Scoliosis in children: signs, treatment and prevention

Scoliosis in children is a very common pathology, which is very common not only among schoolchildren, but also among preschool children.We consider the causes of the development of the disease, its signs, methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention.
The concept of scoliosis How to check if the child has scoliosis or not Scoliosis classification Scoliosis children's symptoms How doctors diagnose scoliosis Scoliosis treatment in children Prognosis of child scoliosis Prevention of the diseaseScoliosis concept
In a healthy person, the spinal column has four naturalBending in the sagittal plane: two anterior( cervical and lumbar lordosis) and two posterior( sacral and thoracic kyphosis).The vertical plane dividing the body into the right and left halves is called the sagittal plane.Perpendicular to it, the same vertical plane, passing between the front and back parts of the body, is called frontal.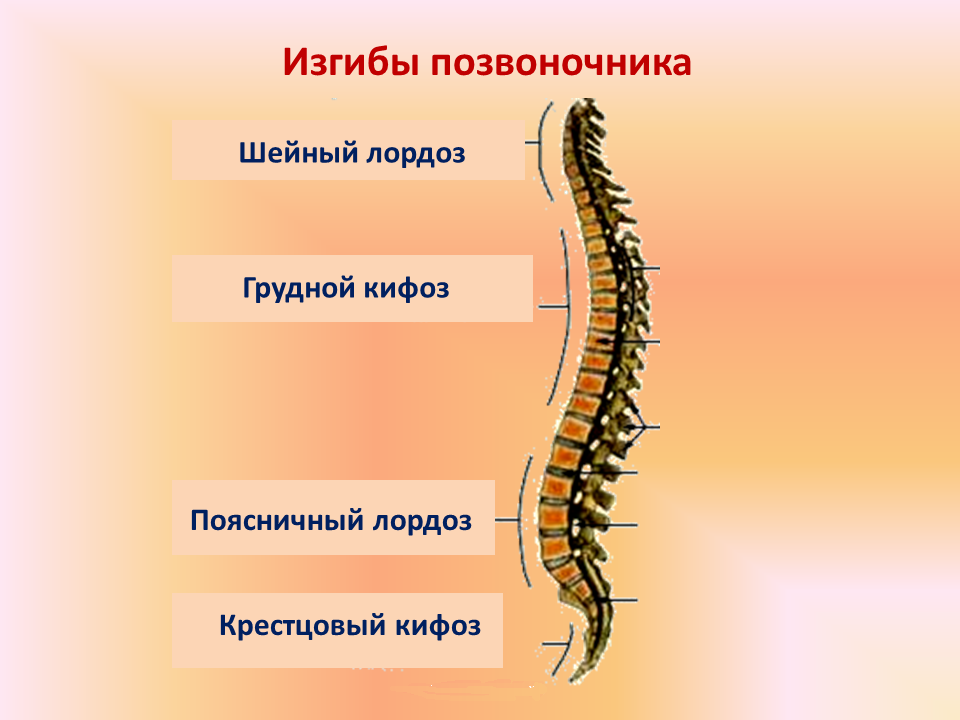
Scoliosis is a pathological curvature of the spine to the left or right in the frontal plane, resulting in later "twisting" of the vertebrae and increasing physiological curves.The resulting squeezing of blood vessels and internal organs causes disruption of the cardiovascular, respiratory, urinary, nervous and other body systems.
It is noticed that girls suffer from scoliosis about 9 times more often than boys.According to medical statistics, almost 10% of children and adolescents have curved spine.Therefore, pediatric orthopedists confidently put scoliosis on one of the first positions among all the pathology of the musculoskeletal system.
In childhood, there are two periods when there is a jump in body growth: from 6 to 7 years and from 11 to 14 years.It is these age intervals that are considered to be periods of high risk of scoliosis.
