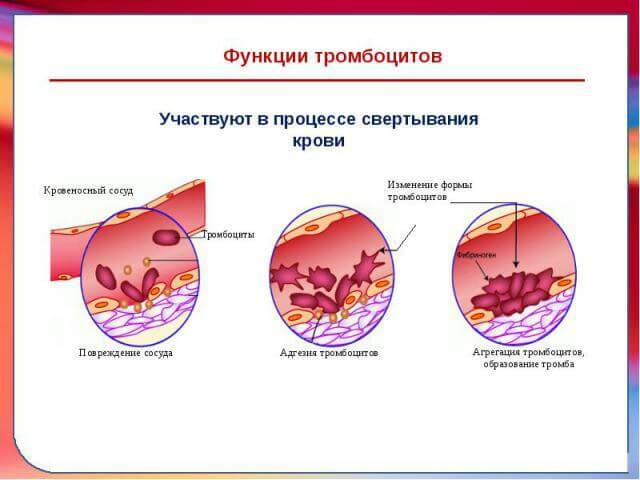
Increased bleeding in this disease is caused by a violation of the process of blood coagulation, lengthening its time.The problem is caused by a change in clotting factors of 12 counts.
Practical medicine faces three types of disease:
- Hemophilia A. It is caused by insufficient content of VIII factor( antihemophilic globulin).This type of disease is basic( classical), as it affects about 85% of patients with hemophilia.This variant of the disease is accompanied by the most severe bleeding;
- Hemophilia B. Develops due to the deficiency of the IX plasma factor( Kristmasa).At this type of pathology, the formation of a coagulation plug of the secondary level is disrupted.Occurs in 10% of cases;
- Hemophilia C. This variant causes a lack of XI clotting factor.To date, excluded from the classification of hemophilia and isolated in a separate disease, because it differs by clinical signs from true hemophilia.It is common among Ashkenazi Jews, men and women are ill.
How is hemophilia manifested.Complaints and symptoms
Hemophilia manifests itself:
-
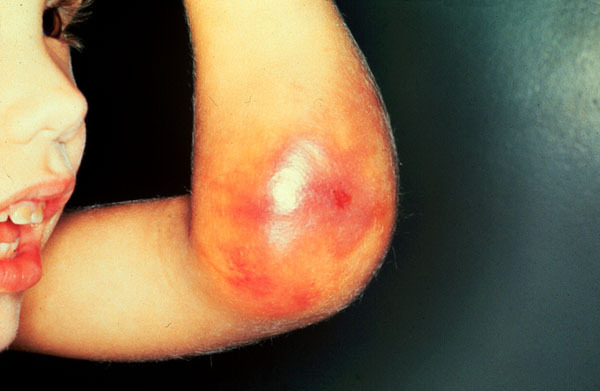 formation of bruising, bruising, subcutaneous bleeding in different locations.Contributing factors: bruises, bumps, traumatic effects, injuries to sharp objects with violation of the integrity of the skin.
formation of bruising, bruising, subcutaneous bleeding in different locations.Contributing factors: bruises, bumps, traumatic effects, injuries to sharp objects with violation of the integrity of the skin. - by the appearance of blood in the urine( hematuria);
- bleeding after surgery, tooth extraction, other traumatic procedures;
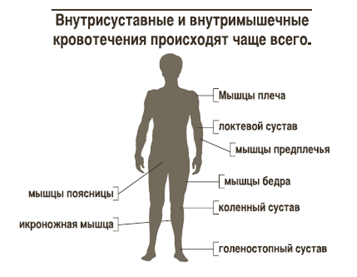
- by the accumulation of blood in the joint cavities( hemarthroses), often recurring and leading to joint diseases( ankylosis) causing pain, overgrowth of connective tissue, limitation of mobility( contracture)
In young children, hematomas often appear on the head, inButtocks, shoulder blades.Physiological teething is accompanied by constant bleeding.Also, there is often a discharge of blood from the nasal mucosa and mouth with a bite of the tongue and cheeks.
The trauma of the eye is particularly dangerous.Bleeding in this case can result in complete blindness.
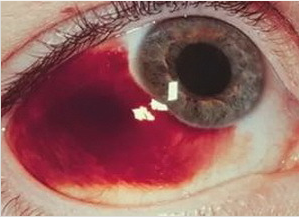
With age, manifestations become more mild, bleeding is smoothed, the danger is no longer so great.
In everyday life there is a myth about cases of bleeding hemophiliacs from the slightest cut or scratch.In fact, this is not so.Dangerous are severe surgical operations and internal bleeding of an unknown origin.Most likely, a combination of mechanisms of bleeding during illness and fragility, permeability of the walls of blood vessels.
Note : patients with hemophilia experience repeated( recurrent) bleeding after trauma.Against the background of a stop, in a few hours or days the process can repeat itself.

Therefore, careful monitoring of such patients is necessary.Frequently repeated bleeding causes anemia with time.
