Sinusitis: simptoma, sprečavanje, liječenje
 The person has four groups of paranasal sinuses, connected by a channel system.In the frontal bone is the frontal sinus, in the maxillary bones - maxillary sinuses.The sphenoid sinus is located in the body of the sphenoid bone, and the latticed labyrinth is formed by the cells of the cranial bone of the skull.Inflammation of mucous membranes of these anatomical formations is denoted by the general term "sinusitis".
The person has four groups of paranasal sinuses, connected by a channel system.In the frontal bone is the frontal sinus, in the maxillary bones - maxillary sinuses.The sphenoid sinus is located in the body of the sphenoid bone, and the latticed labyrinth is formed by the cells of the cranial bone of the skull.Inflammation of mucous membranes of these anatomical formations is denoted by the general term "sinusitis".
Etiology
Inflammation may be a complication of acute rhinitis( rhinitis) or influenza, as well as other bacterial or viral infections( measles, Scarlet fever).Sinusitis can also be a consequence of mechanical injuries of the maxillofacial area.

There are a number of factors that increase the likelihood of sinusitis.
These include:
- frequent ARVI diseases( usually against a background of reduced immunity);
- rhinitis of allergic origin;
- congenital abnormalities of nasal cavity structures;
- curvature of the nasal septum;
- polyps localized in the nasal passages.
Kinds of sinusids
Like most other inflammatory diseases, all sinusitis are divided according to the nature of the current:
- acute;
- are chronic.
On the localization of the pathological process, it is customary to distinguish: 
- maxillary sinusitis( sinusitis of paired maxillary sinuses);
- frontitis( sinus sinusitis of the frontal sinus);
- sphenoiditis( inflammation localized in the sphenoid sinus);
- etmoiditis( lesion of the mucous lattice labyrinth).
In the form of the following:
- exudative;
- productive.
For the etiologic factor that caused the development of the disease, the sinusitis is divided into:
- viral( complications of influenza, ARVI or adenovirus infection);
- bacterial;
- fungal( can develop as a superinfection against a background of viral or bacterial);
- traumatic;
- mixed( there are several etiological factors);
- is allergic;
- medicamentous.
There are also septic and aseptic sinusitis.
The sinusitis( maxillitis) in its etiology is divided into:
- vasomotor;
- allergic;
- is infectious.
Infectious sinusitis( maxillitis) develops due to the penetration of infectious agents of bacterial or viral nature into the cavity of the maxillary sinus.The causative agent falls into maxillary sinuses with a blood flow( hematogenous pathway), through the nose( nasal) or from the periapical region( odontogenic penetration of bacteria is possible with periodontitis of the teeth of the upper jaw).Infection can also be recorded in a sinus with trauma.
The etiology of the frontitis is the same as in the genyantritis, but the symptomatology is more pronounced, and the flow is more severe.
Ethmoiditis most often develops with scarlet fever.Inflammation in the anterior cells of the trellis labyrinth is often accompanied by sinusitis and gonorrhea, and in the posterior cells it proceeds in parallel with sphenoiditis.
Sphenoiditis is rarely diagnosed;Even less often it develops in isolation.As a rule, the pathological process in the sphenoid sinus is a consequence of ethmoiditis with damage to the posterior cells of the labyrinth.
Note: If the pathological process extends to all the sinuses of one half of the face, then they say "gemisinusit", and if the mucous membranes of all sinuses are inflamed on both sides, the patient is diagnosed with "pansinusitis".
