ARI: causes, symptoms, treatment, complications, prevention
 According to the international classification, all respiratory diseases caused by infection are referred to ARI.Annually in our country ORZ carry up to 40 million people, and more than 50% of them are children of different age groups.To this group of diseases are ARVI, including infections caused by the influenza virus.
According to the international classification, all respiratory diseases caused by infection are referred to ARI.Annually in our country ORZ carry up to 40 million people, and more than 50% of them are children of different age groups.To this group of diseases are ARVI, including infections caused by the influenza virus.
The main way of transmission of infectious agents is airborne, which causes rapid spread and quite frequent occurrence of epidemics.Infection is also possible if the rules of personal hygiene are not respected( through poorly washed hands) and food products contaminated by the pathogen.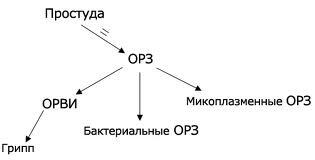 For rhinovirus infection, so-called.The "entrance gates" are the mucous membranes of the nose and conjunctiva.According to statistics, an adult suffers a more or less pronounced acute respiratory disease, on average, up to 2-3 times a year.In children, this figure reaches 6-10 times.
For rhinovirus infection, so-called.The "entrance gates" are the mucous membranes of the nose and conjunctiva.According to statistics, an adult suffers a more or less pronounced acute respiratory disease, on average, up to 2-3 times a year.In children, this figure reaches 6-10 times.
Etiology
Depending on the season, the pathogens of ARI can be various viruses.In autumn, the parainfluenza virus is the most frequent pathogens, and in winter a respiratory syncytial virus is usually found.Adenoviruses( 16.5% of cases) are "all-season" pathogens, and in the warm season there are often outbreaks of enterovirus ARI.Virtually every third patient is caused by influenza A or B viruses, and the proportion of herpes simplex virus and mycoplasma accounts for about 2% of cases.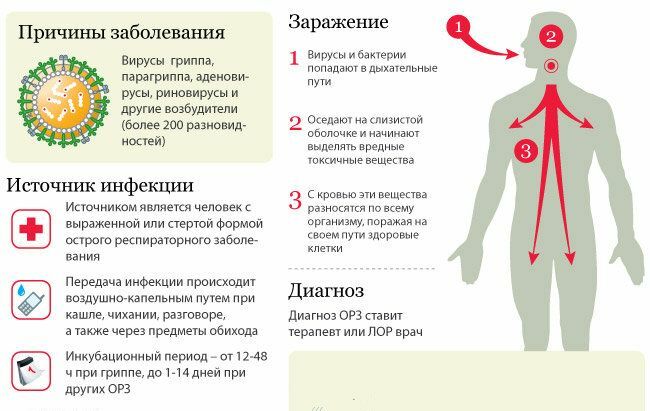 Bacterial diseases are usually caused by pathogens that are permanently present in the organs of the respiratory system.
Bacterial diseases are usually caused by pathogens that are permanently present in the organs of the respiratory system.
ARI and ARVI: difference between diseases
If the diagnosis of ARI is diagnosed, then an airway disease due to any infectious agents( including bacteria or mycoplasmas) is implied.In the abbreviation of acute respiratory viral infection there is a specification, which implies an exclusively viral etiology.For viral infections, the intensity of clinical symptoms is more pronounced.In the early stages, these diseases are virtually indistinguishable.Confirm the viral etiology can only blood test for the so-called."Paired sera".Therefore, when they diagnose "ARD", and the patient suffers from a viral infection, there is no error in this.
Please note: according to the behind-the-scenes rule for all upper respiratory infections, therapists diagnose "ARD", and "ORVI" is entered into the card if the disease at this particular time period becomes epidemic.To better understand the difference between ARI and ARVI, watch this video:
Does the flu apply to ARI?
The share of diseases caused by the influenza virus accounts for more than 30% of all cases of ARI.When it is not an epidemic( or pandemic), the infection is usually caused by strains with a low level of virulence, which most people have already experienced in their life.Due to the fact that the immune response in such cases is quite adequate, the flu disease is relatively easy, and the mass spread of the virus does not occur.
Symptoms ARD
Among the characteristic clinical manifestations of the disease are:
- nasal congestion( runny nose);
- sneezing;
- sensation of perspiration and sore throat;
- cough( initially unproductive, then with phlegm);
- elevated temperature;
- signs of general body intoxication.
Thus, the respiratory events leading to the inflammatory process in the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract come to the fore. All clinical manifestations can be combined into 2 syndromes:
- respiratory tract infection;
- general intoxication.
To inflammatory respiratory infections at various levels are listed:
- rhinitis( inflammation of the nasal mucosa);
- pharyngitis( pharyngeal involvement);
- laryngitis( inflammation of the larynx);
- tracheitis( inflammation of the trachea).
Important: Acute bronchitis and bronchiolitis may also be considered as manifestations of acute respiratory disease, but only if these pathologies are accompanied by upper respiratory tract disease.
