Bronchial asthma: causes, symptoms, treatment
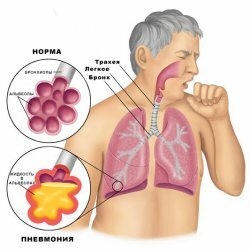
 Asthma is a very serious disease of an immuno-allergic origin that develops as a result of noninfectious inflammation in the respiratory system( the so-called "bronchial tree").For bronchial asthma is characterized by a chronic progressive course with periodic attacks, in which bronchial obstruction and asthma develops.
Asthma is a very serious disease of an immuno-allergic origin that develops as a result of noninfectious inflammation in the respiratory system( the so-called "bronchial tree").For bronchial asthma is characterized by a chronic progressive course with periodic attacks, in which bronchial obstruction and asthma develops.
Pathology occurs as a result of a combination of a number of endo- and exogenous factors.Among external factors - psychoemotional stresses, excessive physical exertion, unfavorable climate, as well as the impact of chemical irritants and allergens.Internal factors include disorders from the immune and endocrine systems, as well as hyperreactivity of the bronchi.
Many patients have a family predisposition to the disease.
Now bronchial asthma in adults and children, unfortunately, is quite common, and finally it is extremely difficult to cure this disease.
Table of contents: Causes of asthma Stages and forms of bronchial asthma Symptoms of bronchial asthma Diagnosis of asthma Treatment of bronchial asthma Asthma in children Asthma in pregnancy Prevention of bronchial asthmaCauses of asthma
The inflammatory process developing in the bronchial tree with asthma is characterized by high specificity.The cause of the pathological process is the effect of the allergic component in combination with immune disorders, which causes the paroxysmal course of the disease.
Please note: is a family history-we suffer from every third person suffering from asthma.With hereditary predisposition, the elements provoking asthma attacks are very difficult to follow;The disease is atopic in nature.

In addition to the main( allergic) component, there are a number of additional factors that determine the course of the disease and the frequency of occurrence of asthma attacks.
These include:
- increased reactivity of smooth muscle cells in the walls of the bronchial tree, leading to spasm in any stimulation;
- exogenous factors causing a massive release of mediators of allergy and inflammation, but not leading to a general allergic reaction;
- swelling of bronchial mucosa, worsening airway patency;
- Inadequate formation of mucous bronchial secretions( cough with asthma is usually unproductive);
- primary lesion of small diameter bronchi;
- changes in pulmonary tissue due to hypoventilation.
 Important: is one of the leading factors leading to asthma, called ordinary house dust.It contains a large number of microscopic ticks, chitin of which is a powerful allergen.
Important: is one of the leading factors leading to asthma, called ordinary house dust.It contains a large number of microscopic ticks, chitin of which is a powerful allergen.
Stages and forms of bronchial asthma
Four stages of asthma development have been identified:
- intermittent( characterized by a relatively mild course);
- persistence of mild degree( medium-heavy course);
- medium persistence( heavy current);
- severe persistence( extremely severe form).
In the early stages, seizures develop relatively infrequently and can be quickly stopped.As the progression of the exacerbation is progressively less sensitive to drug therapy.
Based on the etiology( origin), the following forms are distinguished:
- exogenous( asthma attacks provoke contact with the allergen);
- is endogenous( seizures are provoked by infection, hypothermia, or stress);
- asthma of mixed origin.
The following clinical pathogenetic forms are classified as special forms:
- aspirin( due to salicylate intake);
- is reflux-induced( against a background of gastroesophageal "reverse casting");
- at night;
- professional;
- Physical stress asthma.
Atopic( allergic) bronchial asthma is the most common form of pathology due to the hypersensitivity of the respiratory system to various kinds of allergens.The protective reaction of the immune system provokes a sharp spasmodic contraction of the muscular elements of the bronchi, that is, bronchospasm develops.Atopic asthma is a separately considered variant of the exogenous form.The genetic predisposition to allergy plays a leading role in its pathogenesis.
