Blood Test Methods
 How the blood looks and what bleeding is known to everyone.But information is not every person has to know why it is needed.Let's try to deal with this issue and examine in general terms the methods of the most important and widespread laboratory studies of this single liquid body tissue.
How the blood looks and what bleeding is known to everyone.But information is not every person has to know why it is needed.Let's try to deal with this issue and examine in general terms the methods of the most important and widespread laboratory studies of this single liquid body tissue.
Blood Functions
So, what does a person need blood for?
Numerous tasks are assigned to the blood:
- transporting oxygen and carbon dioxide;
- delivery of various nutrients to the cells of the body;
- removal of harmful and unnecessary products of metabolic processes,
- body temperature regulation;
- protection against pathogens;
- supported by the balance of electrolyte and acid-base balance;
- support the shape of the tissues due to the filling of the vascular bed.
This is not a complete list of the functions of the blood in humans.It consists of a liquid part - plasma( 60%) and shaped elements( 40%), performing multiple tasks in the body.
 Important: detailed examination of cells and blood elements can tell the doctor about very many changes in the human body.That's why there are a lot of ways to analyze the blood.We will try to understand their basic set.
Important: detailed examination of cells and blood elements can tell the doctor about very many changes in the human body.That's why there are a lot of ways to analyze the blood.We will try to understand their basic set.
Blood sampling is done from the finger( capillary blood) or by intravenous injection.In some cases, a study of blood flowing into the cavity( thoracic, abdominal), and also conducted tests for secretions of latent blood( feces, urine, vomit).
Blood Hematology
This type of diagnosis includes a general( clinical) blood test.
It is used to determine:
- the number of red blood cells( erythrocytes) present in them hemoglobin with all its fractions;
- hematocrit indicator( ratio of element to volume);
- count of leukocytes( white blood cells playing a protective role), a leukocyte formula, which can be suspected by a variety of diseases and pathological conditions;
- the number of eosinophils, which allows to draw conclusions about allergic organism and the presence of some specific infections.
- platelet count - the increase or decrease of which indicates the state of the clotting system.
More detailed clinical analysis of the blood is disassembled in the article General blood test: norms, interpretation of the blood test and preparation for analysis.
Biochemical blood test
This is the most informative kind of study.

It allows you to determine from the subject:
- glucose level( blood sugar test), which plays an important role in the diagnosis of diabetes and other diseases with a violation of the metabolism of this carbohydrate;
- cholesterol - a compulsory for the cells component, is part of the structure of cell membranes, acting as a regulator of membrane permeability.Excessive amount of it is characteristic of atherosclerotic processes, leading to heart attacks and strokes.Lack of it occurs in some hereditary diseases.It is estimated not only the content of pure cholesterol, but also its transport complexes - lipoproteins;
- triglycerides, the increase of which is typical for obesity, or vice versa, starvation, large blood loss, anemia, endocrine disorders, kidney disease, poisoning and alcoholism;
- proteins, in particular albumins, increasing in inflammation, globulins, some of which increase with iron deficiency.C-reactive protein is an indicator of the acute phase of an inflammatory reaction.Immunoglobulins - the detection of which indicates the reactions associated with allergies, the proteins of the blood coagulation system.The appearance of some types of proteins, as well as a violation of their ratio may indicate a number of diseases;
- residual nitrogen.Azotemia - an increase in the content occurs with dehydration, kidney disease, tuberculosis, diabetes, cirrhotic changes in the liver, inflammation of the lungs;
- enzymes of blood plasma.Aminotransferase - aspartate aminotransferase( ASAT), alanine aminotransferase( ALaT).Their activity increases mainly in diseases of the heart and liver.Lactate dehydrogenase( LDH), creatine kinase - allow to determine the phase of the course of myocardial infarction.Other enzymes are also of diagnostic importance, which are described in more detail in the article on the biochemical analysis of blood;
- pigments.The most important among them is bilirubin.The determination of its magnitude allows the diagnosis of liver disease;
- potassium - a decrease in the content of this element in the blood indicates dehydration, prolonged use of diuretics, kidney diseases, metabolic diseases.Increased potassium is observed in severe injuries, burns;
- sodium - decreases in the analysis due to insufficient intake with food, with heavy loss of fluid, burns, sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, diuretics.The increase occurs with cardiac problems, increased arterial pressure, renal failure;
- calcium, phosphates - the deviation from the norm of these elements occurs with various pathologies - metabolic disorders, rickets, absorption problems in the digestive tract, kidney failure, etc.;
- acid-base state( CBS).By the degree of change in this indicator, one can find the state of alkalosis and acidosis in the body.
