Endoscopy of the urinary tract
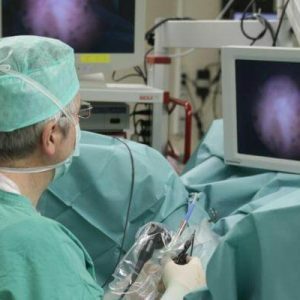
Endoscopy of the urinary tract is one of the most modern and informative diagnostic methods.This low-traumatic study expands the possibilities of diagnosing pathologies of hollow organs.It allows not only to visually assess the condition of tissues, but also to conduct a biopsy sampling in parallel for subsequent laboratory analysis.Early and accurate diagnosis makes it possible to draw up an adequate treatment plan;The technique multiplies the chances for a quick and full recovery of the patient.
Table of contents: When is urinary tract endoscopy necessary?How is endoscopy performed?Types of diagnostic procedure Probable complicationsIn what cases is endoscopy of the urinary tract necessary?
 Endoscopy is the "gold standard" for diagnosing patients with symptoms such as difficulty urinating, micro- and macrohematuria( blood in the urine).
Endoscopy is the "gold standard" for diagnosing patients with symptoms such as difficulty urinating, micro- and macrohematuria( blood in the urine).
The procedure is used for suspected inflammatory disease.It is needed to verify the diagnosis in any doubtful cases.Visualization is necessary to establish the degree of development of the pathological process( stage of the disease).
How is endoscopy performed?
The endoscopy of the urinary system allows examination of the urethra( urethra), bladder, ureters and renal pelvis. Endoscopes - rigid or flexible( plastic or silicone) tubules equipped with optical elements( fiber optics) are used for the study.
As a rule, the diagnosis is carried out by retrograde( transurethral) access. Inspection of the renal pelvis sometimes involves antegrade access, in which the endoscope is inserted through the created puncture lumbar cord access to the kidney or through nephrostomy fistula, left after previous surgical intervention.
In preparation for manipulating the patient, they conduct a conversation to prevent stress and give details of the procedure. Endoscopy involves the provision of preventive antibiotic therapy to avoid infectious complications of .Intravenously injected antibiotic cephalosporin series - Cefazolin( Kefzol).
The patient is recommended to drink abundantly;In addition, intravenously inject up to 1.5 liters of saline and stimulate urinary diversion with a diuretic( Lasix, 40 mg).
To ensure that the patient does not experience discomfort, the endoscopy of the urinary tract is performed under local or epidural anesthesia of the .Excessive lability of the subject's psyche in some cases is an indication for using general anesthesia, that is, anesthesia.
Retrograde access involves rigid( rigid) metal catheters.When examining the ureter, the patient is in the usual horizontal position, and for the examination of the renal pelvis, the Trendelenburg position( lying on the back with a pelvis raised at an angle of 45 ° with respect to the head) can be used.In the mouth of the ureter, special dilators are often introduced to expand it.
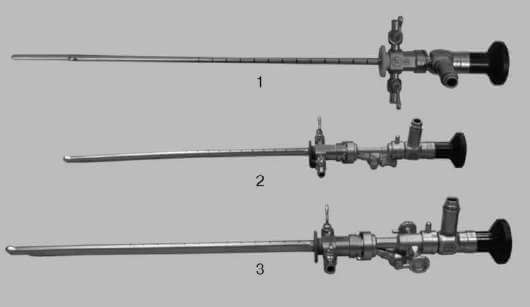
Given the time required for preparation, the procedure lasts an average of 1 hour, although a direct examination of the urinary system takes several minutes.
After diagnostic ureteropyeloscopy, drainage of the pelvis is shown;The catheter is left for 24-48 hours.
Types of diagnostic procedure
Types of endoscopy of the urinary tract depending on the organ being examined:
- urethroscopy;
- cystoscopy;
- ureteroscopy;
- pyeloscopy( nephroscopy).
Cystoscopy is the examination of the walls and inner space of the bladder.First, with the help of a catheter, the remains of urine are removed from the hollow organ and filled with an antiseptic solution of furacilin.The cystoscope is then carefully inserted and the tissues inspected.The method allows to reveal inflammatory changes, presence of neoplasms and concrements.
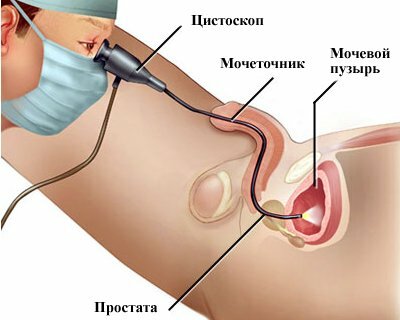
Chromocystoscopy involves the introduction( in / in or / m) of the patient in the preparatory stage of a special dye( indigo carmine).The pigment serves to color the urine in a saturated dark blue color.Through the cystoscope, urine from the ureters is observed.Time must be recorded.The method makes it possible to evaluate the functional activity of the organs of the urinary system.
Dry ureteroscopy serves to examine the anterior part of the urethra in an unmodified state.Irrigation research is needed to assess the condition of the posterior part of the urethra.Distilled water or saline is used for irrigation.
Important: for urethritis and the presence of tumorous neoplasms dry urethroscopy can provoke the development of bleeding, therefore, given these pathologies, preference is given to irrigation.
Pyeloscopy is used for examination of renal pelvis.Diagnosis is carried out through a ureteroscope - a flexible and long ureteral catheter.He is injected into the bladder, and then gently propels the ureter to the kidney.For better visualization, contrast media can be used.
Possible complications
Possible complications of the procedure include catheter trauma and problems associated with local anesthesia or anesthesia( reaction to drugs).
Major hazards of urethro-pialoscopy:
- obstruction of the upper urinary tract;
- acute inflammation of the renal pelvis;
- urinary retention on the background of trauma.
 Handling must only be carried out by an experienced technician with appropriate qualifications.If the device is injected too quickly, it is possible to injure the mucous membranes or the perforation of the bladder.
Handling must only be carried out by an experienced technician with appropriate qualifications.If the device is injected too quickly, it is possible to injure the mucous membranes or the perforation of the bladder.
Note: in very rare cases, pleural injuries( with puncture access to the high-lying kidney) and large intestine are possible.
Accidental perforation of the walls of the organ requires urgent surgical intervention.Damage to the ureter with urinary leakage is an indication for the operation of the kidney drainage.With the development of acute pyelonephritis, antibiotic therapy is prescribed.The fight against obstruction involves the catheterization of the upper urinary tract( in some cases, a stent and a permanent catheter).
Long-term complications include:
- ureter stricture;
- ureteral obliteration;
- reverse the transfer of urine from the bladder to the ureters( reflux).
To prevent complications, it is advisable to carry out diagnostics in the X-ray endoscopic operating room.
Natalia Tavaluk, medical observer of