Symptoms of bronchial asthma
- Suffocation or shortness of breath at rest or under load.To provoke the appearance of such symptoms can be the inhalation of pollen of plants, a sudden change in ambient temperature, etc. An important distinctive feature of asthma attacks at an early stage of the disease is the suddenness of their development.
- Surface breathing of the expiratory type( with prolonged exhalation).Patients are concerned that they can not completely exhale.
- Dry nasal cough that develops in parallel with shortness of breath.Cough for a long time does not work;Only at the end of the attack, there is a loss of a small amount of mucous bronchial secretion( sputum).Dry whistling wheezing when breathing.
- .In some cases, they can be determined at a distance, but are better audible during auscultation.
- Orthopnea is a characteristic forced posture that facilitates the exhalation process.The patient has to take a sitting position with his legs down and keep his hands on the support.
 Important: only a few of the above mentioned signs can indicate a pathological increase in bronchial reactivity.As a rule, at first the attacks are short and do not develop again for a long time.In this case we are talking about a "period of imaginary well-being".Gradually, the symptoms will be more pronounced and often manifested.Earlier, a doctor's appointment with the appearance of the first signs is the key to the effectiveness of therapy.
Important: only a few of the above mentioned signs can indicate a pathological increase in bronchial reactivity.As a rule, at first the attacks are short and do not develop again for a long time.In this case we are talking about a "period of imaginary well-being".Gradually, the symptoms will be more pronounced and often manifested.Earlier, a doctor's appointment with the appearance of the first signs is the key to the effectiveness of therapy.
In the early stages of clinical manifestations are not accompanied by general disorders, but as the disease progresses, they certainly develop.
The following asthma symptoms are associated with this:
- headache and dizziness.Symptoms may be noted with moderate bronchial asthma and indicate the presence of respiratory failure;
- general weakness.If a person suffering from bronchial asthma tries to perform active movements during an attack, the lack of air increases.With an easy flow between attacks, patients normally tolerate adequate physical activity;
- heart palpitations( tachycardia) are noted during an attack.The heart rate is 120-130 per minute.In patients with moderate to severe asthma, a small tachycardia( up to 90 beats per minute) occurs between seizures;
- blueing of the extremities( acrocyanosis) and diffuse cyanosis of the skin.The appearance of this clinical sign is due to the expressed increasing respiratory insufficiency and testifies to the severe form of the course of asthma;
- characteristic change in the shape of the terminal phalanges of the fingers( "drumsticks") and nail plates( "watch glass");
- symptoms of emphysema.Changes are characteristic for long and( or) severe course of the disease.The patient's chest width increases and the supraclavicular areas protrude.With percussion, the expansion of the lungs' boundaries is determined, and when listening, weakening of breathing;
- symptoms of "pulmonary heart".With a severe course of asthma, a steady increase in pressure in the small circulatory system develops, which leads to an increase in the right ventricle and atrium.When auscultation in the projection of the valve of the pulmonary artery, you can identify the accent of the second tone;
- is prone to allergic reactions and allergic diseases.
Important: The static status is a prolonged suffocation that is not stopped by traditional medical therapy.The condition is accompanied by a violation of consciousness, up to complete loss.Asthmatic status can lead to death.
Diagnosis of asthma

Diagnosis of "bronchial asthma" is based on the presence of a symptomatic symptomatology.Differential diagnostics of asthma with chronic bronchitis can be a certain complication.The latter is characterized by alternation of the phases of exacerbation( lasting 2-3 weeks) and remission.
Asthma is characterized by sudden seizures of varying duration( from several minutes to several hours), between which the patient regains his normal state of health.For bronchitis, sudden nighttime attacks are uncharacteristic.Shortness of breath is a "classic" symptom of an asthma attack, regardless of the severity of the course, and with bronchitis it develops only with a long-term obstructive form or a very severe exacerbation.
