Types of anesthesia in dentistry
![An injection [1]](/f/62/fb/62fb9a62327f7221d205229e6231ed62.jpg) Toothache is a problem that almost everyone faced.It is a sign of this or that pathology of the organs of the dentoalveolar system.Such diseases require therapeutic, and in many cases, surgical treatment.Often patients postpone a visit to the dentist for fear of pain in the treatment of teeth.
Toothache is a problem that almost everyone faced.It is a sign of this or that pathology of the organs of the dentoalveolar system.Such diseases require therapeutic, and in many cases, surgical treatment.Often patients postpone a visit to the dentist for fear of pain in the treatment of teeth.
Modern dentistry without pain
More recently, a number of therapeutic manipulations associated with unpleasant feelings for the patient could be carried out without prior anesthesia, So it's no surprise that many people are afraid of a dentist's office.Postponing a meeting with a specialist "to the last", a patient with an ordinary carious lesion risks waiting for the development of complications of the disease, which may require surgical treatment.
Currently, in all clinics and dental offices, doctors perform dental treatment without pain, for which different types of anesthesia are used.
Anesthesia is understood as the decrease or complete disappearance of sensitivity throughout the body or in its individual areas.In most cases, this is achieved through the introduction of medications that disrupt the transmission of pain impulses to the brain from the area of intervention.Anesthesia in dentistry is necessary to ensure that the patient does not experience pain in the treatment of teeth.Calm behavior of the patient gives the doctor an opportunity to conduct therapeutic or surgical manipulations quickly enough, qualitatively and in the necessary volume.
Indications for anesthesia
Anesthesia is indicated by the following manipulations:
- treatment of deep caries;
- extirpation or pulp amputation( depulpation);
- extirpation( removal) of the tooth;
- other surgical interventions;
- preparation of teeth for prosthetics;
- some types of orthodontic treatment.
Note: the average caries can also be an indication for anesthesia, since the area of the border of the enamel and dentine layers is quite sensitive, and the pain in dental treatment is often noted here.
Types of anesthesia in dentistry
Anesthesia is divided into local and general( anesthesia).It is also accepted to distinguish between drug and non-pharmacological anesthesia.
 There are several varieties of non-drug anesthesia :
There are several varieties of non-drug anesthesia :
- audioanalgesia;
- electroanalgesia;
- anesthesia through hypnotic exposure;
- computerized anesthesia.
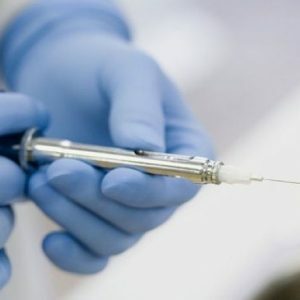
Medical anesthesia presupposes the injection of an anesthetic blocking the holding of a pulse for the time required for medical intervention.After a certain period of time, the drug is cleaved, and the sensitivity is completely restored.Modern painkillers allow completely to avoid unpleasant sensations during treatment.
General anesthesia in the treatment of teeth is used relatively rarely and in the presence of special indications.More often it is used in maxillofacial surgery.
Local anesthesia in dentistry
Local anesthesia is performed before most manipulations.For the body, it is much safer than anesthesia.Until recently, the most common anesthetics were Novocaine and Lidocaine, but now more effective drugs are being used.
There are several types of local anesthesia:
- application;
- infiltration;
- conductor;
- intraligamentary;
- intraosseous;
- stem.
Application anesthesia
This is an anesthetic that provides superficial anesthesia.It is carried out by spraying the spray or applying the preparation in the form of an ointment on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity.The most commonly used 10% of lidocaine in aerosol cans.
Application anesthesia is indicated to reduce the sensitivity of soft tissues in the place where the injection will be made, as well as the treatment of the mucous membrane( with stomatitis and gingivitis) and the opening of small suppuration.In therapeutic practice, it can be used before the removal of mineralized deposits in the cervical region, and in the orthopedic region - when preparing the tooth for prosthetics( turning).
Infiltration anesthesia
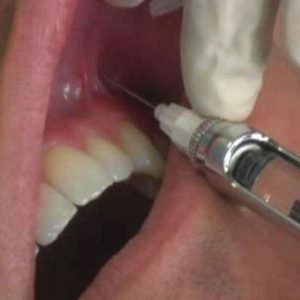 Infiltration anesthesia can numb one tooth or a small area of the mucosa.It is practiced in the removal of the neurovascular bundle, as well as in the treatment of deep caries.
