Echinococcosis. Description of the disease, symptoms and treatment
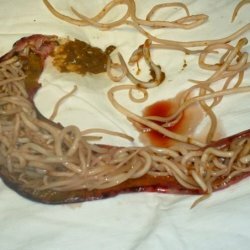
 Echinococcosis. This name of the disease indicates the source of its origin. Echinococcus is a ribbon worm. Its larvae are introduced and grow in various organs of man. And they can get there from dogs, wolves, jackals, foxes. This parasite lives in their small intestine. It consists of a head, neck and several segments. The fourth of them is mature and largest in size.
Echinococcosis. This name of the disease indicates the source of its origin. Echinococcus is a ribbon worm. Its larvae are introduced and grow in various organs of man. And they can get there from dogs, wolves, jackals, foxes. This parasite lives in their small intestine. It consists of a head, neck and several segments. The fourth of them is mature and largest in size.It is this already mature segment that is independently released from the body of the worm, scattering its eggs. They stand out together with the feces outside. Dogs, being carriers of helminths, contaminate the eggs with echinococcus pastures and ponds, premises for keeping pets, as well as human dwellings. Development of the parasite larva begins only from the moment of ingestion of either the joint or its eggs.
The embryo, using digestive juice, is easily released from the shell and sent to the gastrointestinal tract, applying its own hooks. And then it is easily spread by lymph or blood throughout the body. He can stop in any organ( kidney, liver, lungs, muscles, etc.).They settle firmly in them, turns into a common larva. After 15 days it takes the form of a bubble. Months through five bubbles reaches a diameter of not less than 5 mm.
The bubble begins to grow. He grows very slowly. And in twenty years increases its size very much. Its volume reaches ten liters.
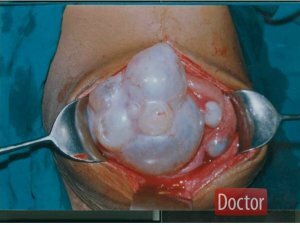
Now it looks like a capsule, which has walls of quinine. Its cavity is filled with a pale yellowish liquid, which has a neutral reaction. It also contains grape sugar, sodium chloride, succinic acid, tyrosine and albumin.
The chitin sheath has two layers: the outer and the inner. Outer is very dense, up to 0.5 cm thick. Internal( embryonic).From this layer, daughter bubbles are formed in a very large amount( up to 1000).
In the body of people, changes associated with mechanical pressure on the internal organs of the cyst begin, which begins to grow. The surrounding tissues become inflamed, experiencing constant irritation due to the products of vital activity of the helminth.
The course of the disease
Echinococcosis is divided into four stages. The first stage is hidden. From the moment the larva penetrates the body and before the appearance of the first subjective signs. The second stage already has almost unexpressed, very subjective symptoms. The third stage is marked with sharply objective symptoms. The fourth stage is characterized by complications.
The period of the course of the stages is almost impossible to establish because of the very slow growth of the echinococcal cyst. One can only say that the rate of increase in symptoms is directly related to the localization of echinococcus.
Not at all worried about a cyst that develops in the peripheral parts of the liver. But if it starts squeezing the hepatic passages, then it causes jaundice. The compressed portal zone leads to the development of ascites. Echinococcal cyst gives dangerous complications when suppuration or rupture of it with seeding of the peritoneum or any other area.
Treatment
This serious illness can be cured only with the help of surgical intervention. The following surgical methods are available:
Radical echinococcectomy. It consists in the complete removal of the cyst along with the fibrous membrane.
An autopsy of the cyst. This is done in order to remove the liquid, all the daughter bubbles and chitinous shells. The open cavity is wiped with a disinfecting solution, drained or tightly sewn.
At autopsy cysts necessarily isolate the body cavity and tissues from the fluid of echinococcus. Otherwise, it can penetrate the abdominal or thoracic cavity, the walls of the wound and lead to their contamination.
An autopsy of the cyst. This is done in order to remove the liquid, all the daughter bubbles and chitinous shells. The open cavity is wiped with a disinfecting solution, drained or tightly sewn.
At autopsy cysts necessarily isolate the body cavity and tissues from the fluid of echinococcus. Otherwise, it can penetrate the abdominal or thoracic cavity, the walls of the wound and lead to their contamination.