Cough accompanies bronchitis both during the period of exacerbation and during remission, and for asthmatics this symptom occurs only directly during an attack.Increased body temperature often accompanies exacerbation of bronchitis, and for asthma, hyperthermia is not appropriate.
Note: differential diagnosis is important in the initial stages of chronic bronchitis and bronchial asthma.The prolonged course of both pathologies inevitably leads to similar changes in the respiratory system - bronchial obstruction.
Treatment of bronchial asthma
Treatment of bronchial asthma is carried out in stages.Each of the stages of development requires the introduction of adjustments to the plan of therapeutic measures.To assess asthma in the dynamics and degree of disease control, a peak flow meter should be used.


The main medicines used to treat asthma have a number of side effects.The manifestation of undesirable effects can be minimized by applying the most rational combination of drugs.
Basic( basic) therapy involves maintenance treatment aimed at reducing the inflammatory response.Symptomatic therapy is a measure taken to relieve attacks.
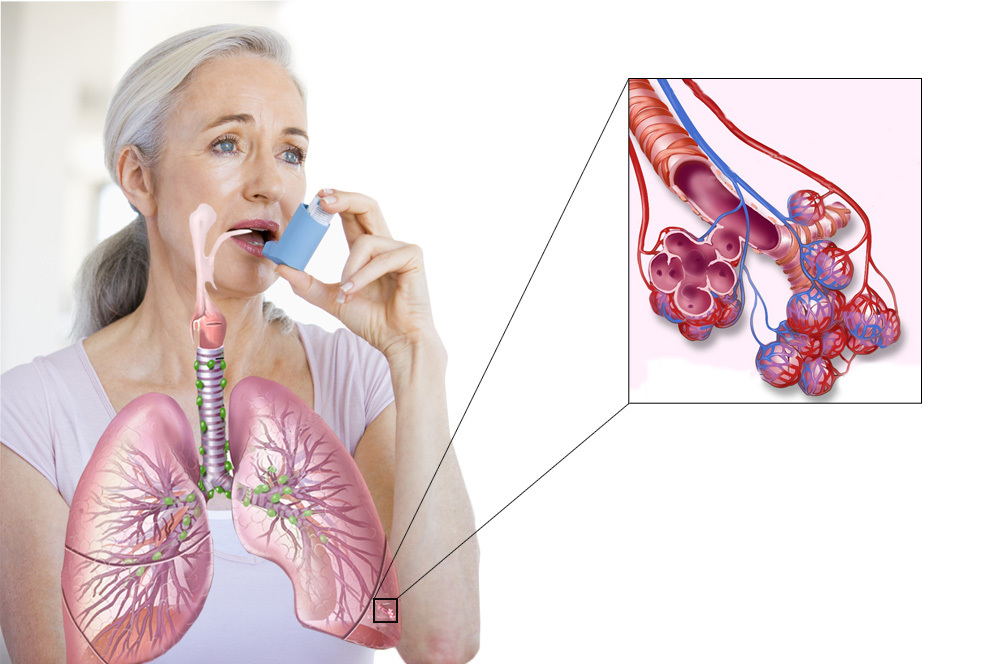
Specialists note that the appointment of hormonal drugs( glucocorticosteroids) allows you to monitor the pathological process.Drugs of this group not only relieve symptoms during an attack, but also are able to influence the main links of pathogenesis, blocking the release of mediators of allergy and inflammation.Rational hormone therapy, started as soon as possible, significantly slows the development of asthma.
The main groups of medicines used to treat bronchial asthma:
- glucocorticosteroids.These funds are assigned for light and medium compensated flow of the process.In emergency cases, they are ineffective in the tablets, but inhalations with these pharmacological preparations help to repair the asthmatic status of the patient;
- leukotriene antagonists( prescribed for bronchial obstruction);
- methylxanthines.For basic therapy, tablet forms are used, and for the relief of attacks, injections are required( Euphyllin in high dosages);
- monoclonal antibodies.Injections are indicated when the allergic component is established.For the removal of attacks do not apply;
- Kromones.Inhalations of this group are indicated for the basic treatment of mild forms.The attack is not relieved;
- b2-adrenomimetics.For maintenance treatment, prolonged inhalers are used, and short-acting agents( Salbutamol, Ventolin) for stopping the attack;
- anticholinergics.In special inhalers are indicated for emergency care for bronchial asthma during an attack.