Infiltration anesthesia can numb one tooth or a small area of the mucosa.It is practiced in the removal of the neurovascular bundle, as well as in the treatment of deep caries.
Injection, as a rule, is carried out in the projection of the apex of the root.In this case, the anesthetic drug blocks the pain impulse at the level of the nerve branch.Most often, the upper teeth are anaesthetized in this way, because the relatively small thickness of the upper jaw bone allows the anesthetic to enter relatively easily into the nerve endings.
Conducting anesthesia
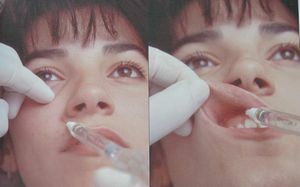 It is needed when infiltration does not give the desired effect or it requires anesthetizing several nearby teeth.It is also used for extirpation of teeth, for dissecting abscesses with periostitis and exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, and for draining a purulent focus.Injection of anesthetic will temporarily "disconnect" the entire nervous branch.
It is needed when infiltration does not give the desired effect or it requires anesthetizing several nearby teeth.It is also used for extirpation of teeth, for dissecting abscesses with periostitis and exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, and for draining a purulent focus.Injection of anesthetic will temporarily "disconnect" the entire nervous branch.
Most often, before surgery on the upper jaw, a tubular and palatal conductive anesthesia is performed( if necessary, supplemented with incisive anesthesia), and for the analgesia of the lower jaw, a torus or mandibular anesthesia.
Intraligamentary( intramuscular) local anesthesia
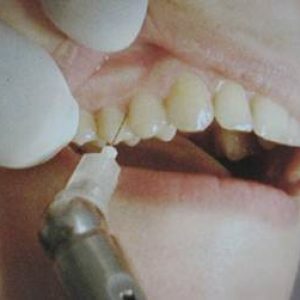 Often practiced in pediatric dentistry in the treatment of deep caries and its complications, and also in those cases where the tooth is to be removed.
Often practiced in pediatric dentistry in the treatment of deep caries and its complications, and also in those cases where the tooth is to be removed.
Injection administration of the drug is carried out in the periodontal ligament, which is located between the alveolar wall and the root of the tooth.Mucous membranes do not lose sensitivity, which excludes accidental biting of the cheek, tongue or lips by the child.
Intraosseous anesthesia
 It is indicated in the operation for extirpation of the tooth.Initially, an anesthetic drug is injected into the gum, and after the onset of local numbness - into the spongy jawbone layer in the interdental space.In this case, only the sensitivity of a certain tooth and a small portion of the gum disappears.The effect develops almost instantly, but it remains relatively short time.
It is indicated in the operation for extirpation of the tooth.Initially, an anesthetic drug is injected into the gum, and after the onset of local numbness - into the spongy jawbone layer in the interdental space.In this case, only the sensitivity of a certain tooth and a small portion of the gum disappears.The effect develops almost instantly, but it remains relatively short time.
Stem Anesthesia
Stem anesthesia in dentistry is possible only in a hospital.Indications for it can be pain of a high degree of intensity, neuralgia( in particular - the facial nerve), as well as serious injuries of the jaws and zygomatic bone.This type of anesthesia is also practiced before the beginning of surgical interventions.
Injection of anesthetic is performed in the area of the base of the skull, which allows you to disconnect immediately the upper and lower jaw nerves.The effect of stem anesthesia is characterized by power and long duration.
Contraindications
Before conducting anesthesia, the dentist must find out if the patient has serious physical illnesses or allergies to medicines.
Contraindications to the use of painkillers may be :
- allergic reactions after the administration of anesthetics;
- acute cardiovascular diseases in history( heart attacks or strokes less than six months ago);
- diabetes mellitus;
- some other hormonal disorders against the background of pathologies of the endocrine system( thyrotoxicosis, etc.).
Important: In case of decompensated forms of endocrine diseases, the patient should be treated exclusively in a hospital.Particular care should be taken when anesthetizing children and pregnant women.
Modern painkillers
 Lidocaine( 2% for injections and 10% for applications) and Novocain( currently less commonly used) can be used for local anesthesia.To enhance and prolong the effect in the solutions of these drugs, before admission, as a rule, "traces" of adrenaline are added.
