Causes of convulsive syndrome in children and adults

Seizures are involuntary muscle contractions caused by hyperactivity or irritation of neurons.Convulsive seizures are observed in about 2% of adults, most have a single fit during their lifetime.And only a third of these patients have recurring seizures, which makes it possible to diagnose epilepsy.
Seizure is a separate episode, and epilepsy is a disease.Accordingly, one can not call any seizure of epilepsy.With epilepsy, seizures are spontaneous and repetitive.
Table of Contents: Causes Types of seizures Partial seizures Generalized seizures Epilepticusia Seizure syndrome in children Febrile convulsions Respiratory spasms Spasmophilia Diagnosis TreatmentCauses
Seizure is a sign of increased neurogenic activity.This circumstance can provoke different diseases and conditions.
Causes leading to seizures:
-
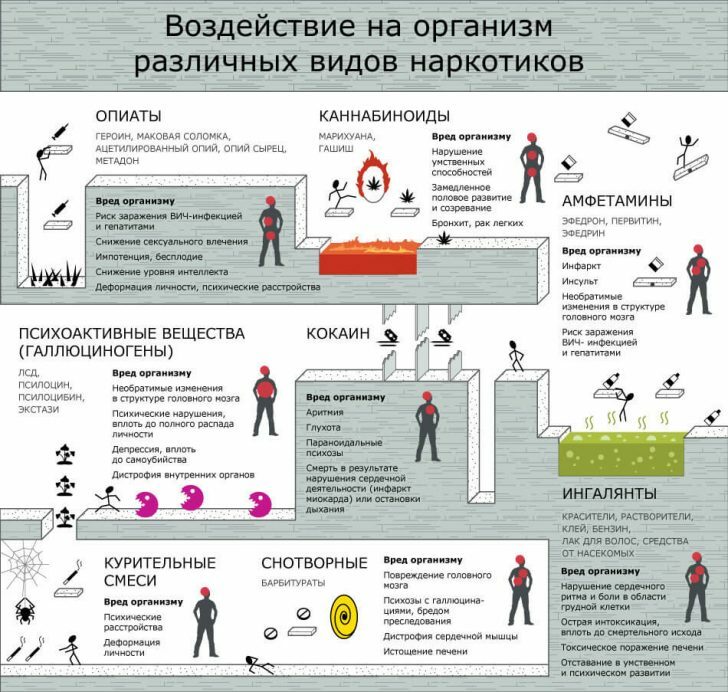
 Genetic disorders - lead to the development of primary epilepsy.
Genetic disorders - lead to the development of primary epilepsy. - Perinatal disorders - effects on the fetus of infectious agents, medications, hypoxia.Traumatic and asphicic lesions during labor.
- Infectious brain damage( meningitis, encephalitis).
- Action of toxic substances( lead, mercury, ethanol, strychnine, carbon monoxide, alcohol).
- Abstinence syndrome.
- Eclampsia.
- Administration of medications( aminazine, indomethacin, ceftazidime, penicillin, lidocaine, isoniazid).
- Craniocerebral trauma.
- Disorders of cerebral circulation( stroke, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and acute hypertensive encephalopathy).
- Metabolic disorders: electrolyte disorders( eg, hyponatremia, hypocalcemia, hyperhydration, dehydration);Disorders of carbohydrate( hypoglycemia) and amino acid metabolism( in phenylketonuria).
- Tumors of the brain.
- Hereditary diseases( eg, neurofibromatosis).
- Fever.
- Degenerative diseases of the brain.
- Other reasons.