Immunological blood test
 Detection of some types of lymphocytes and immunoglobulin complexes and a blood test for antibodies allow you to draw conclusions about the state of the body's defenses.Lymphocytes are involved in reactions of recognition of foreign antigens( toxins of microorganisms and foreign substances), as well as in the production of antibodies( protein formations, immunoglobulins) involved in the neutralization of poisons.
Detection of some types of lymphocytes and immunoglobulin complexes and a blood test for antibodies allow you to draw conclusions about the state of the body's defenses.Lymphocytes are involved in reactions of recognition of foreign antigens( toxins of microorganisms and foreign substances), as well as in the production of antibodies( protein formations, immunoglobulins) involved in the neutralization of poisons.
Note: immunoglobulins, specific proteins, antibodies, being on the lymphocyte membranes, in the blood serum and in the tissue fluid, perform the functions of neutralizing foreign bacteria, viruses and poisons.
Immunoglobulins are divided into 5 classes( A, M, G, D, E,).
Each class performs its specific tasks:
- immunoglobulin A( Ig A) protects the mucous membranes;
- immunoglobulin M( Ig M) characterizes the onset of the pathological process;
- immunoglobulin G( Ig G) appears as a residual response of immune forces to the disease-causing principle and may persist elevated throughout life;
- immunoglobulin E( IgE) increases in the presence of parasites;
Immunoglobulin D functions are in the phase of scientific research.
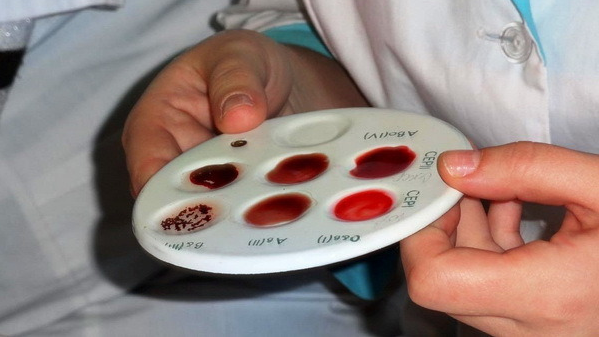
Types of basic immunological techniques for blood testing :
- determination of blood groups and Rh factor;
- determination of reactivity( sensitivity) to nonspecific pathogens - the reaction of hemolytic activity( binding) of complement, the content of certain inflammatory factors in the blood, the determination of acute phase proteins, and variants of interferon.Analysis of the phagocytic ability of white blood cells;
- analysis of specific immune responses is performed by detecting different types of T and B lymphocytes responsible for immune responses at the cellular level.Also, the quantitative and qualitative composition of immunoglobulins participating in the humoral form of immunity, immune complexes is investigated;
- detection of C-reactive protein, rheumatoid factor and antistreptolysin activity, allowing to diagnose a group of rheumatic diseases;
- serological tests - allow the diagnosis of syphilis through the reaction of microprecipitation( RMP), a group of viral hepatitis, determination of salmonellosis, dysentery, typhoid, diphtheria and other specific infections( passive hemagglutination and complement fixation).
Bacteriological blood tests
These types of diagnostics involve taking blood and sowing it on various nutrient media, followed by incubation from 10 days to 6 weeks.The result allows to detect the presence of pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms in the blood - staphylococci, streptococci, Klebsiella, Salmonella and other bacteria.
