Celiac Disease: Symptoms and Treatment

Celiac disease( gluten enteropathy) is a disease of the small intestine, manifested by atrophy of the mucosa in response to the introduction of gluten.The prevalence of gluten enethropathy varies considerably in different geographic areas.The disease is most frequent in European countries( 1-3: 1000), with less - in African countries.It is believed that at least 1% of the world's population suffers from this disease.Gluten enteropathy is more often recorded among women.
Table of contents: Causes Symptoms of celiac disease Symptoms of atypical celiac disease Complications Diagnosis TreatmentCauses
Small intestine lesion in celiac disease occurs under the influence of gluten, a protein contained in cereal crops.Gluten consists of several components: prolamin, glutenin, albumin, globulin.A striking effect on the mucosa of the gut is exactly prolamin.Its number in different cereals is not the same.So, millet, rye, wheat contain this protein in large quantities.In less quantity, prolamine is found in barley, oats, corn.Prolamin is heterogeneous in its structure, the wheat prolamine is called gliadin, barley is called hordein, and oat is called avene.

The key factor in the development of the disease is a genetic predisposition.In humans with this peculiarity, specific antibodies are produced by contact of gluten with villi in the intestine.This is how the autoimmune inflammation of the intestinal tissues develops, leading to a gradual atrophy of the mucous membrane of the organ.
Symptoms of classical celiac disease
Developing with celiac atrophy of villi, dystrophic changes in enterocytes lead to a decrease in the surface of absorption of the small intestine.As a result, the absorption of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals is impaired.These changes lead to the appearance of characteristic clinical symptoms.Gluten disease can occur in three forms: classical, atypical, latent.
Glutenous enerropathy occurs mainly in childhood.Children are lagging behind in growth, muscular weakness, apathy, enlarged abdomen, steatorrhea, spastic abdominal pain.Kids are emotionally labile, quickly get tired.But in some patients the disease manifests itself not from childhood, but already in adulthood.
In general, classical celiac disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Weight reduction( 5 to 30 kg);
- Decreased appetite;
- Diarrhea;
- Weakness, fast fatigue;
- Abdominal pain;
- Dyspeptic symptoms: flatulence, nausea, vomiting;
- Edema;
- Glossitis, gingivitis;
- Iron deficiency anemia;
- Hypocalcemia with osteoporosis;
- Hypovitaminosis.
 The most constant symptom of celiac disease is repeated diarrhea, their frequency can reach ten or more times a day.The stool is mushy, light, liquid, foamy.
The most constant symptom of celiac disease is repeated diarrhea, their frequency can reach ten or more times a day.The stool is mushy, light, liquid, foamy.
Persistent, severe abdominal pain for celiac disease is not typical.However, in patients with gluten enteropathy, cramping abdominal pain may occur before or after defecation.And with flatulence, dull, diffuse pains arise.
When examining a person with celiac disease, attention is drawn to the enlarged abdomen.
Symptoms of atypical celiac disease
In most cases, celiac disease is abnormal.In the clinical picture of the disease, gastroenterological symptoms may be absent or be little expressed. Extraintestinal symptoms come to the fore:
- Anemia;
- Ulcerative stomatitis;
- Osteoporosis, frequent fractures;
- Arthritis;
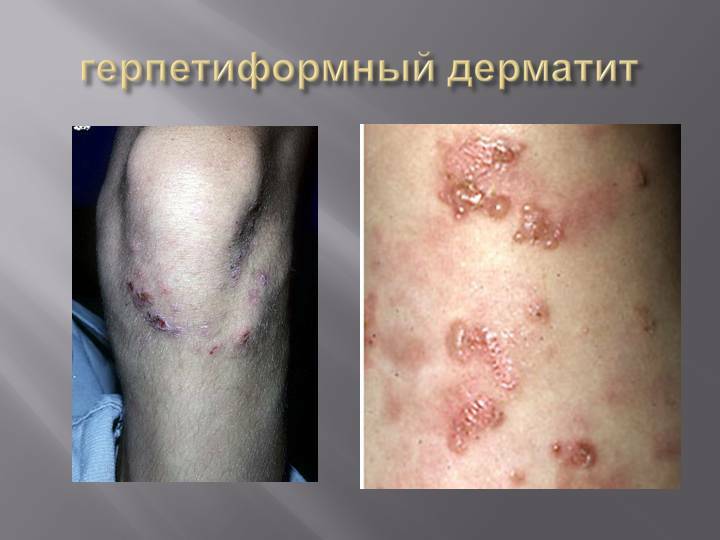
- Herpetiform dermatitis( characterized by the appearance of itching papulo-vesicular rashes on the elbows and buttocks);
- Hemorrhagic syndrome;
- Associated autoimmune diseases( autoimmune thyroiditis, diabetes mellitus, Addison's disease);
- The defeat of the nervous system( depressive disorders, ataxia, epilepsy, polyneuropathy);
- Deterioration of potency, menstruation, infertility.
Complications of
In the absence of celiac disease, complications of the disease may occur. The most common complications include:
- Malignancy;
- Chronic non-granulomatous ulcerative nausea and colitis;
- Neuropathy.
In patients with celiac disease, lymphoma and small intestinal cancer develop much more frequently than in the population.In addition, cancer of the esophagus, stomach, and rectum is more common.Unreasonable deterioration of the patient's condition, as well as laboratory indicators, despite adherence to the gluten-free diet, should lead to the idea of a possible development of the malignant process.