How to check if the child has scoliosis or not
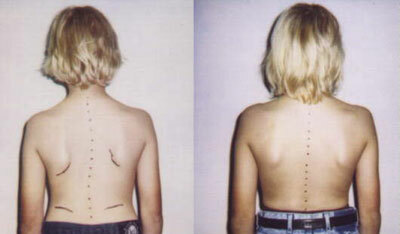
 Ask the child to stand up, turn his back on you, lower his arms along the trunk and do not strain.If you notice that one shoulder is located above the other, or one shoulder is above the other, or in the waist area, the distance from hand to body from one side is greater than the other, ask the child to lean forward.In this position, you can see that not all vertebrae lie on the same line.The presence of at least one of these signs is a reasonable reason to go to a pediatric orthopedic clinic to exclude scoliosis.With this disease, the principle operates: early treatment is a favorable outcome.The child's organism is not fully formed yet, it continues to grow, so it is much easier to resist the progression of scoliosis in a child than in an adult.
Ask the child to stand up, turn his back on you, lower his arms along the trunk and do not strain.If you notice that one shoulder is located above the other, or one shoulder is above the other, or in the waist area, the distance from hand to body from one side is greater than the other, ask the child to lean forward.In this position, you can see that not all vertebrae lie on the same line.The presence of at least one of these signs is a reasonable reason to go to a pediatric orthopedic clinic to exclude scoliosis.With this disease, the principle operates: early treatment is a favorable outcome.The child's organism is not fully formed yet, it continues to grow, so it is much easier to resist the progression of scoliosis in a child than in an adult.
Classification of scoliosis
In orthopedics, various classifications of scoliosis are used depending on the causes of their development, the degree of severity of the pathological process, the time of manifestation of the disease, etc.
If the scoliosis manifests between the first and second year of the child's life, it is called infantile.If the disease manifests itself at the age of 4-6 years, talk about juvenile scoliosis, at 10-14 years - about adolescence.
Two basic types of scoliosis:
- Congenital scoliosis of , which is formed in the prenatal period due to abnormal development of bone-cartilaginous structures.The reasons for it can be:
- anomalies of the development of the spine( semicircular, sphenoid vertebrae);
- dysplasia of the sacro-lumbar region;
- additional ribs or fusion of ribs.
In this case, the transitional parts of the spine suffer more often( lumbosacral, cervicothoracic, lumbosacral).But usually there is no big curvature, since single vertebrae are involved in the process.Therefore, congenital scoliosis is manifested not earlier than 5-7 years.
- Acquired scoliosis of is formed in a child after birth under the influence of certain factors.
Depending on the origin and causes of the disease, five groups of scoliosis are identified:
- Scoliosis of of muscular origin.They are formed due to the pathology of muscles and ligamentous apparatus, for example, in muscular dystrophy, muscle hypotension, congenital dislocation of the hip, contracture of the hip or knee joint, congenital crooked.
- Scoliosis of of a neurogenic of origin.They develop as a result of spinal cord trauma, Friedreich ataxia, suffered poliomyelitis, cerebral palsy, syringomyelia and other pathology of the nervous system.
- The dysplastic scoliosis is all congenital scoliosis.
- Scoliosis based on injuries and diseases of the chest ( fractures of the spine, empyema of the pleura, extensive burns, thoracoplasty, etc.) and other pathological conditions ( rickets, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, Hunter syndrome, Marfan syndrome, Juvenile osteochondrosis, tumors of the spinal cord and spine, etc.).
- Idiopathic scoliosis, the causes of which are not established.This group includes the majority of scoliosis developing in childhood and adolescence.
Factors contributing to scoliotic curvature of the spine:
- inactivity;
- asthenic conditions;
- is not age-appropriate load on the spine;
- incorrect posture;
- continuing to 18 years of formation of the musculoskeletal system.
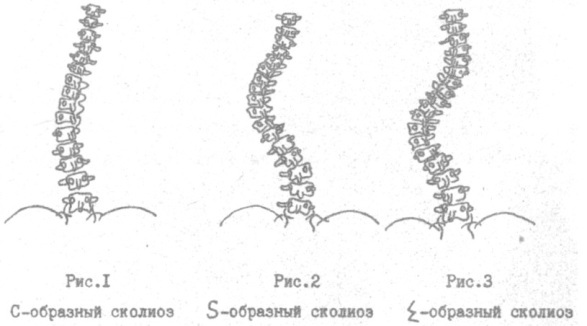
The shape of curvature of scoliosis is as follows:
- C-shaped when the spine has one arc in the frontal plane;
- S -like - two arcs;
- Z -like - three arcs.