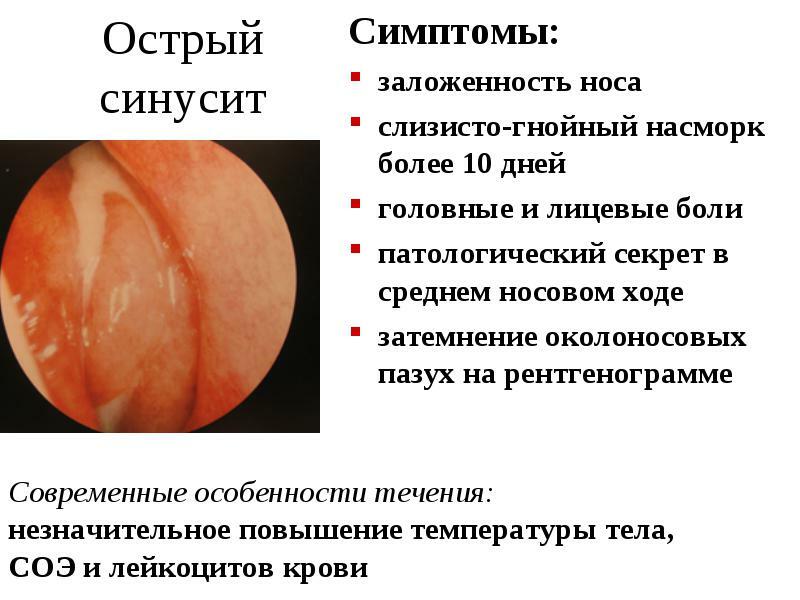
Symptoms of sinusitis

Among the most important clinical manifestations suggesting sinusitis include:
- feeling of heaviness in the frontal or near-nasal area;
- increase in the overall temperature( typical for an acute process);
- painful sensations with sharp turns and inclinations of the head;
- secretion of a thick exudate from the nasal passages.
Feeling of discomfort in the nose, nose bridge or eye socket as the process progresses gradually increases.Pain syndrome usually increases in the evening.Gradually, the localization becomes less concrete, and the whole head or half begins to ache.
Nasal breathing becomes hampered, almost constant bilateral nasal congestion is noted.As a rule, transparent or yellow-green exudate is allocated from the nasal passages.If the outflow from the sinuses is broken, then there may not be excretions.

Acute sinusitis is accompanied by a temperature rise up to 39 ° C;A chronic inflammatory process can occur against a background of normal or subfebrile temperature.The patient has symptoms of general intoxication of the body - high fatigue, malaise, general weakness, sleep disturbance and decreased appetite.The patient often sneezes, and with the accompanying pharyngitis feels a pain in the throat.
One of the characteristic symptoms of sinusitis becomes severe pain of the pulling character in the near-nasal regions, which arises or intensifies when the head or trunk is tilted forward.
With frontaches, severe pain is localized in the forehead area.They are more pronounced in the morning hours.Often the pain syndrome becomes difficult to bear.In the severe course of the pathological process, patients complain of fear of bright light, pain in the eyes and deterioration of the olfactory function.
In acute inflammation of the frontal sinus as a result of disturbance of the local circulation, collateral edema may develop in the region of the forehead and upper eyelid.Skin covers in the projection of the affected area are often hyperemic( have a reddish color).
With sphenoiditis patients complain of headaches in the parietal, occipital or ophthalmic region, and also "inside the head."The pain syndrome in the area of the crown can be evidence of chronic inflammation.Unilateral inflammation of the sinus is often accompanied by pharyngitis, in which there are pains in the throat.Inflammation can affect the area where the optic nerves cross, which is accompanied by a rapidly progressing drop in visual acuity.
Note: Symptoms of sinusitis in children are more pronounced than in adults, and the risk of sinus inflammation is much higher, because the immune system in children is not completely formed.Guards parents should have such symptoms as a thick discharge from the nose and a dry, unproductive cough that lasts more than 1-1.5 weeks.Do not postpone the visit to the ENT doctor!
Diagnosis
 The diagnosis is based on the patient's complaints, the presence of a characteristic clinical picture, as well as data obtained during examination and additional studies( rhinoscopy, radiography and computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses).
The diagnosis is based on the patient's complaints, the presence of a characteristic clinical picture, as well as data obtained during examination and additional studies( rhinoscopy, radiography and computed tomography of the paranasal sinuses).
Rhinoscopy can detect pathological changes in the nasal mucosa, as well as its proliferation( polyposis).
Radiographic examination reveals blackouts in the affected sinuses.
Treatment of sinusitis
When the diagnosis of sinusitis is established, the patient is given complex therapy, which is aimed at eliminating etiological factors( in particular, infection), as well as preventing possible complications and reducing the severity of clinical manifestations( pain and inflammation).
 An important condition for the effective treatment of sinusitis in an adult patient or child is to ensure a good outflow of exudate from the sinus.Drainage is provided either by conservative( medicamental) methods, or through surgical intervention.
An important condition for the effective treatment of sinusitis in an adult patient or child is to ensure a good outflow of exudate from the sinus.Drainage is provided either by conservative( medicamental) methods, or through surgical intervention.
