Pain in the intestines: probable causes, general principles of treatment
 Pain in the intestine is a characteristic symptom for all diseases of its thin and / or thick section.The mechanism of pain development is simple - under the influence of toxins or some damaging factor there is a strong contraction of the smooth muscles of the intestinal wall, which in medicine is classified as a spasm.It is this reduction that provokes the accumulation in the cells of a large amount of lactic acid, and it, in turn, irritates the nerve endings and causes a feeling of pain. If you have pain in the intestine, you need to contact a surgeon, gastroenterologist or proctologist - depending on the likely cause of the onset of the onset of pain.
Pain in the intestine is a characteristic symptom for all diseases of its thin and / or thick section.The mechanism of pain development is simple - under the influence of toxins or some damaging factor there is a strong contraction of the smooth muscles of the intestinal wall, which in medicine is classified as a spasm.It is this reduction that provokes the accumulation in the cells of a large amount of lactic acid, and it, in turn, irritates the nerve endings and causes a feeling of pain. If you have pain in the intestine, you need to contact a surgeon, gastroenterologist or proctologist - depending on the likely cause of the onset of the onset of pain.
The most likely causes of bowel pain
Of course, accurate diagnosis of pain in the intestineAnd the doctor must determine the true cause of their appearance.
But there are a number of the most likely factors that lead to the appearance of the symptom in question:- Autoimmune diseases.It is, first of all, the ulcerative colitis of nonspecific origin, which occurs against the background of disturbances in the immune system, characterized by the production of antibodies against the tissues of the large intestine.
- Dysbiosis.This is the name of the pathological condition, in which there is a violation of the quantitative ratio of bacteria of normal intestinal microflora and conditionally pathogenic flora.If a person increases the number of opportunistic bacteria, this provokes a digestive disorder, accompanied by increased gas production.Bacterial toxins and accumulated gases are the cause of the appearance of pain in the intestines.To conditionally pathogenic bacteria, the intestinal microflora in this case include streptococci, Escherichia coli and staphylococci.
- Inflammation of the intestinal mucosa.This pathological process may occur under the influence of infection or autoimmune processes, and, inflammation can occur in the small intestine( enteritis), and in its thick section( colitis).Sigmoid colon and appendix may be inflamed, which are also part of the intestine, and lead to the development of sigmoiditis and appendicitis, respectively.
- Parasitic diseases.Helminthes of the class of round worms( for example, roundworms) and flatworms, whose bright representatives are bovine / pork tapeworm and wide ribbon, can parasitize in humans.These helminths lead an active lifestyle in the intestine and not only release toxins, but also have a mechanical effect on the intestinal walls, which is the reason for the appearance of the symptom in question.
- Atony of the intestine.This pathological condition is associated with the accumulation of food and mechanical stretching of the intestinal walls, which occurs against a background of decreased peristalsis( movement of the intestinal wall, which facilitates the movement of the food lump to the lower parts).
- Chronic pancreatitis.This is an inflammation of the pancreas, which leads to a decrease in the amount of enzymes produced by it.The lack of these enzymes adversely affects the digestive process - they become insufficient, and simultaneously, the processes of fermentation with the release of gases are activated.
- Mesenteric thrombosis.So in medicine is called a condition in which there is a blockage of thrombus arteries feeding the intestine.As a result of blockage, necrosis of the intestine develops, which is accompanied by intense pain, which is not removed even after taking strong analgesics.
- Irritable bowel syndrome.
- Acute intestinal obstruction.This pathological condition is accompanied by a cessation of movement of food masses, which may be due to the progression of the tumor in a particular part of the intestine( benign or malignant) or the presence of a foreign body.
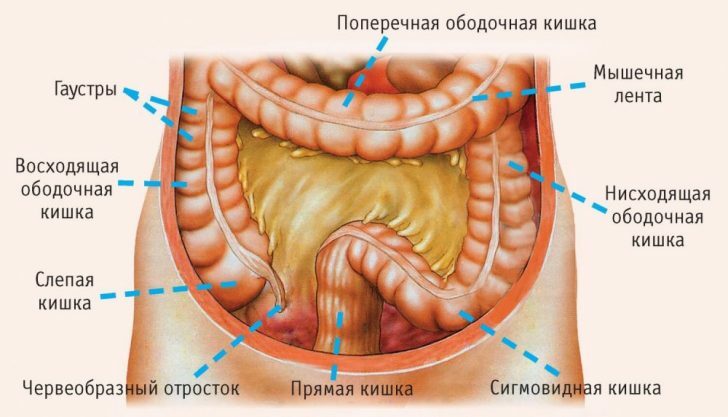
In addition, intestinal pains often disturb pregnant women, but this is not considered as a pathological condition of ( of course, if possible diseases are excluded by examination).To explain the occurrence of the symptom in question during the gestation period is simple - the enlarged uterus exerts a strong pressure on the intestinal loops.
