tretman celulitis

Phlegmon is called diffuse purulent inflammation of subcutaneous fat or cell spaces.With phlegmon the purulent process is not limited to one area, but spreads through the cell spaces.This is a serious purulent process, the progression of which can lead to sepsis.
Table of contents:Reasons for
Phlegmon develops when a pathogenic microflora penetrates into the cellulose.The causative agents are most often staphylococci, streptococci, proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterobacteria, E. coli.
First, there is serous infiltration of the cellulose, then the exudate becomes purulent.Foci of necrosis appear, merging with each other, thereby forming large areas of necrosis of tissues.These sites are also subjected to purulent infiltration.Purulent-necrotic process extends to adjacent tissues and organs.Changes in tissues depend on the pathogen.So, anaerobic infection entails necrotizing tissues with the appearance of gas bubbles, and coccal agents - purulent tissue melting.

Microorganisms invade fatty tissue by contact or hematogenous way.
Among the most common causes of phlegmon are:- Soft tissue injuries;
- Purulent diseases( furuncles, carbuncles, osteomyelitis);
- Infringement of antiseptics during medical manipulations( injections, punctures).
All phlegmons are divided into superficial( when subcutaneous tissue is affected to the fascia) and deep( when deep cellular spaces are affected).The latter usually have separate names.So, the inflammation of the rectum is generally called paraproctitis, and the pericarp cellulose is called paranaphrite.
Depending on the location, different types of phlegmon are differentiated:
- Subcutaneous;
- submucosal;
- Subfascial;
- Intermuscular;
- .
Symptoms of phlegmon
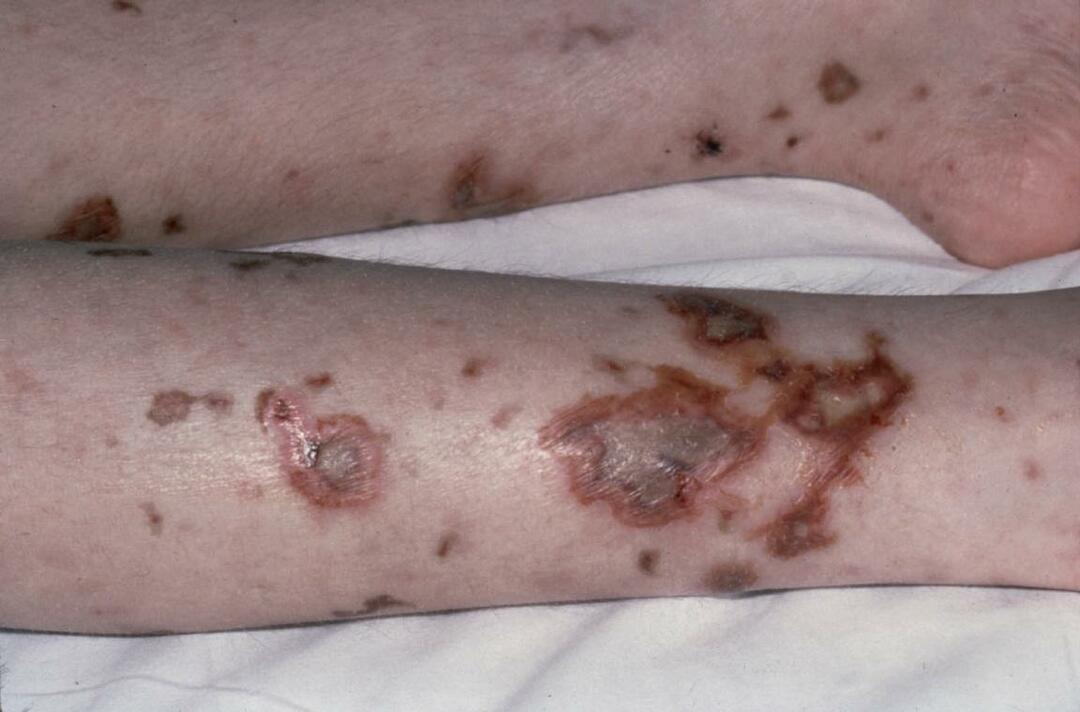
 With superficial( subcutaneous) localization of phlegmon, severe pain, reddening of the skin without clear boundaries, local increase in temperature.On the skin there is a swelling, which then softens slightly in the center.There is a symptom of fluctuations.
With superficial( subcutaneous) localization of phlegmon, severe pain, reddening of the skin without clear boundaries, local increase in temperature.On the skin there is a swelling, which then softens slightly in the center.There is a symptom of fluctuations.
With deep phlegmon, a painful dense consistency of the infiltration is palpated without sharply defined boundaries.Regional lymph nodes are enlarged.With a deep phlegmon, the symptoms of general intoxication are always very pronounced.Patients complain of weakness, fever.There is also an increase in heart rate, a drop in blood pressure, shortness of breath, and headache.
Deep neck phlegmon