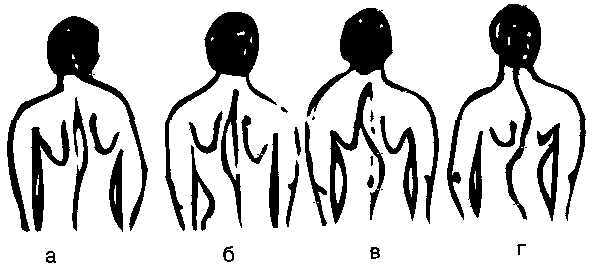
Several types of scoliosis are distinguished by the location of the apex of the lateral curvature of the spine:
- cervicothoracic( level III-IV of the thoracic vertebrae);
- thoracic( at the level of VIII-IX thoracic vertebrae);
- lumbosacral( at the level of the XI-XII thoracic vertebrae);
- lumbar( at level I-II of the lumbar vertebrae);
- lumbosacral( at level V of the lumbar and I coccygeal vertebrae).
There are several different clinical and radiological classifications of scoliosis in terms of severity.Our doctors use the classification of the outstanding domestic orthopedic traumatologist VD Chaklina., compiled in 1973.
I degree , in which the lateral curvature of the spine is noticeable in the vertical position of the body and disappears in the horizontal.If the child is standing, the asymmetry of the shoulder blades and shoulder lines or waist is visible, which depends on the localization of the curvature.The angle of scoliosis on radiographs does not exceed 10 °;
II the degree of , when the lateral deformation of the spine is more pronounced, and it does not disappear in the prone position.The rib hump begins to form, a compensatory arc appears.On the side of the curvature along the spine is determined the muscular roller.The angle of scoliosis on the X-ray image is more than 11 °, but less than 30 °;
III the degree of , in which a pronounced lateral curvature of the spinal column is combined with a formed compensatory arc.The costal hump reaches a large size, the thorax is deformed.Unloading the spine does not give any result.The angle of scoliosis on the roentgenogram is 31 ° -60 °;
IV degree when the scoliosis angle exceeds 60 °.In addition to pronounced musculoskeletal deformities, there are disruptions in the work of internal organs( heart, lungs, etc.).
Depending on the nature of the course of the scoliosis may be progressive and non-progressive.
Symptoms of Child Scoliosis
Children with scoliosis of I-II degree do not present any complaints as such.But the surrounding people note that they always have a lowered head, an asymmetry of the back, and a collapsed shoulders.At the III-IV degree of deformity, the child sometimes begins to complain of back pain, it can be disturbed by shortness of breath, he notices temporary pain in the heart and heart palpitations.The stiffness of movements increases, the child becomes inattentive, quickly becomes tired.Small children may have difficulty walking, stumbling, losing balance.
Scoliosis is not only a physical, but also a cosmetic defect.Sick children may complain of a bad mood, depression.They have broken relationships with peers, self-esteem falls.Therefore, parents in the first place, as well as psychologists and doctors should help the child overcome these problems.
Doctors diagnose scoliosis
Doctors of all specialties working with children know how important early diagnosis of scoliosis is.Therefore, a doctor of a child's institution, a district pediatrician, a surgeon, a children's neurologist, a physiotherapist, a dermatologist, etc., may be suspected of deforming the spinal column and directing the patient for further examination. 
A pediatric orthopedist leads a child with scoliosis or is suspected of it, and in the absence of this doctorIn the polyclinic - a surgeon.For diagnosis, the doctor examines the child from behind and in front, from both sides, in standing position straight and tilting forward, as well as sitting and lying down.In the presence of signs of scoliosis( asymmetry of the back, rib hump, etc.), he determines the degree of curvature of the vertebral column in degrees using a scoliosis meter.If the spine is diverted from the vertical axis by more than 5-7 °, the doctor directs the patient to a radiological examination.
