Biliary dyskinesia: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of the disease
Bile is a liquid produced by the liver and is involved in the breakdown of fats and certain types of protein that come with food, as well as activating the contractile activity of the intestines. The human liver secretes up to 2 liters of bile per day. It enters the appropriate part of the intestine through a collection of ducts called the biliary tract.
Dyskinesia is a painful condition in which changes in the functioning of the gallbladder and excretory ducts (VDT) and valve defects provoke problems with the outflow of bile. ICD-10 disease code (international classifier of diseases): K82.8.0.
Content
- 1 Causes of DVD
-
2 Symptoms of the disease in various forms of DWD
- 2.1 Symptoms of the hypertensive form of the disease
- 2.2 Symptoms of the hypotonic form of the disease
- 3 Diagnosis of the disease
-
4 Dyskinesia treatment
- 4.1 Treatment of the hypertensive form of vein dysplasia
- 4.2 Treatment of hypotonic VDD
- 4.3 Features of the treatment of DWD in pregnant women
- 4.4 Features of the treatment of DWD in children
- 5 Do they take into the army with DVZHP
- 6 Prevention of DWD
Causes of DVD
There are many reasons that can cause the disease. Let's highlight the common ones:
- Predisposition to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (ulcer, cholecystitis).
- Improper nutrition, violation of the normal diet (too long intervals between adjacent meals). Excessive consumption of fatty, fried or spicy foods, foods containing preservatives.
- Food allergy, atopic dermatitis.
- Stress, mental disorders also provoke the development of dyskinesia, since constant excitement leads to a decrease in the activity of the muscles of the biliary tract. In this case, the secretion of bile decreases, and stagnant processes will begin in the gallbladder.
- Hormonal disruptions and menopause often act as the cause of the appearance of LHD in women.
- Endocrine diseases such as thyrotoxicosis and diabetes mellitus.
- Postponed viral hepatitis.
- An inactive lifestyle or increased sports loads for a long time.
In children, DWHP will occur against the background of stress or due to the fact that there is a congenital pathology in the structure of the gallbladder. A negative impact is exerted by a violation of the food intake regime, force-feeding.
It is not recommended not to pay attention to the disease, since dyskinesia of the biliary tract provokes the consequences - worsening sleep, lack of appetite, can lead to biliary sludge with the formation of gallstones, contribute to the development of a serious complication (inflammation of the bile bubble). Patients often complain of debilitating pain, persistent digestive problems, dermatitis, weakness, and general fatigue.
Symptoms of the disease in various forms of DWD
Depending on the characteristics of the contraction of the muscles of the biliary system, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- Hypertensive DVP (hypertensive type, hypermotor dyskinesia). The cause of this type of disease is increased motility (motor mode) of the muscles of the biliary tract (BHA). The disorder is common in young people.
- Hypotonic DWD (hypotonic type, hypomotor dyskinesia) is caused by decreased muscle tone of the biliary system. This form of the disease is often detected in neuroses, occurs in older people (after 40 years).
Disease of DVP
- Hypokinetic (by hypokinetic type) DWD is associated with lethargy and slow outflow of bile.
- Hyperkinetic (by hyperkinetic type) DWHP is associated with a sharp release of bile.
Doctors-gastroenterologists use a more complex classification, but for a non-specialist there is enough information about two types of DWD: hypotonic and hypertensive.
The clinical signs of any form of dyskinesia are pain in the right hypochondrium, but the nature of the pain will be different. Elevated body temperature for this disease is uncharacteristic and will manifest itself in the event of a secondary infection.
Symptoms of the hypertensive form of the disease
Hypertensive dyskinesia manifests itself as follows: there are sharp, but short-term pain in the right hypochondrium after eating. Such pain is often accompanied by dyspeptic symptoms: diarrhea, painful stools. The pain increases with physical exertion, during stress and during menstruation in women.
Symptoms of the hypotonic form of the disease
Hypotonic dyskinesia, which is caused by insufficiently intense contraction of the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, also causes pain on the right, but in this case the pain will be prolonged, bursting. Patients complain of lack of appetite, nausea, and a feeling of fullness in the area where the gallbladder is located. Examination of such patients reveals painful sensations on palpation in the area of the gallbladder, which works as a contractile reservoir.
A heavy meal or stress factor also leads to increased pain. Patients with hypomotor-type DVD are called indirect symptoms: flatulence, poor appetite, constipation, belching or nausea, specific bitterness in the mouth.
Diagnosis of the disease
To make a correct diagnosis, it is important not to confuse dyskinesia with other serious diseases with similar symptoms. Diagnosis of dyskinesia, in addition to examining the patient, includes a number of examinations. Among them:
- Blood biochemistry. In patients with an exacerbation, an increased level of alkaline phosphatase and other liver enzymes, increased bilirubin are revealed.