The pustules that then become the source of the phlegmon of the neck are pustules in the scalp and face area, as well as inflammation in the mouth( dental caries, tonsillitis, stomatitis), in the upper respiratory tract,Esophagus, osteomyelitis of the cervical vertebrae, penetrating neck injuries.
Features of the appearance of phlegmon in the neck are caused by the following factors:
- Presence of a highly developed network of lymphatic vessels;
- Features of the structure of cervical fascia, between which there are delimited spaces filled with loose fiber.
With the phlegmon of the neck a swelling of the skin is formed in the region of the sternocleid-mastoid muscles, the lower jaw, and the chin.The swelling is initially dense, sometimes bumpy.
 With superficial submandibular phlegmon in the chin area, the skin becomes red, swelling and soreness is observed.And with deep phlegmon there is a very pronounced edema in the region of the bottom of the mouth and lower jaw.Patients note a sharp soreness, which is worse when chewing.
With superficial submandibular phlegmon in the chin area, the skin becomes red, swelling and soreness is observed.And with deep phlegmon there is a very pronounced edema in the region of the bottom of the mouth and lower jaw.Patients note a sharp soreness, which is worse when chewing.
With a phlegmon stretching along the cervical neurovascular bundle, due to severe pain, patients avoid any head movements and therefore keep it turned and slightly deflected to the sore side.
Purulent mediastinitis
This is a purulent process in the mediastinum cellulose.Basically, mediastinitis is a complication of perforation of the trachea and esophagus, suppurative processes in the throat and mouth, in the lungs, neck phlegmon, mediastinal bruising, sternum osteomyelitis and thoracic spine.
Purulent mediastinitis usually develops rapidly, accompanied by an increase in temperature, as well as pain behind the sternum, which spreads into the back, neck, epigastric region.There is swelling in the neck and chest.Patients, trying to alleviate the pain, take a sitting position and try to keep the head tilted forward.

In addition, there is an increase in heart rate, lowering of blood pressure, pain when swallowing and breathing, and expansion of the cervical veins.
Deep limb phlegmon
 This is a purulent inflammation that spreads through intermuscular, circulatory spaces.The cause of purulent inflammation of the limbs can be any skin damage( burns, wounds, bites), as well as diseases such as osteomyelitis, purulent arthritis, panaritium.
This is a purulent inflammation that spreads through intermuscular, circulatory spaces.The cause of purulent inflammation of the limbs can be any skin damage( burns, wounds, bites), as well as diseases such as osteomyelitis, purulent arthritis, panaritium.
The disease is characterized by diffuse pain in the limbs, fever, marked weakness.The onset of the disease is acute, precipitous.There is edema of the tissues, an increase in regional lymph nodes, the limb increases in size.
With superficial location of phlegmon( for example, in the femoral triangle) there is hyperemia and swelling of the skin, a symptom of fluctuations.
Phlegmon of the retroperitoneal space
This is an acute process in the retroperitoneal tissue of the lumbar and iliac regions that arises as a result of acute appendicitis, osteomyelitis of the pelvic bones, spinal column, inflammatory processes in the kidney, intestinal perforations. Depending on the location of the suppurative process in the retroperitoneal tissue, the following are distinguished:
- Paranifet;
- Paracolit;
- To the phlegmon of the iliac fossa.
 In the initial period of the disease, clinical signs are not clearly expressed.First, there are nonspecific symptoms of inflammation in the form of fever, weakness, headache.Local symptoms in the form of pain, swelling of the tissues appear somewhat later.The localization of pain corresponds to the location of the purulent process.Often, the doctor manages to palpate the inflammatory infiltrate through the anterior abdominal wall.Because of the pains, the person mixes with difficulty, so to ease the state, he tends to bend forward with a slant to the sore side.
In the initial period of the disease, clinical signs are not clearly expressed.First, there are nonspecific symptoms of inflammation in the form of fever, weakness, headache.Local symptoms in the form of pain, swelling of the tissues appear somewhat later.The localization of pain corresponds to the location of the purulent process.Often, the doctor manages to palpate the inflammatory infiltrate through the anterior abdominal wall.Because of the pains, the person mixes with difficulty, so to ease the state, he tends to bend forward with a slant to the sore side.
With phlegmon of retroperitoneal space, the hip contracture is formed - hip flexion of the flexion position with rotation to the inside and a slight reduction.The psa-symptom arises from the reflex reduction of the lumbosacillary muscle.Attempting to straighten the limb increases pain.
Paraproctitis
Recommended to read:This is a purulent inflammation of the cellulose surrounding the rectum.The causative agents of the disease are often E. coli, staphylococci, which enter the near-rectum space through the cracks of the back process, from inflamed hemorrhoids.
The following paraproctitis forms are distinguished:
- Subcutaneous;
- Ischiorectal;
- submucosal;
- Pelviorectal;
- Retrorectal.

