Chronic pneumonia: symptoms, clinical picture, treatment
 At the beginning of the 19th century, he first mentioned and introduced into medical terminology the concept of chronic pneumonia, Dr. Bale. Further, during almost the entire 20th century, the question of the specific nature of this disease was studied. Work was carried out to investigate the onset of the process of suppuration of pulmonary tissues and the pathology of the respiratory organs. A great contribution to the study was made by many employees and professors of medicine, such as Davydovsky, Khazanov, and after decades - Kodolova, Esipova and others.
At the beginning of the 19th century, he first mentioned and introduced into medical terminology the concept of chronic pneumonia, Dr. Bale. Further, during almost the entire 20th century, the question of the specific nature of this disease was studied. Work was carried out to investigate the onset of the process of suppuration of pulmonary tissues and the pathology of the respiratory organs. A great contribution to the study was made by many employees and professors of medicine, such as Davydovsky, Khazanov, and after decades - Kodolova, Esipova and others.
Causes of Chronic Pneumonia
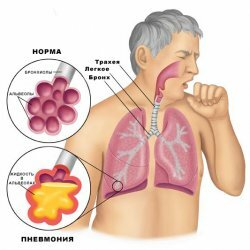
Chronic pneumonia is a disease in which the working cycle of the respiratory system becomes difficult and the process of their inflammation triggered by pathogenic bacteria begins. The causes of the development of the disease can be many. Weakened immunity, foreign microorganisms, various viruses and infections, as well as damage to lung tissue or the respiratory tract, is a list of factors that can contribute to the development of pneumonia. As a rule, the disease becomes chronic if its treatment at the initial stage( acute pneumonia) was treated scornfully. Negligent attitude towards the fight against severe viral diseases, for example, bronchitis or tuberculosis, as well as harmful habits - smoking and alcoholism, can serve as catalysts for the inflammation process. People with congenital pathology of the components of the chest or bronchial development are most prone to chronic pneumonia.
Symptoms of patients with chronic pneumonia in various stages of the disease
At the initial stage of the disease, impressive symptoms of the disease are usually not observed. Patients may have a satisfactory condition and a slight cough.
If the patients did not receive due care or did not follow the preventive measures, the disease becomes more impressive. Those who are sick then feel a general malaise and lack of energy. The temperature fluctuates to a very high rate, a frequent cough with sputum, a predominantly light green hue, possibly with purulent discharge, indicating a progressive inflammatory process. Patients complain of frequent shortness of breath, headaches and pain in the muscles, heart palpitations. People who get pneumonia also experience chills, frequent discharge in the form of sweat, sometimes vomiting - the body's reaction to intoxication. Often, pain in the chest can be felt, mainly on affected areas.
The question of the transition from the stage of protracted pneumonia to chronic is controversial and little studied. With the progression of the disease, the above symptoms become more acute, become chronic. If you do not take measures to eliminate the disease, a fatal outcome is possible.
Clinical picture of the disease
The picture of the disease directly depends on the current stage of the disease. If the stage is primary, in which as such clinical signs are often absent.
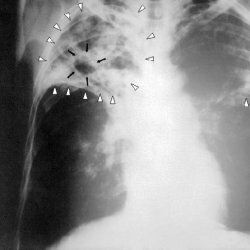
Chronic pneumonia has both internal and external manifestations, which form a common pattern of the disease. When listening to the lungs, there are extraneous noises, wheezing due to stagnant sputum, other crunchy sounds from the friction of the lung tissue and pleura. The general structure of the respiratory organs changes, the lung tissue becomes firmer and deformed( small recessions or bulges), in connection with which the patient decreases lung volume, the stock of absorbed oxygen decreases. In size, the mostly affected parts of the respiratory organs are reduced, often covered with splices of pleural tissue. The result of pathology can be the so-called carnification - a process in which the lung tissue takes the form of raw meat, as well as rebuilding the architecture of epithelial tissues - a consequence of the inflammatory reaction. With a fluorographic examination, one can find that the color structure of the lungs changes insignificantly - in places, weak shading, darkened contours.
The blood test shows a change in the leukocyte composition in the larger direction, the amount of plasma protein - fibrinogen and aminosugars increases, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate( ESR) increases and other biochemical reactions change. With the weakening of the signs of the disease, the above indicators are normalized.
During the study bronchography( section of radiology, studying the behavior and working cycle of the bronchial tree) shows a change in the bronchi, their areas are enlarged, the lumen is seen unevenly, often the presence of cavities of decay.
The picture of the disease directly depends on the current stage of the disease. If the stage is primary, then as such, clinical signs are often absent.
Consequences of chronic pneumonia.
Traces of the disease may not remain with a small area of the respiratory organs, and if the treatment was started on time. If the area of the lesion was sufficiently extensive( bilateral pneumonia), and the treatment was not properly performed, serious consequences could arise. This is in particular other diseases that can develop against a background of chronic pneumonia: abscess of lung tissue or asthma. As a result of the inflammatory process, and also because of the small enrichment of the lung tissue with oxygen, heart failure or gangrene of the respiratory system may develop. In addition to this, the consequences of this disease can be permanent pain in the chest.
Treatment of chronic pneumonia
If the disease is poorly progressive, then treatment can be prescribed within the outpatient setting. At an exacerbation of the diagnosis the patient should be prescribed hospitalization. Bed rest and protein nutrition are an integral part of the healing process.
The main task of the therapeutic procedure is the restoration of the drainage function of the bronchi, ensuring their normal patency. To help in this task come various drugs, such as the root of the althaea, potassium iodide, etc. It is also useful to use inhalation folk remedies - garlic cloves, onions, potato peelings. Massage on the chest area will be a pleasant complement to the healing process, it cleanses the bronchi and provides the best expectoration.
At the advanced stage of the disease, antibiotics and therapeutic methods can be prescribed - physiotherapy, heat therapy, ultrashort wave therapy, etc. Often used prolonged drugs, normalizing the process of oxygen supply.
Preventative measures
The main rule of prevention of chronic pneumonia is timely treatment of the disease at the initial stage. It is necessary to strengthen their immunity and maintain the general tone of the body. To avoid the onset of the disease, it is advisable to avoid contact with pathogens, as well as with substances that adversely affect the work of the respiratory organs. It is necessary to protect yourself from injuries and burns of the chest and lung tissue. Plus, everything is worth abandoning bad habits - smoking and alcoholism.