- Duodenal intubation. This procedure is used both to collect bile for analysis and to flush the duct with mineral water in case of stagnation.
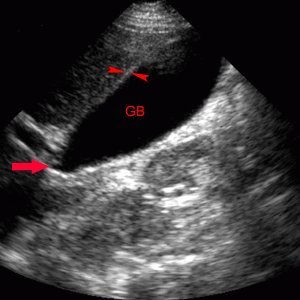
- An ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder allows you to determine the state of the organ and ducts and see the presence of stones. An ultrasound option for a more accurate diagnosis of problems is functional monitoring, in which the examination carried out twice, on an empty stomach and after a special "choleretic breakfast", including eggs, heavy cream or sour cream.
- Tests using ultrasound diagnostics and special choleretic drugs (secretin, etc.).
- Cholecystography is an X-ray examination of the bladder and ducts with the introduction of an intravenous contrast agent, which allows you to get a clear image of the organ in the picture.
Dyskinesia treatment
It is necessary to treat DVP in a comprehensive manner, treatment necessarily includes diet therapy, a normal regimen sleep and rest, therapy of concomitant infectious diseases, taking vitamins and eliminating symptoms disease.
Recommendations will directly depend on the form of the disease. Since the primary manifestations of dyskinesia are very often psychosomatics, supervision by a neurologist and psychotherapy is recommended.
Treatment of the hypertensive form of vein dysplasia
With the hyperkinetic form of the disease, antispasmodics are prescribed (no-shpa, duspatalin, trimedat). The disadvantage of such drugs is that they have an effect on all the muscles of the internal organs, including the muscles of the urinary tract and blood vessels. The painful attack is stopped by analgesics. To facilitate the passage of bile, choleretic drugs are used: Allochol, Hofitol.
Patients are recommended to take mineral waters of a low degree of mineralization, as well as physiotherapy: electrophoresis with antispasmodic drugs (papaverine hydrochloride) on the gallbladder area and applications with ozokerite.
A frequently prescribed herbal remedy is Iberogast, which has an antispasmodic effect on the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract. This remedy is not used directly for the treatment of dyskinesia, but it is often used to restore gastrointestinal motility.
Treatment of hypotonic VDD
The diet of patients with a hypotonic form of the disease includes choleretic products (butter, sour cream, eggs), you can also take choleretic herbs (ginseng, eleutherococcus) and fees. It is recommended to drink mineral water.

Drugs that stimulate the activity of the biliary tract (sorbitol, xylitol) are used. Choleretic drugs with hepatoprotective properties are also used: ursosan, ursofalk. Some doctors for the treatment of dyskinesia, in addition to traditional drugs, also use homeopathy.
Exercise therapy, tonic physiotherapy (acupuncture) and massage often help to cure this form of the disease.
Features of the treatment of DWD in pregnant women
During pregnancy, a hypotonic form of DVP often develops, which is associated with increased activity of hormones that relax the muscles of the internal organs. The pressure of the growing uterus on the gallbladder and the liver also has an effect, due to which the outflow of bile will be disturbed and dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas occurs.
It was found that dyskinesia in pregnant women does not have a negative impact on the development of the fetus. With severe symptoms, it is necessary to consult a doctor and pass all the necessary tests to exclude more serious diseases with similar symptoms. Only a doctor will prescribe adequate treatment that will not harm the pregnancy.
Features of the treatment of DWD in children
Most often in children, in contrast to adults, a hypertensive (spastic) form of DVT is detected, hypotonic is much less common. For treatment, the same methods are used as in adult patients: diet therapy, physiotherapy, unloading the nervous system, healthy work and rest, special exercises.
In the treatment of dyskinesia in children, drugs are also used in a reduced dosage. During periods of exacerbation, hospitalization is possible, in which the nursing process plays an important role: a system of measures for patient care, allowing to improve the condition.
The activities of nurses should be aimed not only at fulfilling all the prescriptions prescribed by the doctor, but also help the child cope with stress in a hospital setting: emotional experiences can exacerbate the patient's condition JVP.
Do they take into the army with DVZHP
A young man with dyskinesia is not exempt from the draft. The conscript is sent for examination to establish the degree to which the function of the organs is impaired.
If during the examination no other diseases are detected, the young man is assigned the category "B-Z", that is, he is taken into the army with a restriction on the type of troops. If an exacerbation of the disease occurs during the period of service, such a soldier will be provided with qualified medical care in a hospital or medical unit.
Prevention of DWD
Prevention for dyskinesia, like the rehabilitation of patients, includes the following measures:
- Regulation of nutrition, eating food in small portions. Restriction in the diet of fatty, fried, alcohol, carbonated drinks. Force-feeding is excluded for children.
- An active lifestyle, morning exercises, sports within reasonable limits.
- Reasonable mode of work and rest, full night sleep.
- Elimination of psycho-emotional overload.
- Regular preventive examinations.