Lidocaine( 2% for injections and 10% for applications) and Novocain( currently less commonly used) can be used for local anesthesia.To enhance and prolong the effect in the solutions of these drugs, before admission, as a rule, "traces" of adrenaline are added.
Also used are modern anesthetics such as:
- Artikine;
- Mepivacaine;
- Ultracaine;
- Ubistezin;
- Scandinavian;
- Septonest.
 These preparations are delivered in special containers-carpets, which are placed in the body of a metal carpool syringe.Separately, a disposable needle is screwed onto the syringe, the thickness of which is several times smaller than that of conventional needles for injections.
These preparations are delivered in special containers-carpets, which are placed in the body of a metal carpool syringe.Separately, a disposable needle is screwed onto the syringe, the thickness of which is several times smaller than that of conventional needles for injections.
An obvious advantage of carpal anesthesia is that injections are virtually painless.In addition, a number of solutions already include adrenaline or norepinephrine for a stronger and longer-lasting effect.
Anesthesia in pediatric dentistry
Anesthetics, which could be called absolutely safe for children, do not exist.In childhood, the body is extremely sensitive to any medication, so the risk of complications after injections is particularly high.
Earlier Lidocaine and Novocaine were used for anesthesia, and now Arikain and Mepivacaine are considered the safest drugs for children.
In the treatment of children, dentists practice the following types of anesthesia :
- Application;
- Infiltration;
- Intraligmentary;
- Conducting.
Note: in young patients, the risk of developing psychogenic complications is very high, since the child's psyche is not completely formed.The most frequent complication is a short-term loss of consciousness due to strong emotions( fright).
The most common complications of local anesthesia
Possible complications for anesthesia include:
- allergic reactions( with hypersensitivity to the drug);
- toxic reactions( with overdose);
- prolonged impairment of sensitivity due to trauma to the nerve branch by the needle( if the injection rules are violated);
- pain and burning at the injection site( occurs often and is considered the norm).
There is also the likelihood of the following complications:
- formation of bruising( swelling and bruising) after the injection as a result of damage to the blood vessel;
- fracture of the needle during injection( extremely rare);
- infection of tissues( if the doctor does not comply with the rules of asepsis and antiseptic when pricking into the infected area of the mucous membrane);
- transient spasm( trismus) of the masticatory muscles( with nerve damage or muscle fibers):
- random biting of soft tissues( lips, cheeks, tongue) due to temporary loss of sensitivity.
The use of modern painkillers allows to minimize the probability of development of most complications.
Recommendations for patients
On the eve of treatment and immediately before visiting a dentist, refrain from drinking alcoholic beverages, since ethyl alcohol can reduce the analgesic effect of most drugs.
In case of emotional stress for the night, it is recommended to take a sedative( Afobazol, Valerian extracts or Leonurus extracts).
In case of malaise, in particular - against a background of acute respiratory viral infection or influenza, a visit to a doctor should be postponed.
Patients during menstruation should also be delayed with dental treatment, if possible.In this period, nervous excitability and susceptibility to drugs increase.Dental extraction and other surgical interventions during menstruation can cause prolonged bleeding.
General anesthesia in dentistry
 Under general anesthesia is understood the total loss of sensitivity, accompanied by various degrees of impaired consciousness.
Under general anesthesia is understood the total loss of sensitivity, accompanied by various degrees of impaired consciousness.
General anesthesia in the treatment of teeth is used relatively rarely and according to strict indications, since this method of anesthesia is far from safe.He is involved in serious surgical interventions in the maxillofacial area.
Please note: Nowadays, in the treatment of teeth( including children), inhalation anesthesia with nitrous oxide( "fun gas") is increasingly used.
Indications for general anesthesia in dentistry are :
- allergy to funds for local anesthesia;
- Mental illness;
- panic fear of dental manipulation.
Contraindications include:
- respiratory diseases;
- Serious pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- intolerance of drugs for anesthesia.
Prior to planned interventions involving the introduction of a patient into anesthesia, the patient should undergo a test including:
- ECG removal for an objective evaluation of the heart condition;
- general blood test;
- blood test for HIV and hepatitis.
In the preoperative period, the patient should refrain from alcohol, nicotine, as well as eating and drinking.In the presence of acute diseases, the operation should be postponed until the onset of a period of remission or complete reconvalescence.
General anesthesia in the treatment of teeth can be conducted only with the participation of anesthesiologist-resuscitator.
Video:
Plisov Vladimir, dentist