These or other reasons for the occurrence of convulsive seizures are typical for certain age groups.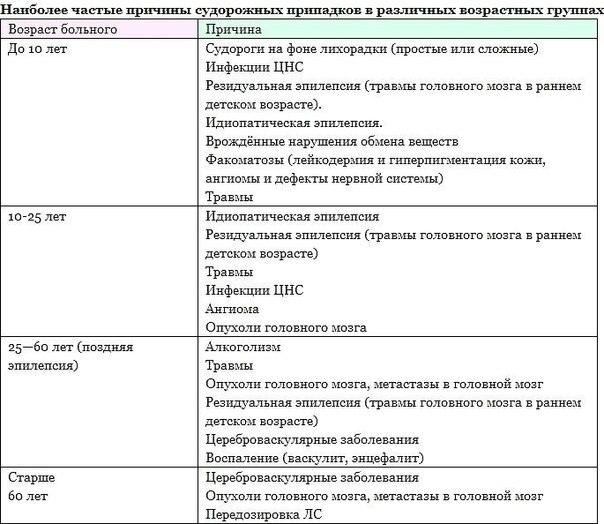
Types of seizures
In medicine, many attempts have been made to create the most appropriate classification of convulsive seizures. All types of seizures can be divided into two groups:
- Partial;
- Generalized.
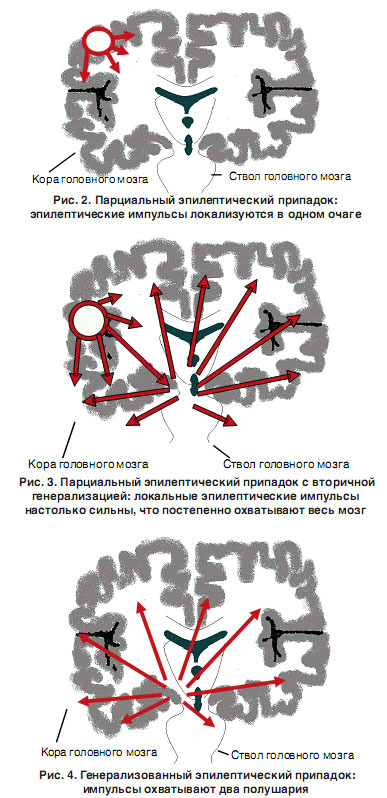
Partial seizures are provoked by excitation of neurons in a specific area of the cerebral cortex.Generalized seizures are caused by the hyperactivity of the vast area of the brain.
Partial seizures
Partial seizures are called simple if they are not accompanied by a disturbance of consciousness and complex if they are present.
Simple partial seizures
Flows without disturbance of consciousness.On the part of the brain in which the epileptogenic focus appeared, the clinical picture depends. There may be such signs:
- Convulsions in the limbs, as well as turning the head and trunk;
- Feeling crawling on the skin( paresthesia), light flashes in front of the eyes, changing the perception of surrounding objects, a sense of unusual smell or taste, the appearance of false voices, music, noise;
- Mental manifestations in the form of deja vu, derealization, depersonalization;
- Sometimes in a convulsive process, different muscle groups of one limb are gradually involved.This condition was called the Jacksonian march.
The duration of such a seizure is only a couple of seconds to several minutes.

Complicated partial seizures
Accompanied by a violation of consciousness.A characteristic sign of a seizure is automatism( a person can lick lips, repeat some sounds or words, rub one's palms, walk along one trajectory, etc.).
The duration of the seizure is one to two minutes.After a fit, there may be a brief dullness of consciousness.The person does not remember the event.
Sometimes partial seizures are transformed into generalized seizures.
Generalized seizures of
Flow along with loss of consciousness.Neurologists distinguish tonic, clonic and tonic-clonic generalized seizures.Tonic cramps are a persistent contraction of the muscles.Clonic - rhythmic muscle contractions.
Generalized seizures can occur as:
- Large seizures( tonic-clonic);
- Absenses;
- Myoclonic seizures;
- Atonic seizures.
Tonic-clonic seizures
The person suddenly loses consciousness and falls.There comes a tonic phase, the duration of which is 10-20 seconds.There is an extension of the head, bending of the hands, stretching of the legs, tension of the trunk.Sometimes there is a kind of scream.Pupils are dilated, do not respond to light stimulus.The skin acquires a cyanotic color.Unintentional urination may occur.
