BCG vaccination: features of vaccination of children and newborns
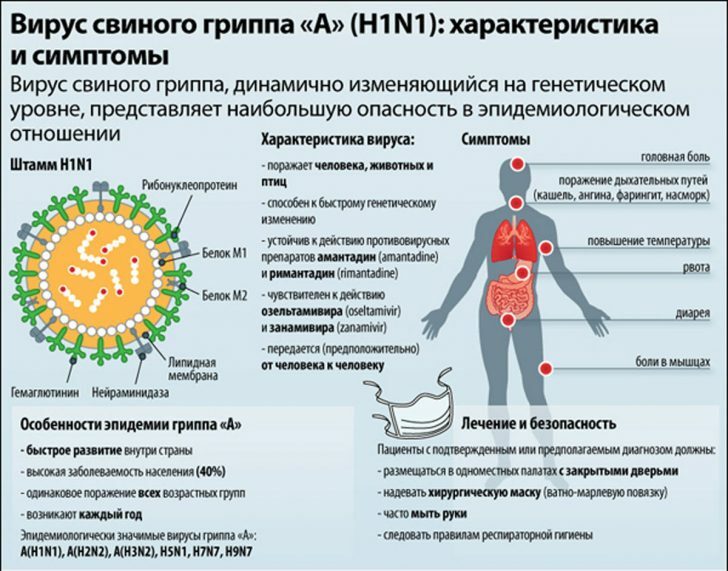
Tuberculosis is a dangerous infectious disease, which affects more than 50,000 people every year in Russia, including children under 14 years old.To protect the child population from the most severe forms of tuberculosis in many countries of the world, mass immunization of newborns with BCG or BCG-m vaccine is carried out.
Table of contents: History of vaccine use Effectiveness of BCG vaccination Do BCG?BCG: timing of BCG: contraindications Scarring after BCG vaccination Possible complications after BCG vaccinationHistory of use of
vaccine BCG is the only existing and recognized by the world community vaccine against tuberculosis, it is prepared from weakened bovine tubercle bacilli grown in artificial conditions.The first doses of this drug, suitable for use in humans, were created back in 1921, but the widespread immunization of tuberculosis was received only after the end of World War II.
 Today, BCG vaccination is included in national immunization schedules in Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Moldova, Hungary, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia and other countries.Some countries in Europe have refused mass immunization of young children from tuberculosis and are vaccinating older children and toddlers belonging to risk groups.
Today, BCG vaccination is included in national immunization schedules in Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Moldova, Hungary, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia and other countries.Some countries in Europe have refused mass immunization of young children from tuberculosis and are vaccinating older children and toddlers belonging to risk groups.
In 1985, BCG-m vaccine was introduced to children with contraindications for the use of the BCG vaccine.This immunobiological preparation has a lower antigenic load( the amount of mycobacteria in a single dose of the drug) and is considered more sparing for the vaccinated.
Effectiveness of BCG vaccination
The issue of vaccination effectiveness of BCG has recently received special attention.Such a stir is caused by large discrepancies in the results of studies of the effectiveness of anti-tuberculosis vaccine in different regions. Scientists suggest that such ambiguity of the obtained data is related to the following factors:
- Genetic features of mycobacterium tuberculosis that are contained in the vaccine( not all vaccines are used the same way).
- Genetic features of different populations of people.
- Influence on the formation of antituberculous immunity of nontuberculous mycobacteria.
- A decrease in the activity of the immunological response to BCG in the presence of parasites in the body.
 Important! The only proven fact that does not require confirmation is the protective effect of BCG against two forms of tuberculosis in children( they are the most severe) - tuberculosis meningitis and disseminated tuberculosis.But the infection with mycobacteria and the activation of the "sleeping" tuberculosis vaccines do not prevent.This significant disadvantage of the current BCG vaccine provides an incentive for the development and testing of new tuberculosis vaccines with more pronounced protective properties of .
Important! The only proven fact that does not require confirmation is the protective effect of BCG against two forms of tuberculosis in children( they are the most severe) - tuberculosis meningitis and disseminated tuberculosis.But the infection with mycobacteria and the activation of the "sleeping" tuberculosis vaccines do not prevent.This significant disadvantage of the current BCG vaccine provides an incentive for the development and testing of new tuberculosis vaccines with more pronounced protective properties of .
While there are no more effective immunobiological products, WHO recommends the use of BCG.And in countries with a high incidence of tuberculosis and the presence of open forms of the disease in many patients( when the patient secretes mycobacteria into the environment), all children who do not have contraindications should be vaccinated within the next few days after birth.
Adult vaccination against tuberculosis is not carried out, since practically all of them have a positive Mantoux test, and regardless of the cause of such a reaction( BCG vaccination in childhood or mycobacterium obtained from the environment), additional doses of the immunobiological drug antituberculous immunityNot strengthen.Do
Do BCG?