Chronic non-granulomatous ulcerative nausea and colitis is characterized by the appearance on the mucosa of the lean, ileum, large intestine ulcerative defects.Ulcers can bleed, perforate.
Neuropathy manifests itself in the form of numbness, tingling, weakness in the lower limbs.The defeat of the nerve fibers of the upper limbs is observed less often.When lesions of the cranial nerves are observed diplopia, dysphonia, dysarthria.
Diagnosis
Symptoms of celiac disease are so diverse and nonspecific that certain studies should be carried out to confirm the suspected diagnosis.Since the key factor in the occurrence of gluten enteropathy is a genetic predisposition, it is necessary to find out a family history of gluten intolerance.
The main diagnostic method is serological. In patients with gluten enteropathy, specific antibodies are detected in the blood:
- Antigliadins( AGA IgG, IgM);
- Endomysial( EMA IgA);
- Antibodies to tissue transglutaminase( tTG).
No less important diagnostic method is the morphological examination of the small intestine mucosa.With endoscopy and histological examination of the intestinal tissues, signs of atrophic lesion of the mucous membrane with a shortening of the villi, elongation of intestinal crypts are determined.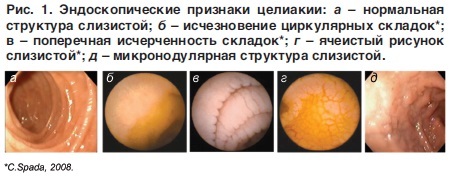
Additional research methods:
- Clinical blood test - anemia is defined;
- Biochemical blood test - determined hypoproteinemia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia;
- Coprological examination - a large amount of fat and soaps is detected.
Treatment
Celiac disease is the disease that can be corrected by diet.When diet is observed, the mucosa of the small intestine is restored and soon the person stops worrying with unpleasant symptoms of the disease.
Principles of the diet for celiac disease:
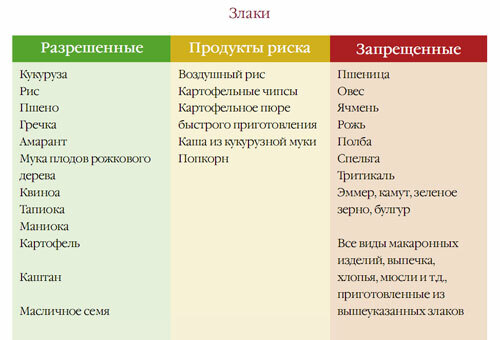
- Elimination of gluten-containing foods from the diet( bread, pasta and confectionery);
- Mechanical and thermal sparing of the digestive tract( dishes are steamed or cooked, eaten or grinded);
- Exclusion of fermentation products( milk, beans);
- Restriction of products that stimulate the secretion of the pancreas and stomach( rich meat broths, fatty meat).
In case of an exacerbation of the disease, in addition to the gluten-free diet, medicinal treatment is performed to eliminate metabolic disturbances. The following groups of drugs are used:
-
 Protein-containing preparations( albumin, plasma, protein) - are used to correct protein deficiency;
Protein-containing preparations( albumin, plasma, protein) - are used to correct protein deficiency; - Glucocorticosteroids( prednisolone) - when gluten-free diet is ineffective;
- Vitamins;
- Preparations of iron, calcium;
- Enzyme preparations.
Important: prevention of recurrence of the disease is a lifelong observance of the diet.Consumption of even a small amount of gluten affects the state of the intestinal mucosa.Incomplete dieting leads to the progression of celiac disease, and also increases the risk of complications.
Grigorova Valeria, medical reviewer