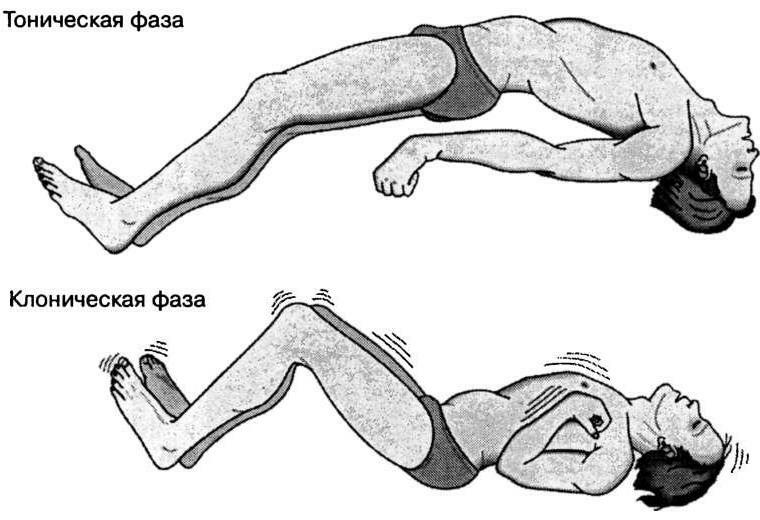
Then comes the clonic phase, characterized by a rhythmic twitching of the whole body.Also rolling of eyes and allocation of foam from a mouth( sometimes bloody if the tongue is bitten) is observed.The duration of this phase is one to three minutes.
Sometimes, in a generalized seizure, only clonic or tonic convulsions are observed.After an attack the consciousness of the person is restored not at once, the drowsiness is marked.The victim does not remember what happened.To suspect a fit allows muscle pain, the presence of abrasions on the body, traces of bite in the tongue, a sense of weakness.
Absenses
Absenses are also called small seizures.This state is characterized by a sudden turn off of consciousness for a few seconds.The person falls silent, freezes, the view is fixed at one point.The pupils are enlarged, the eyelids are somewhat lowered.There may be a twitching of the muscles of the face.
It is characteristic that the person does not fall during the absence.Because the attack is not long, it often remains unnoticed by the surrounding people.After a few seconds, consciousness returns and the person continues to do what he did before the attack.The person does not realize the event.
Myoclonic seizures
These are seizures of short-term symmetrical or asymmetric contractions of the muscles of the trunk and extremities.Seizures can be accompanied by a change in consciousness, but because of the short duration of the attack, this fact often remains unchecked.
Atonic seizures
 Characterized by loss of consciousness and decreased muscle tone.Atonic seizures are a true companion to children with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.This pathological condition is formed against a background of all kinds of abnormalities of brain development, hypoxic or infectious brain damage.For the syndrome, not only atonic, but also tonic seizures with absences are inherent.In addition, there is a delay in mental development, paresis of limbs, ataxia.
Characterized by loss of consciousness and decreased muscle tone.Atonic seizures are a true companion to children with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome.This pathological condition is formed against a background of all kinds of abnormalities of brain development, hypoxic or infectious brain damage.For the syndrome, not only atonic, but also tonic seizures with absences are inherent.In addition, there is a delay in mental development, paresis of limbs, ataxia.
Epileptic status
This is a formidable condition characterized by a series of epileptic seizures between which a person does not regain consciousness.This is an emergency that can end with death.Therefore, the status epilepticus should be stopped as soon as possible.
In most cases, epistaxis occurs in people with epilepsy against the cessation of use of antiepileptic drugs.Nevertheless, the status epilepticus can also be the initial manifestation of metabolic disorders, cancer, abstinence syndrome, craniocerebral trauma, acute disorders of cerebral blood supply, or infectious brain damage.