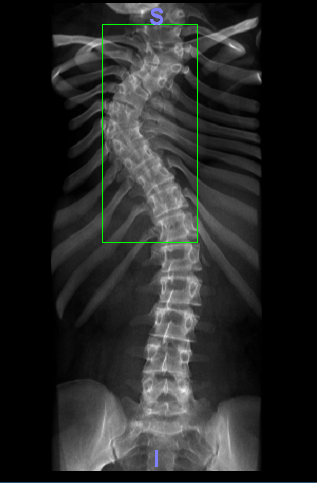 To reveal the pathology of the spinal column, radiography is performed in the vertical and horizontal positions of the patient in two projections.The radiologist doctor at the conclusion indicates the degree of scoliosis, determining it by Chaklin's method.For more detailed information and in the absence of contraindications, X-ray tomography, MRI or CT of the vertebral column, myelography are performed.During treatment, the non-radial method of computer optical topography is used to control its effectiveness.Children's orthopedists often use the camera at all stages of observation and treatment of the patient.Comparing the photographs taken at different times and from different angles, the doctor indirectly can judge the course of the disease.
To reveal the pathology of the spinal column, radiography is performed in the vertical and horizontal positions of the patient in two projections.The radiologist doctor at the conclusion indicates the degree of scoliosis, determining it by Chaklin's method.For more detailed information and in the absence of contraindications, X-ray tomography, MRI or CT of the vertebral column, myelography are performed.During treatment, the non-radial method of computer optical topography is used to control its effectiveness.Children's orthopedists often use the camera at all stages of observation and treatment of the patient.Comparing the photographs taken at different times and from different angles, the doctor indirectly can judge the course of the disease.
If there are indications, the child with scoliosis is advised by a gastroenterologist, cardiologist, lung specialist, neurologist who can prescribe an additional examination( laboratory tests, ECG, ultrasound, etc.).
Treatment methods for scoliosis in children
 The orthopedist doctor chooses the treatment tactics strictly for each child strictly individually.It is determined by the age of the patient, the degree of severity of scoliosis, the course of the disease( with or without progress).All methods of treating this type of deformation of the spine are divided into conservative and surgical.
The orthopedist doctor chooses the treatment tactics strictly for each child strictly individually.It is determined by the age of the patient, the degree of severity of scoliosis, the course of the disease( with or without progress).All methods of treating this type of deformation of the spine are divided into conservative and surgical.
Conservative treatment implies orthopedic treatment, massage, physiotherapy, physical therapy, manual therapy, wearing a corset.The orthopedic regime includes constant monitoring of correct posture, sleep on a hard board, unloading of the spine by the horizontal position of the body several times a day.
If the child has scoliosis of I-II degree, and the disease does not progress, all measures are taken to eliminate the causes contributing to the curvature, the organization of the correct motor activity of the patient and the unloading of the spine.The main thing is to prevent the progress of the pathological process.The child is prescribed an orthopedic regimen, a massage of the entire back, therapeutic gymnastics, swimming.
 If the scoliosis of I-II degree progresses, to the above-listed appointments, the orthopedist is added by a special complex of physiotherapy exercises, manual therapy( soft techniques), physiotherapy( magnetotherapy, mud and hydrotherapy, SMT therapy, electromyostimulation, heat treatment, etc.)Wearing an orthopedic corset, correcting the position of the spinal column.
If the scoliosis of I-II degree progresses, to the above-listed appointments, the orthopedist is added by a special complex of physiotherapy exercises, manual therapy( soft techniques), physiotherapy( magnetotherapy, mud and hydrotherapy, SMT therapy, electromyostimulation, heat treatment, etc.)Wearing an orthopedic corset, correcting the position of the spinal column.
