Pregnancy examination
Comprehensive examinations of expectant mothers that are conducted during pregnancy make it possible to detect fetal development abnormalities.Timely and comprehensive examination in the future is a guarantee of the birth of a healthy baby.
Table of contents: Which examinations during pregnancy need to be completed?What methods are used?Ultrasound in pregnancy Biochemical blood tests for pregnancyWhat examinations during pregnancy do you need to pass?
Prenatal screenings are examinations of all pregnant women or expectant mothers.The goal of prenatal screening is to create risk groups.They include women who are particularly at risk of having a child with a genetically determined pathology.These patients are sent for a number of additional studies( analyzes).
Recommended reading:What methods are used?
 Prenatal screening involves two basic methods of research - biochemical analysis and ultrasound.
Prenatal screening involves two basic methods of research - biochemical analysis and ultrasound.
Note: ultrasound scanning makes it possible to determine pronounced anatomical abnormalities in a future child.
The purpose of laboratory( biochemical) prenatal diagnostics is the determination of a particular chromosomal pathology in a child.
With a positive result, a pregnant woman is considered to be at a certain risk group.Subsequently, such patients are subject to extensive examination using invasive methods.

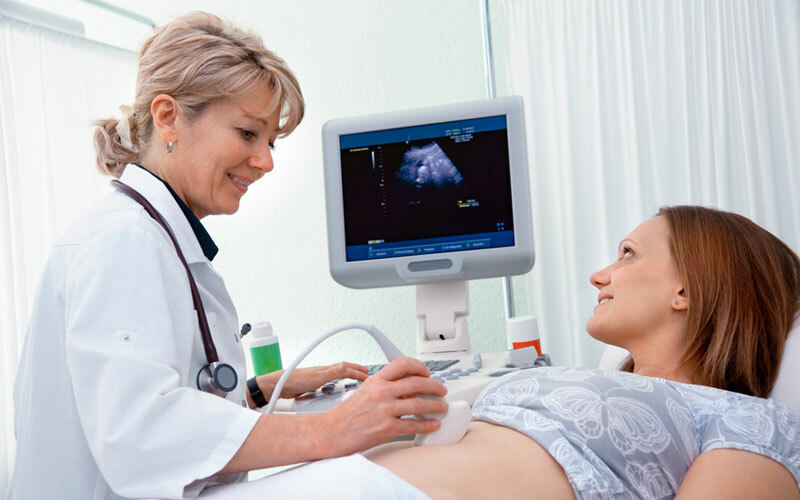
Ultrasound in pregnancy
Ultrasound scanning should be performed at least three times during the gestation period.
Important: contrary to popular belief, ultrasound does not harm the unborn child.
Recommended dates for the implementation of prenatal ultrasound screening:
- First study at 10-14 weeks;
- The second study is at 20-24 weeks;
- The third( last) scan - at a time of 30-32 weeks.
At 10-14 weeks of ultrasound scanning already makes it possible to identify the most pronounced pathologies of intrauterine development of the embryo.In particular, the umbilical hernia, cervical hygroma( cystic formation), and also such incompatible with life pathology as absence of a brain are defined.In this period, the thickness of the collar space is determined.
Note: this parameter is normally not more than 3 mm.Excess can be a marker of anomalies of embryo development( chromosome or other genesis).
At a period of 20 to 24 weeks, ultrasound examination makes it possible to detect the vast majority of pronounced developmental anomalies.
Significant anatomical abnormalities that are detected in this gestation period:
- kidney development anomalies;
- underdevelopment of limbs;
- strongly pronounced violations of the formation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- serious heart defects.
Fetal development defects found in early pregnancy are usually not subject to correction.The revealed anomalies are the basis for raising the issue of the artificial termination of pregnancy.
At these dates, it is already possible to detect the so-called.Markers of chromosomal pathology.
These include:
- apparent delay in the rate of fetal development;
- expansion of the ventricles of the brain;
- small nasal bone;
-
 polyhydramnios;
polyhydramnios; - anhydrase;
- hyperechogenicity of the lower parts of the digestive tract;
- enlarged renal pelvis;
- abnormally small length of tubular bones;
- cystic formations in the vascular plexuses of the brain;
- abnormal inclusions in the cardiac muscle( manifested by hyperechogenicity with ultrasound).
At a period of 30-32 weeks, ultrasonic screening makes it possible to detect defects that are characterized by late appearance and relatively small expression in terms of anatomy.
In later terms, it is possible to identify:
- dropsy of the brain;
- most heart defects;
- significant narrowing or complete obstruction of the urinary system.