To complications of the epistatus include:
- Respiratory disorders( respiratory arrest, pulmonary edema of the neurogenic nature, aspiration pneumonia);
- Hemodynamic disorders( arterial hypertension, arrhythmias, cessation of cardiac activity);
- Hyperthermia;
- Vomiting;
- Metabolic disorders.
Seizure syndrome in children
Convulsive syndrome among children occurs quite often.This high prevalence is associated with imperfections in the structures of the nervous system.Convulsive syndrome is more common in premature infants.
Febrile convulsions
These are seizures that develop in children age from six months to five years against the background of body temperature above 38.5 degrees.
To suspect the onset of a seizure is possible by the wandering gaze of the baby.The child ceases to respond to sounds, melteshenie hands, objects in front of the eyes.
There are such types of seizures:
- Simple febrile seizures.These are single convulsive seizures( tonic or tonic-clonic), lasting up to fifteen minutes.They do not have partial elements.After a fit, consciousness is not broken.
- Complicated febrile seizures.These are longer seizures that follow one after the other in the form of series.May contain a partial component.
Febrile seizures occur in about 3-4% of babies.Only 3% of these children develop epilepsy in the future.The probability of developing the disease is higher if the child has a history of complicated febrile seizures.
Affective-respiratory cramps
This type of seizure is considered to be a manifestation of hysteria.Respiratory cramps are often recorded among children aged 6-18 months, less often until the age of five.
This is a syndrome for which there are episodes of apnea, loss of consciousness, and convulsions.The attack is provoked by strong emotions, such as fright, anger.The baby begins to cry, there is apnea.Skin covers acquire a cyanotic or purple color.The average period of apnea lasts 30-60 seconds.After that, loss of consciousness, body softening, followed by tonic or tonic-clonic seizures may develop.Then a reflex inspiration takes place and the baby comes to himself.
Spasmophilia
This disease is a consequence of hypocalcemia.Reduction of calcium in the blood is observed with hypoparathyroidism, rickets, diseases accompanied by excessive vomiting and diarrhea.Spasmophilia is registered among children between the ages of three months and one and a half years of age.
There are such forms of spasmophilia:
- Explicit;
- Hidden.
An obvious form of the disease is manifested by tonic cramps of the muscles of the face, hands, feet, larynx, which are transformed into generalized tonic convulsions.
Suspicion of the latent form of the disease is possible by characteristic features:
-
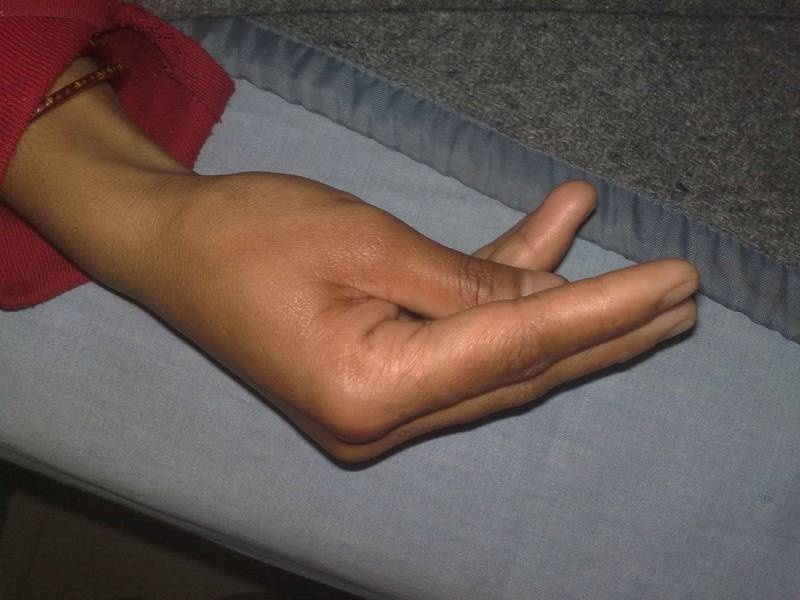 Symptom Tissot - cramps of the muscles of the hand arising from compression of the neurovascular bundle of the shoulder;
Symptom Tissot - cramps of the muscles of the hand arising from compression of the neurovascular bundle of the shoulder; - The symptom of the tail is the contraction of the muscles of the mouth, nose, eyelids, arising in response to the beating with a neurological hammer between the corner of the mouth and the zygomatic arch;
- Lust's symptom is the back flexing of the foot with the outward turn of the foot, which occurs in response to the malar pinch on the peroneal nerve;
- Maslov's symptom - when the skin tingles, a brief respiratory hold occurs.