Parasitological types of blood tests
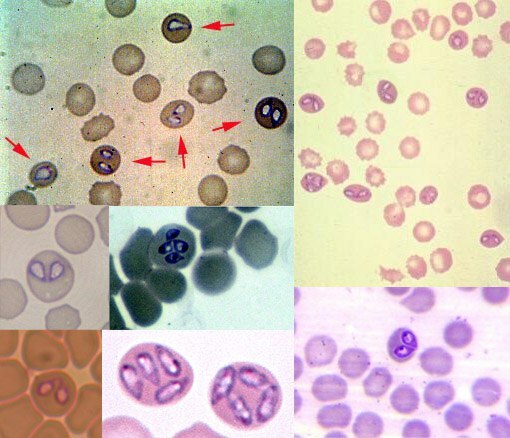
Designed for detection in the blood of protozoa - pathogens of malaria, leishmaniasis, toxoplasmosis, recurrent typhus and other parasitic diseases caused by unicellular organisms.
Study of the
Coagulation System( hemostasis) Analyzes of this group are important in surgery, gynecology, traumatology, combustiology,( medical specialty dealing with the treatment of burns), angiology( vascular disease).
Diagnosis of clotting consists of the definition:
- of blood coagulation time, duration and volume of capillary bleeding;
- samples for fragility of capillaries;
- platelets, number, size, aggregation-adhesive capacity, platelet factors;
- plasma recalcification time;
- of coagulation factor deficiency;
- basic physiological anticoagulants.
The state of fibrinolysis( the ability of the blood to dissolve clots) is also evaluated.These indicators are very important in the practice of cardiology( with myocardial infarction), in neurology( with strokes of the brain).
Blood tests for tumor markers
These analyzes identify specific substances that are secreted by tumors.Also oncomarkers can act as cells secreted by normal tissues in response to the oncological process.The higher the content of these substances, the more likely the presence of a tumor.
Important: can increase in other diseases, so it is not always the main diagnostic criterion for the detection of pathology.
With an increase in the level, additional testing is necessary.
Please note: oncomarkers detected a large number and go further scientific developments, improvement of detection techniques.
Blood tests used to investigate the functions of organs
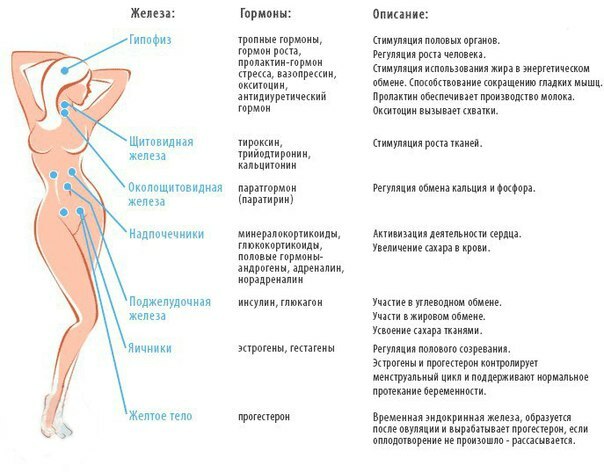
In thyroid diseases, hormone production levels are determined.The content of triiodothyronine, tetraiodothyronine and thyroid-stimulating hormone is estimated.The level of their indicators helps in the diagnosis of diseases such as thyroiditis, diffuse toxic goiter, hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism.Blood tests for thyroid hormones are very valuable for diagnosing these diseases.