Defects of intrauterine development of this type can be surgically corrected immediately after the birth of the baby.In many cases, timely surgical intervention makes it possible to completely eliminate these defects.
Biochemical blood test for pregnancy
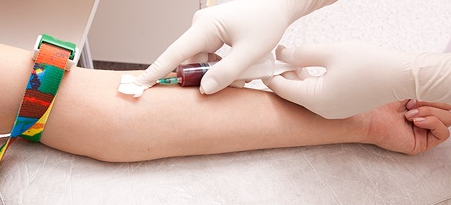
Biochemical screening is carried out under laboratory conditions;The material for the study is the blood of a pregnant woman.
Important: , the presence of certain serum markers is the basis for placing the patient at risk for a particular chromosomal pathology of the fetus.
In the body of a pregnant woman a fetoplacental complex is formed, which includes the fetus and its membranes( chorion + amnion).Shells synthesize special proteins that fall into the blood of a future mother.Almost any changes in their condition lead to the fact that in the serum of the future mother there are special markers.
The modern biochemical test is carried out in two stages.The first screening for serum markers is carried out at a period of 10-14 weeks, and the second - at 16-20 weeks.Thus, the study is conducted in the first and second trimesters.
Analysis of RAPP-A and hCG in the 1st trimester
During the biochemical analysis conducted in the first trimester, the levels of specific placental proteins - hCG( chorionic gonadotropin) and PAPP-A( plasma protein type A) are detected.
Note: for biochemical analysis is necessary."Double" test.Differences in protein levels in plasma suggest some violations in a future child.In particular, a decrease in the level of PAPP-A in combination with an elevated level of free ß-hCG is the basis for suspicion of Down's disease.
The test for two specific proteins allows to diagnose up to 85% of the presence of Down's syndrome.
Triple test for pregnancy( 2nd trimester)
Most often in this period of pregnancy is used so-called."Triple" screening.In this study, the level of α-protein( AFP), hCG and unbound estriol is determined.
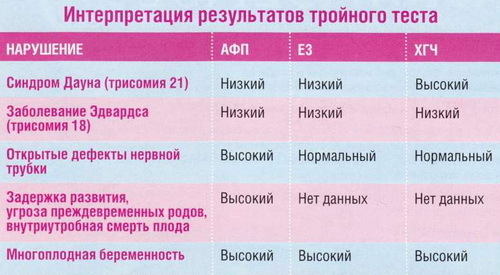
The level of AFP and hCG is of greatest importance for mass screening.If there is a significant increase in the content of alpha-protein in the plasma, there is a possibility of serious violations of the intrauterine development of the central nervous system of the unborn child.Other serious pathologies that may be indicated by a high level of AFP include teratomas, atresia of the duodenum, etc.
Important: , a high level of α-protein may indicate the presence of Rh-conflict, the probability of spontaneous interruptionPregnancy, as well as the death of a child.
If a woman is diagnosed with multiple pregnancies, then a high AFP level is considered the norm.
A low α-protein level suggests that Down's disease is present.A decrease in this indicator may indicate a low location of the placenta, obesity of the pregnant woman or the presence of a future mother with a disease such as diabetes mellitus.
Important: as a whole, a decrease in the level of AFP is considered an unfavorable symptom, but it can also be fixed during normal pregnancy.
According to some experts, the level of α-protein depends on the race of the woman.
Chorionic gonadotropin and unconjugated estriol are placental proteins.An increase or decrease in the level of these proteins indicates a change in the state of the placenta.In some cases, this may indicate chromosomal abnormalities.The change in the level of plasma content of these proteins often indicates a threat of spontaneous abortion, as well as the presence of immunological incompatibility or infection.
 Important: , a change in the level of placental proteins can also occur with a normal pregnancy.
Important: , a change in the level of placental proteins can also occur with a normal pregnancy.
A decreased level of unbound estradiol in combination with an increase in chorionic gonadotropin is one of the hallmarks of Down syndrome.A triple test provides an opportunity to identify this pathology in 60% of cases.
Note: in different laboratories may have their own standards for serum markers, depending on the type of reagents used. As a rule, international relative units are used for valuation, which are denoted as MoM.
Norm
For each of the markers, regardless of the gestational age, the reference values are 0.5-2.0 MoM.
Increase or decrease in the serum content of one of the biochemical markers has no clinical significance;Indicators are evaluated only in a complex.
Recommended to read:Plisov Vladimir, medical reviewer