Diagnostics
 Diagnosis of convulsive syndrome is based on clarifying the patient's medical history.If you can establish a link between a specific cause and convulsions, then you can talk about a secondary epileptic fit.If seizures occur spontaneously and repeat, suspicion of epilepsy should be suspected.
Diagnosis of convulsive syndrome is based on clarifying the patient's medical history.If you can establish a link between a specific cause and convulsions, then you can talk about a secondary epileptic fit.If seizures occur spontaneously and repeat, suspicion of epilepsy should be suspected.
EEG is used for diagnosis.To register electroencephalography directly during an attack is not an easy task.Therefore, the diagnostic procedure is carried out after the seizure.In favor of epilepsy, focal or asymmetric slow waves may be indicative.
Note: Often electroencephalography remains normal even when the clinical picture of convulsive syndrome does not allow to doubt the presence of epilepsy.Therefore, EEG data can not play a leading role in determining the diagnosis.
Treatment
Therapy should focus on eliminating the cause of the seizure( removal of the tumor, elimination of the effects of withdrawal symptoms, correction of metabolic abnormalities, etc.).
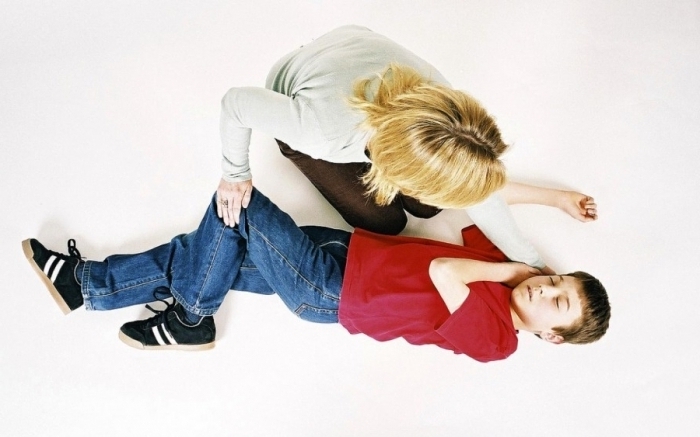
During an attack, a person must be placed in a horizontal position, turned over to the side.This position will prevent the popperation of gastric contents.Under the head should be put something soft.You can slightly hold the head, the human body, but with moderate strength.
Note : During a seizure attack, do not put any objects in your mouth.This can lead to injury to the teeth, as well as jamming of objects in the airway.
You can not leave a person until the moment of complete restoration of consciousness.If seizures occur for the first time or convulsive seizure is characterized by a series of seizures, a person must be hospitalized.
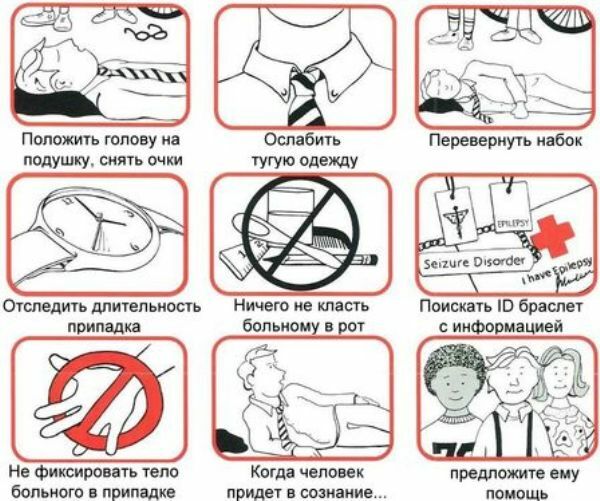
In a seizure lasting more than five minutes, the patient is given oxygen through a mask and also enters ten milligrams of diazepam on glucose for two minutes.