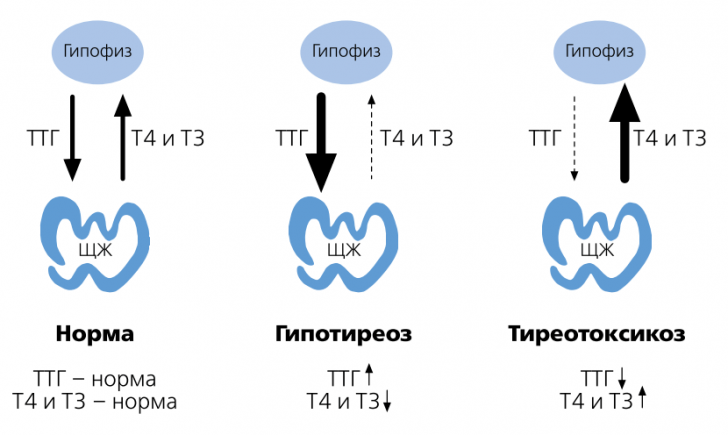
The following are the minimum and maximum levels of hormones in the blood:
| hormone | minimum value | maximum value |
| free T3 | 2,6 pmol / L | 5,7 pmol / L |
| T3 common | 1, 2 nmol / l | 2,2 nmol / l |
| T4 free | 9.0 pmol / l | 22.0 pmol / l |
| T4 common | 54 nmol / l | 156Nmol / l |
| TTG | 0.4 mU / l | 4 mU / l |
| Antibodies to thyreoglobulin | 0 U / ml | 18 U / ml |
| Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase | & lt; 5,6 U / ml | |
| Calcitonin | 5,5 nmol / l | 28 nmol / l |
To evaluate the functions of the ovaries, assessments are used to assess the content of luteinizing hormone( LT), follicle stimulating hormone( FSH), estradiol, progesterone and prolactin.
Standards blood sex hormones for women of reproductive age:
| index | rate for men | rate for women |
| follicle-stimulating hormone( FSH) | 1-11 mIU / mL | 1-11.8 mIU / mL |
| Luteinizing hormone( LH) | 0.8-8.4 mIU / mL | 1-8.8 mIU / mL |
| Prolactin | 105-540 mME \ L | 67-726 mME \ L |
| Testosteron | 5,76 - 28,14 nmol / l | 0,45 - 3,75 nmol / l |
| DHEA-c | 80-560 g / l | 35-430 g / l |
| Estradiol | 7.63-42.6 pg / mL | 43.8-211 pg / mL |
| Progesterone | 0.7-4.3 nmol / l | 5.3-86 nmol/ l |
norms in blood levels of sex hormones for women in menopause and for children:
| index | rate for | childrenrate for women( postmenopausal) |
| Follicle stimulating hormone( FSH) | 0,3-6,7 mIU \ ml | 31-130 mIU \ ml |
| Luteinizing hormone( LH) | 0,03-3,9 mIU \ | 18,6-72 ml mIU \ ml |
| Prolactin | 91-526 mIU \ l | 67-726 mIU \ l |
| Testosterone | 01-1.12 nmol / l | 0.1-1.42 nmol / l |
| DHEA with | 0.025-1.45 μg / ml | 0.1-0.6 μg / ml |
| Estradiol | 5-21 pg / ml | 5-46 pg / ml |
| Progesterone | - | - |
Note: progesterone in children and women over 45 years is not defined.
also common analysis of a blood sample on the content of stress hormones - ACTH, cortisol, catecholamines and biogenic amines.
Pregnancy blood test
Of the modern methods of diagnosis of early pregnancy should be allocated , blood test for hGh.
The rates of hCG for weeks of gestation are presented in the table:
| gestation weeks obstetric | display hCG mIU / ml |
| nonpregnant women | 0 - 5 |
| results questionable | 5 - 25 |
| Pregnancy 3-4 week | 25 - 156 |
| 4-5 week Pregnancy | 101 - 4870 |
| 5-6 week Pregnancy | 1110 - 31500 |
| 6-7 week Pregnancy | 2560 - 82300 |
| Pregnancy week 7-8 | 23100 - 151000 |
| 8-9 Week Pregnancy | 27300 - 233000 |
| 9-13 Week Pregnancy | 20900 - 291000 |
| 13-18 Week Pregnancy | 6140 - 103000 |
| pregnancy week 18-23 | 4720 - 80100 |
| pregnancy week 23-41 | 2700 - 78100 |
Equally important is the prenatal screening.Get more information about this form of blood tests pregnant you can, looking at video review:
Stepanenko Vladimir, a surgeon