Subcutaneous paraproctitis is located in the anus area.A person is concerned about the sharp pain in this area, which is increasing with defecation.Clearly determined swelling and flushing of the skin.A rise in temperature is also recorded.
Submucoid paraproctitis is located in the submucosal layer of the rectum and proceeds less painfully.
 Ischiorectal paraproctitis is more severe.A purulent process seizes fiber of the sciatic and rectum caverns and pelvis.The patients feel a throbbing pain in the rectum.It is noteworthy that the edema and hyperemia of the skin occur in the late stages of the disease.
Ischiorectal paraproctitis is more severe.A purulent process seizes fiber of the sciatic and rectum caverns and pelvis.The patients feel a throbbing pain in the rectum.It is noteworthy that the edema and hyperemia of the skin occur in the late stages of the disease.
Pelvoreectal paraproctitis occurs above the pelvic floor.In the early days of a person's illness, general symptoms are disturbed: weakness, fever.Then there is pain in the perineum and lower abdomen, frequent urination, stool retention, tenesmus.
Retrorectal paraproctitis differs from pelviorektual only in that first the purulent focus is located in the cell in the back of the rectum, and only then it can descend into ischiorectal cellulose.
Postinjection phlegmon
The appearance of postinjectional phlegmon is caused by a violation of the technique of administering medications, rules of antiseptic during manipulations.The role and properties of the drug itself play a role.So, hypertensive and oily solutions of drugs( cordiamin, vitamins, analgin, magnesium sulfate) often provoke the formation of post-injection purulent complications.
Please note: medication should not be injected into the subcutaneous tissue, but into muscle tissue.This will prevent post-injection purulent complications.
To the appearance of phlegmon also have the presence of chronic diseases that reduce immunity, excessive contamination of the skin with microorganisms, obesity.So, in full people, subcutaneous fat is heavily developed and when the medicine is injected with short needles, it simply does not reach its end point - the gluteus muscle.Therefore, when carrying out injections in such situations, the drug falls not in the muscle, but in the subcutaneous tissue.

The disease often occurs suddenly with the appearance of swelling, redness and pain at the injection site.Patients with fever, as well as lymphadenitis.
Treatment of phlegmon
Important! Treatment of patients with phlegmon is always performed in a hospital.At the initial stages of the disease conservative therapy is possible, the basis of which is intramuscular injection of antibiotics.It is allowed to use physiotherapy procedures.
With progressive phlegmon, surgical treatment should be performed as soon as possible.The operation is under general anesthesia.The surgeon performs phlegmon dissection by dissecting the skin, subcutaneous tissue throughout the entire length.

After tissue dissection, evacuation of pus is carried out.Then the surgeon makes a revision of the purulent cavity and excision of necrotic tissues.For better drainage, additional incisions are made-counterparts.
After surgical procedures, the wound is treated with a hydrogen peroxide of 3%, then tamponed with gauze soaked in an antiseptic.
In the postoperative period, wound dressings are regularly performed, and antibiotics are prescribed.
If no improvement is observed after the surgery, a complication should be suspected: phlegmon progression, thrombophlebitis, erysipelas, sepsis.
Grigorova Valeria, medical reviewer