After the first case of seizures, antiepileptic drugs are usually not prescribed.These medications are attributed in cases where the patient is given a final diagnosis of epilepsy.The choice of medication is based on the type of seizure.
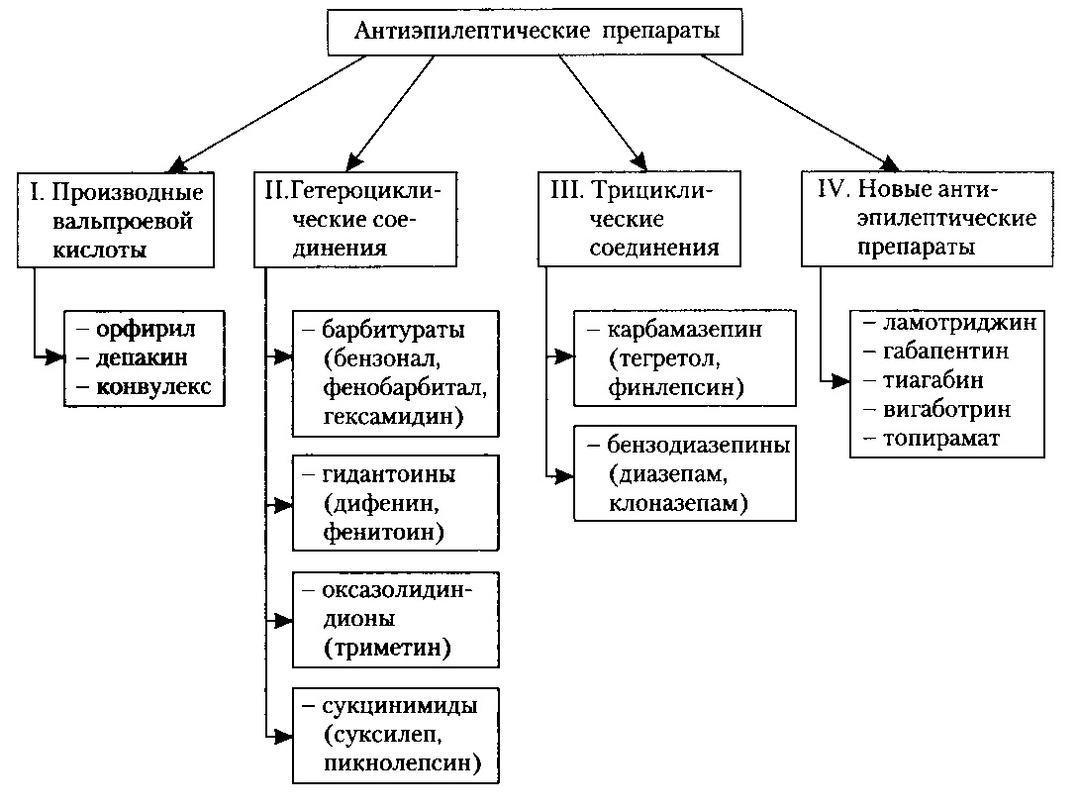
For partial as well as tonic-clonic seizures, use:
- Carbamazepine;
- Diphenine;
- Valproic acid;
- Phenobarbital;
- Lamotrigine.
For Absanasas designate:
- Ethosuximide;
- Valproic acid.
For myoclonic seizures, designate:
- Valproic acid;
- Clonazepam.
In most cases, the expected effect can be achieved against the background of therapy with a single drug.In resistant cases, several drugs are prescribed.
Grigorova Valeria, medical reviewer