If conservative treatment does not give the desired effect, and the disease progresses, if the angle of scoliosis exceeds 40 °, and the child has impaired internal organs functions, he is shown surgical treatment of the disease.The doctors try to do the operation after 10, but up to 14 years, since this age interval is considered optimal for its conduct.
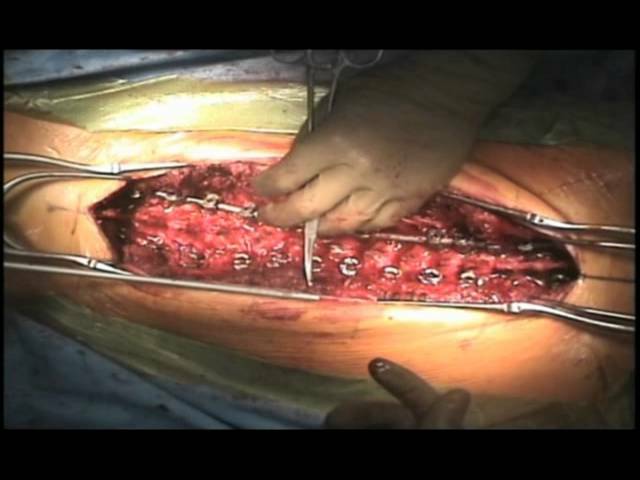
Surgical treatment means implantation in the chest of special devices( distractors, endocorrectors, etc.), fixing the spine in the maximum possible rectified state.The surgical intervention is always preceded by the extension of the spinal column.Other options for surgical treatment are bone-plastic( resection of the vertebrae), mobilizing( removal of the intervertebral disc, etc.) and cosmetic( resection of the humerus, angle of the scapula, etc.) of the operation.After any surgical intervention, the child undergoes a long course of rehabilitation therapy.
Prognosis of children's scoliosis
Scoliosis, manifesting in a child of 10-12 years, is less aggressive.The disease occurring before the age of 6 years usually has a progressive course, accompanied by early development of deformity of the spinal column.Completely cure the disease is impossible, but to suspend the pathological process and reduce the severity of the curvature is quite realistic.
Children with scoliosis are subject to long-term follow-up by an orthopedist and must receive specialized treatment at least twice a year.The prognosis in terms of mobility and independence is determined by the degree of scoliosis.Sick children with mild forms of curvature move freely, participate in active games on a par with peers.With a severe degree of scoliosis, independence can be limited because of a disequilibrium in the body, and the child will need a cane or walker.In this case, mobility is most often limited, especially the torso of the body.
 For girls with deformities of the spine, the prognosis in terms of pregnancy is quite favorable, since special sets of exercises have been developed that facilitate the bearing of the child and prepare the woman for childbirth.
For girls with deformities of the spine, the prognosis in terms of pregnancy is quite favorable, since special sets of exercises have been developed that facilitate the bearing of the child and prepare the woman for childbirth.
Young men of draft age suffering from scoliosis are not subject to or subject to restrictions on conscription in the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, which is determined by the degree of severity of deformation.
Prevention of the disease
 Scoliosis, like many diseases, is easier to prevent than treat.No one is better than the parents of the child to cope with the prevention of deformity of the spine.Only parents have the opportunity to constantly monitor their child.
Scoliosis, like many diseases, is easier to prevent than treat.No one is better than the parents of the child to cope with the prevention of deformity of the spine.Only parents have the opportunity to constantly monitor their child.
Recommendations for Parents:
- Do not hurry up a child under the age of one year: do not put it on pillows if it can not sit on its own, and do not use a walker if the baby is not standing by himself;
- write your son or daughter to the pool as early as possible, as swimming is the most effective sport in terms of scoliosis prevention;
- always monitor the correctness of posture in the child, his physical activity and motor conditions;
- with a personal example, teach him to do morning exercises;
- purchase a child to sleep an orthopedic mattress;
- properly organize his workplace, for school, buy a knapsack.
Remember that in the treatment and prevention of scoliosis, only patience and perseverance, combined with confidence and optimism, will lead you to success.
Zaluzhanskaya Elena Aleksandrovna, pediatrician