For bacterial sinusitis, patients are shown systemic antibiotic therapy.Before its beginning, the sensitivity of microflora to antibacterial drugs is determined.Approximately the same effectiveness of treatment of bacterial sinusitis is achieved with the appointment of macrolides, cephalosporins and drugs of the penicillin series.In particular, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin and amoxicillin are used in high dosages.
In the room where the patient is constantly staying, it is necessary to provide air humidification.The patient needs an abundant drink to speed up the removal of toxins from the body.In addition, an insufficient supply of fluid in the body contributes to the thickening of the nasal secretions.To stop the pain syndrome, non-narcotic analgesics are prescribed, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used to reduce inflammation.
In addition, vitamin therapy is shown, and immunomodulators can be used to increase the resistance of the body.
Local vasoconstrictors( decongestants based on naphazoline, oxymetazoline or xylometazoline) can be used to reduce edema of the nasal mucosa and improve discharge of the discharge.
Reduction in the intensity of rhinorrhea( outflow from the nose) can be achieved by topical application of a 0.06% solution of ipratropium bromide.
Reduction in the severity of clinical symptoms is noted with the course( 2-3 weeks) using local steroids.
It is advisable to wash the nasal passages with solutions of antiseptics, such as sodium hypochlorite and furacilin.
Important: for sinusitis of viral etiology antibiotics are useless.Patients are shown saline solutions( applied intranasally), as well as funds from groups, mucolytics( preparations that dilute the secret), and topical steroids.Decongestants( preparations from the common cold) can be used even in the treatment of viral sinusitis in children.
 If it is impossible to provide outflow with conservative methods to remove the accumulation of purulent exudate from the sinus, a puncture is performed.Indications for surgical intervention are also complications of problems with the choice of the optimal antibacterial drug and low effectiveness of antibiotic therapy.Getting a sample of the sinus content makes it possible to select the most effective drug in a particular case.
If it is impossible to provide outflow with conservative methods to remove the accumulation of purulent exudate from the sinus, a puncture is performed.Indications for surgical intervention are also complications of problems with the choice of the optimal antibacterial drug and low effectiveness of antibiotic therapy.Getting a sample of the sinus content makes it possible to select the most effective drug in a particular case.
In some situations, with particularly severe sphenoiditis, resection( surgical removal) of the posterior part of the median cone of the sphenoid bone can be performed.
In the phase of remission, the patient is shown physioprocedures - ultra-high-frequency and ultraviolet irradiation of the nasal cavity and sinuses.
Treatment of sinusitis at home
If there is no indication for hospitalization, then conservative treatment of sinusitis is possible at home.It is necessary to strictly observe the regime.Smoking during the period of treatment is completely excluded.The diet should be regular, and the diet should be balanced.It is recommended to refrain from coffee in order to avoid dehydration( dehydration) of the body.It should also be remembered that alcoholic beverages and antibiotics are incompatible.
At home, procedures such as washing the nose with a mild saline solution or furacilin can be performed using a conventional rubber pear or spray.A good moisturizing and antibacterial effect is also provided by steam inhalations with eucalyptus extract.
More detailed recommendations regarding the treatment of sinusitis by folk remedies are presented in the video review:
Complications of
A frequent consequence of "untreated" acute inflammation is chronic sinusitis.
In the absence of timely medical care, cavernous sinus thrombosis is possible, which may result in sepsis.
Acute front with insufficient outflow often changes into chronic.The involvement of the periosteum and bone in the process causes necrosis of the tissues with the formation of fistulas and areas of tissue necrotic tissue( sequesters).Necrotic processes in the posterior sinus wall cause life-threatening complications - brain abscesses and extradural abscesses.Also, there is a high probability of severe inflammation of the meninges( meningitis).
Disturbance of outflow due to swelling with etmoiditis can cause empyema( accumulation of pus) with the spread of the process to the fiber of the orbit.Such serious complications as phlegmons and abscesses of the eyeball can develop, in which vision loss is not excluded.
Forecast
With the timely and properly administered treatment of sinusitis, the prognosis is very favorable.
Prevention of sinusitis
In order to prevent the development of sinusitis, rational and timely treatment of the underlying disease and sanation of foci of odontogenic infection( dental patients) is necessary.
Related Videos:
Konev Alexander Sergeevich, the therapist