Relationship between localization, character and duration of pain and possible disease
In general, doctors often make a preliminary diagnosis only on the basis of the characteristic of pain in the intestine, but localization of the symptom in question will give some options for preliminary diagnosis:
- pain localized on the lower right - this may indicate the rapid development of appendicitis;
- pain in the intestine is present specifically on the left and below - evidence of the development of the inflammatory process in the sigmoid colon( sigmoiditis);
- The girdling pain of the entire abdomen is characteristic for the development of enterocolitis - a pathological condition in which the inflammatory process is spread to all parts of the intestine;
- Pain in the perepuscular region is characteristic of enteritis - inflammation of the small intestine.
Some conclusions can be drawn about the nature of pain in the intestines:
-
 blunt and aching arises against a background of sluggish inflammatory process of any part of the intestine, and most likely it will be a chronic disease;
blunt and aching arises against a background of sluggish inflammatory process of any part of the intestine, and most likely it will be a chronic disease; - Acute pain is probably indicative of the development of acute appendicitis or ulcerative colitis - a condition in which seeking qualified medical care should be prompt;
- cramping pain occurs only against the background of strong spasms of the walls of the intestine, and this can occur, for example, in irritable bowel syndrome.
Another factor that will help in the diagnosis is the duration of pain:
- , long-lasting pain is characteristic of dysbiosis, irritable bowel syndrome and ulcerative colitis;
- Short-term acute pain indicates acute appendicitis, intestinal infection or acute poisoning;
- pain that occurs only after ingestion is inherent in insufficient digestive enzyme production.
Diagnostic measures for pain in the intestine
Patients consult doctors about the symptom in question almost always in time, but this is not due to the "consciousness" of the patients, but to the intensity of pain.The doctor, before making a diagnosis and prescribing treatment, will certainly conduct a series of examinations to reveal the true cause of the pain in the intestine. As part of the diagnostic activities,
-
 performs laboratory tests of feces( coprogram), which allow us to draw conclusions about the usefulness of digesting food;
performs laboratory tests of feces( coprogram), which allow us to draw conclusions about the usefulness of digesting food; - bacteriological study of stool, which is conducted to determine the causative agent of intestinal infection and the ratio of opportunistic bacteria and normal intestinal microflora;
- endoscopic examination, which enables a specialist to assess the state of the intestinal mucosa;
- X-ray examination, which is carried out using a contrast medium and allows you to see the structural changes in the intestine, determine the cause of the accumulation of food masses.
General principles of treatment for pain in the intestines
Doctors emphasize the importance of diagnosis in this case, because taking even the most powerful pain medication can only reduce the intensity of pain in the intestines( and not in all cases!), But not to ridFrom the cause of their appearance.
The pain in the intestine will stop worrying the patient only after the underlying disease is treated, and it will be long and complex. Within the framework of the treatment:
- Etiotropic therapy.It is aimed at eliminating the immediate cause of the appearance of pain in the intestines.This stage of treatment implies the appointment of:
- antibacterial drugs for intestinal infections;
- probiotics( live bacteria of normal microflora) with dysbiosis;
- immunosuppressors in the diagnosis of ulcerative colitis.
Note: treatment of appendicitis and acute intestinal obstruction is to perform a surgical intervention, and this is also included in the concept of etiotropic therapy.
- Pathogenetic therapy.It is aimed at improving the digestive function of the intestine, which ensures the intake of specific enzyme preparations.Also, in the context of pathogenetic therapy, doctors prescribe to patients the sorbents , which are able to bind and remove toxins from the intestine.
- Symptomatic therapy.Naturally, doctors will do their best to ease the patient's condition - antispasmodics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs will help reduce the intensity of pain in the intestines.
Pain in the intestine is a symptom that indicates the development of a pathology, so they can not be ignored.However, this does not work out - the pain is almost always intense.But you can not take antispasmodics yourself or any painkillers, the same prohibition also applies to the use of decoctions / tinctures from medicinal plants.It is necessary to first find out the cause of the pain in the intestines and only after that to take some medical measures.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical reviewer, therapist of the highest qualification category