Russia, Ukraine and other post-Soviet states belong to countries in which tuberculosis is widespread.Both adults and children are ill with it.Many of these patients secrete mycobacterium tuberculosis and are not isolated at the same time, so they pose a great danger to others.
In such an unfavorable epidemiological situation, a newborn child can meet this terrible infection anywhere: at the entrance( after all, one can not be sure that all neighbors are healthy), a clinic, a store and even a home( close families may well not know aboutHis disease).Therefore, all young children must necessarily have protection from tuberculosis, which today can only be given by BCG vaccination.
BCG: timing of
In accordance with the Russian national vaccination calendar, vaccination against tuberculosis is carried out at the maternity hospital on the 3rd-7th day of life of a newborn( usually before discharge).If there are contraindications, immunization is postponed, and when the time comes, they are no longer doing it in the hospital, but in the polyclinic to which the child is assigned.

The postponement of vaccination BCG has significant disadvantages:
- If a child at the time of the planned vaccination will be more than 2 months, he must first make a Mantoux test.
- Conducting BCG vaccination not on schedule results in the displacement of all other vaccinations( after BCG it is not possible to administer any immunobiological drugs for at least 1 month).
- There is no certainty that during the delay there will be no infection with mycobacteria and the child will not develop a severe form of tuberculosis .
These disadvantages are worth paying special attention to those parents who spare their child and postpone vaccinations "for later".
Vaccination against tuberculosis, in contrast to other infectious diseases controlled by immunoprophylaxis, is not carried out by all children who received the BCG vaccine in infancy.Indication for revaccination, which occurs at the age of 6-7 years, is negative Mantoux test( this result indicates the lack of immunity to tuberculosis).
BCG: contraindications
TB vaccination in the hospital is not performed if the following contraindications are present:
-
 Low birth weight( less than 2, 5 kg). If the baby weighs more than 2 kg and has no other contraindications, he is given a BCG-m vaccine.
Low birth weight( less than 2, 5 kg). If the baby weighs more than 2 kg and has no other contraindications, he is given a BCG-m vaccine. - Any acute diseases( signs of intrauterine infection, hemolytic disease).
- Severe neurological disorders.
- HIV infection in mother's baby.
- Generalized infectious disease associated with the introduction of BCG, in the siblings of the newborn.
- Primary immunodeficiency.
Children with contraindications after full recovery are vaccinated with a weakened BCG-m vaccine.
Revaccination also has its contraindications:
- Positive or questionable Mantoux test.
- Tuberculosis in the present or in the past.
- Any acute illness.
- Allergic conditions.
- Pathological response to BCG vaccination.
- Immunodeficiencies.
- Cancer.
- Treatment with immunosuppressants and radioactive rays.
- Contact with an infectious patient( revaccination is carried out after the end of quarantine).
Scar after BCG vaccination
The BCG vaccine is injected into the left shoulder strictly intracutaneously.In this place, on average, after 4-6 weeks, a reddening appears - this is a local specific reaction, which indicates the formation of immunity to tuberculosis.The consolidation is gradually transformed into an abscess, after the resolution of which remains a small hem.The
 The BCG-m vaccination also provokes a local reaction to the baby's shoulder, but it is less pronounced and the hem does not leave.After a revaccination, a small infiltrate and a subsequent abscess appear for a few weeks faster, because the body is already "familiar" with the injected agent.
The BCG-m vaccination also provokes a local reaction to the baby's shoulder, but it is less pronounced and the hem does not leave.After a revaccination, a small infiltrate and a subsequent abscess appear for a few weeks faster, because the body is already "familiar" with the injected agent.
To be afraid of these dermal postvaccinal reactions is not necessary.All that needs to be done is not to interfere with their course: treat antiseptics and cauterize the abscess, bandage the shoulder, rip off the crust from the wound and carry out other similar manipulations.
Note: is afraid of the same need for a lack of response to BCG.The absence of changes on the skin of the child within the indicated time limits may indicate a low effectiveness of the vaccination.
Possible complications after BCG vaccination
After vaccination and revaccination of BCG, the child may develop complications, but rarely.Among the complications most often occur local, that is, arising from the injection site, lymphadenitis( inflammation of the regional lymph nodes), major infiltration, abscess, ulcer, keloid( coarse) scar, defeat of the humerus.All these consequences develop mainly because of incorrect vaccination.
In weakened children with immunodeficiency, vaccination can provoke a generalized form of BCG infection, and in children prone to allergies - cause a violent allergic reaction.
All children who gave an abnormal response to the introduction of BCG are taken under the control of phthisiatricians, if necessary, a specific treatment is prescribed.In the future, such patients will not be revaccinated with BCG.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical reviewer, epidemiologist