Combination means for inhalation can be prescribed for both emergency aid( Simbicort preparation) and for regular use( Seretide, Berodual).
Bronchial asthma in children
Children do not always manage to make a diagnosis on time, as bronchial asthma often manifests the same symptoms as ARD.Characteristically, with asthma, the temperature does not rise, and so-called."Harbingers".Symptoms-precursors:
- restless behavior of the baby for 1-2 days before the attack;
- mucous-watery discharge from the nose in the morning immediately after awakening;
- frequent sneezing;
- after a few hours - a mild dry cough.
Seizure in children develops usually before going to bed or immediately after waking up.The intensity of cough is reduced if the child is given a sitting or vertical position.Breathing becomes intermittent with short, frequent breaths.
 Note: in children older than 1 year may exhibit atypical symptoms such as lacrimation, itchy skin and rashes.
Note: in children older than 1 year may exhibit atypical symptoms such as lacrimation, itchy skin and rashes.
Bronchial asthma in children is more likely to cause illness in boys, since they have a diameter of the lumen of bronchial tubes than in girls.
Obesity in children increases the risk of developing asthma, since the diaphragm in this case is higher and ventilation is difficult.
Modern medications do not completely cure bronchial asthma in children, but drugs help to relieve the attack and minimize allergic and inflammatory reaction.The specificity of therapy is that inhalations are indicated as the main method of administration of medicinal substances.
About bronchial asthma in children is described in detail in this video review:
Asthma in pregnancy
 During pregnancy, an asthma attack not only negatively affects the woman's body, but can also cause a hypoxia( oxygen starvation) of the fetus.
During pregnancy, an asthma attack not only negatively affects the woman's body, but can also cause a hypoxia( oxygen starvation) of the fetus.
The control of the disease allows to minimize the possible risk for the future child.Basic therapy should not be interrupted.Of course, you can not refuse and the funds needed for emergency care for bronchial asthma.Loss of control threatens preeclampsia( with placenta damage), hypermeasis( pronounced toxicosis), complications during childbirth and premature birth.Do not exclude the delay of fetal development.
Most of the drugs used to treat this disease are practically safe for the fetus.
Note: The safest hormonal( corticosteroid) drug for inhalations is Budesonide.
In the second half of pregnancy, the course of asthma can become more severe.A future mother needs constant monitoring of her pulmonary function.In severe form after the 32nd week of pregnancy, ultrasound of the fetus is required.
Prevention of bronchial asthma
 Unfortunately, at present no sufficiently effective measures have been developed to prevent bronchial asthma.Persons with hereditary predisposition can be recommended to minimize contact with allergenic substances, if possible, to exclude hypothermia and pay increased attention to changes in health.
Unfortunately, at present no sufficiently effective measures have been developed to prevent bronchial asthma.Persons with hereditary predisposition can be recommended to minimize contact with allergenic substances, if possible, to exclude hypothermia and pay increased attention to changes in health.
Children are recommended to breast-feed for at least 1 year.If you need to transfer the baby to the artificial feeding of the mixture should be selected, after consulting with the pediatrician.It is undesirable to have pets if there is a small child in the house.Even an aquarium should not be kept, since dry food is a powerful allergen.Use pillows, blankets and mattresses only with hypoallergenic stuffing.
Hardening and rational nutrition will help to strengthen the body's defenses, which will reduce the likelihood of an inadequate immune response.
About the problem of increasing the number of patients with bronchial asthma and methods of diagnosis and prevention of this disease tell specialists:
Konev Alexander, the therapist