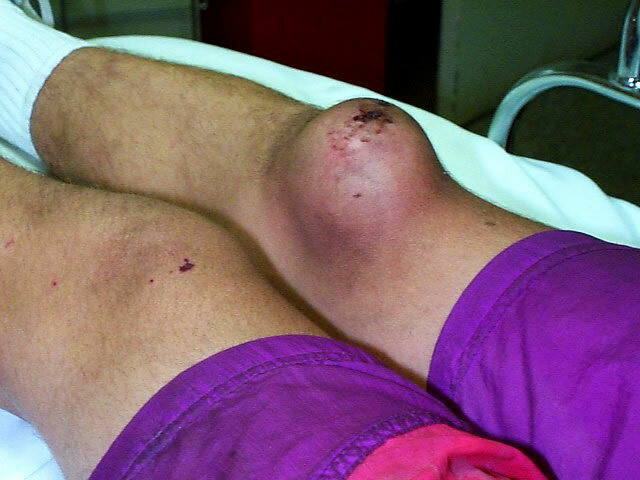
Intra-articular bleeding occurs in 70% of all cases.The share of subcutaneous tissue accounts for about 20%, most often in the area of maximum muscle loads.About 5-7% of bleeding occurs in the gastrointestinal and cerebrovascular.
Developed hematomas can last up to 2 months.In case of complications( suppuration), it is necessary to perform her autopsy and removal of necrotic masses.
Hemorrhages in the joints( hemarthrosis) can lead to disability.
Complications of bleeding from the kidney tissue can be:
- pain syndrome;
- renal colic( mechanical irritation of the urinary tract by a blood clot);
- Inflammation of renal pelvis( pyelonephritis);
- hydrops of the kidneys( hydronephrosis);
- destruction and sclerotic changes in the capillaries of the kidneys.
How to suspect hemophilia in a newborn
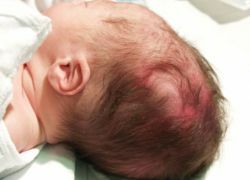 Non-stop, prolonged bleeding from the umbilical cord, bruises and bruises on the head, bulging parts of the baby's body require immediate blood test for hemophilia.Supplement these studies should be a thorough interview with a relative to identify cases of the disease in the family.
Non-stop, prolonged bleeding from the umbilical cord, bruises and bruises on the head, bulging parts of the baby's body require immediate blood test for hemophilia.Supplement these studies should be a thorough interview with a relative to identify cases of the disease in the family.
Confirmation of the diagnosis of hemophilia by laboratory data
The diagnosis of hemophilia is characterized by the following blood parameters:
- with a decrease in concentration( main sign) and coagulation factor activity( VII in Form A, IX in Form B) below 50%;
- increase in clotting time more than 10 minutes;
- unchanged amount of fibrinogen;
- increased thrombin time;
- decreased prothrombin index( PTI);
How to treat hemophilia and complications
There are no radical ways to influence the cause of the disease.Symptomatic, facilitating the treatment of maintenance drugs.To this end, patients are administered:
- solutions of concentrates of the missing coagulation factors( 4 to 8 doses per day with heparin 1500 ED), drugs prepared from donors blood, also from hematological components of animal tissue;
- fresh plasma preparations, cryoprecipitate( depending on the severity of 10 to 30 units per 1 kg of weight, once a day), antihemophilic( 300 to 500 ml in 8-12 hours) and donor plasma( 10-20 mlPer kg per day).Injections can be done every day, or every other day;
- with severe anemia - blood transfusion, erythrocyte mass;
- solution of glucose by drop, polyglucin, rehbyrin, etc.;
- plasmapheresis( for the removal of antibodies to coagulation factors), prednisolone.
In combination with the above methods, hemarthroses are supplemented with puncture of the articular bag for aspiration( selection) of bloody contents followed by the administration of hormonal preparations.The painful limb requires maximum immobility, up to immobilization.Rehabilitation is performed with the use of physiotherapy exercises and physiotherapy methods.
Complicated cases with the appearance of contractures, osteoarthritis, pathological fractures can be supplemented by surgical treatment in orthopedic departments.
Note : the appointment of patients with hemophilia nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is categorically contraindicated because of the danger of possible development of bleeding.
Preventive measures
 Begin with the need for counseling in medical genetic counseling, determining the hemophilia gene in the X chromosome.
Begin with the need for counseling in medical genetic counseling, determining the hemophilia gene in the X chromosome.
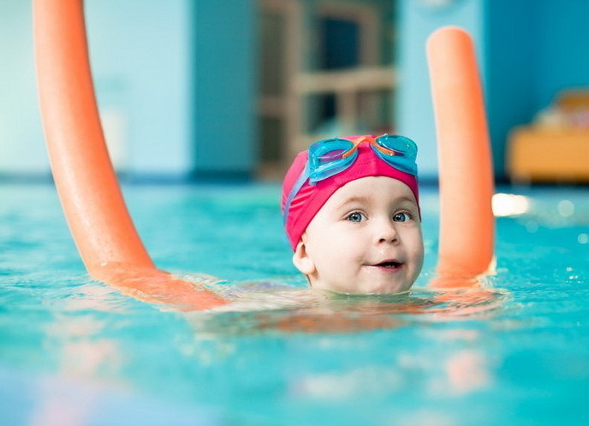
With the existing disease, you need a dispensary account, maintaining a daily and lifestyle regime that excludes physical overload and traumatism.We recommend swimming lessons, a gym with shells that do not cause injury.
To prevent complications, relatives are trained to help with bleeding.In some cases, once every three months, injections of coagulation factor concentrates are made.
Detailed information on the history of "disease of kings" and its manifestations is presented in the video review:
Alexander Lotin, radiologist, narcologist