The flu usually begins with a feeling of "aches" in the bones and muscles, a general malaise and a high fever.Type A is characterized by hyperthermia for 2-5 days, and for Type B it can persist for a week.It is also characterized by photophobia and pain in the eyeballs.Respiratory manifestations in the form of a not very pronounced rhinitis and dry cough, as a rule, join on day 2-3 from the onset of the disease.With parainfluenza, the onset of the disease is sufficiently "smooth", the temperature remains within the subfebrile values.
Adenovirus infection is characterized by pronounced prolonged hyperthermia, but relatively well-being may be maintained against its background, since the level of intoxication is relatively low.Rhinoviral ARI usually occurs generally without a rise in temperature.With mycoplasmal involvement of the respiratory tract, the development is gradual, and the symptoms are not very pronounced, but they persist for a long time even with adequate therapy.
Diagnosis of
 Diagnosis is based on patient complaints and examination data.When examined, as a rule, hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the throat is revealed.It is important to differentiate the "usual" cold from flu, because the effectiveness of treatment depends on the correctly diagnosed diagnosis.In this case, it is important to pay attention to such pathognomonic( characteristic) symptoms for influenza as pain in the eyes and photophobia.Rhinovirus infection affects mainly the epithelium of the nasal mucosa, and adenoviruses - palatine tonsils and pharynx.Parainfluenza is characterized by inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa.
Diagnosis is based on patient complaints and examination data.When examined, as a rule, hyperemia of the mucous membranes of the throat is revealed.It is important to differentiate the "usual" cold from flu, because the effectiveness of treatment depends on the correctly diagnosed diagnosis.In this case, it is important to pay attention to such pathognomonic( characteristic) symptoms for influenza as pain in the eyes and photophobia.Rhinovirus infection affects mainly the epithelium of the nasal mucosa, and adenoviruses - palatine tonsils and pharynx.Parainfluenza is characterized by inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa.
Important: should be aware that even during an influenza pandemic, the patient may well suffer from a bacterial infection.The epidemic is not the basis for prescribing antiviral drugs to all without exception, patients with malaise and respiratory symptoms.
Treatment of ARD
Recommended to read:Patients with ARI are shown bed rest before fever subsides.The diet should be balanced and enriched with easily digestible proteins and vitamins( recommended reception of multivitamin complexes).It is also necessary abundant warm drink to accelerate the removal of toxins from the body.
For severe bacterial infections and suspicions of complications, antibiotics effective against bacteria and mycoplasmas are shown, and in ARVI( including influenza) - antiviral drugs of the first and second generation.But in order to confirm the viral nature of the disease, you need to make an expensive blood test, the result of which will be known only a week later.In the majority of patients( approximately 90%) during this time the main symptoms subsided, and the period of convalescence( recovery) begins.Thus, in acute respiratory infections, symptoms largely determine treatment.It is important to be able to distinguish bacterial infection from influenza.
If the disease has a viral etiology, antibiotics not only will not be of use, but will deplete the normal( saprophytic) microflora.Such a dysbacteriosis further undermines immunity and leads to disturbances in the digestive process.Analgesics( anesthetics), antipyretics( antipyretic) or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed as agents for symptomatic treatment of acute respiratory disease. Paracetamol is the most common analgesic-antipyretics, and as an NSAID, ibuprofen or acetylsalicylic acid is usually prescribed.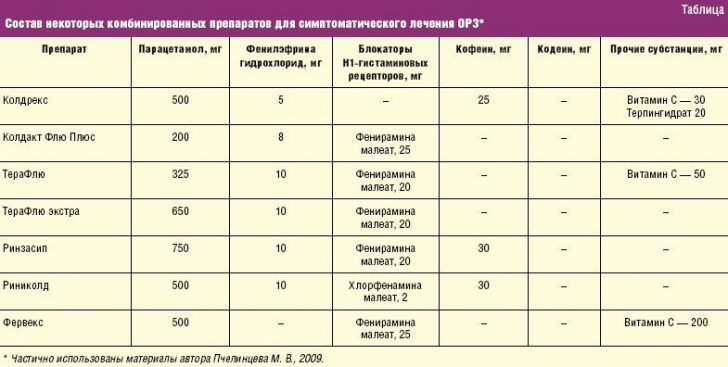
Complications of ARD
Unlike most pathogenic bacteria, as well as other infections that cause ARI, the influenza virus leads to more pronounced suppression of immunity and often causes serious consequences. Among the complications of the flu are:
- pneumonia( pneumonia);
- sinusitis( in particular - sinusitis);
- Inflammation of the renal pelvis( pyelonephritis);
- myocarditis( cardiac muscle damage);
- meningitis( inflammation of the meninges).
Pneumonia that develops against the background of influenza can be:
- primary( developed 1-3 days after the onset of the first symptoms);
- secondary bacterial( develops on day 3-7);
- mixed.
Against the background of this infection, the "dormant" chronic pathologies are often aggravated.One of the most formidable complications of ARI is a shock of infectious-toxic genesis. Its manifestations may be:
- cerebral edema;
- pulmonary edema;
- acute cardiovascular failure;
- DIC-Syndrome.
ARI caused by the parainfluenza virus can cause the development of croup( stenosing laryngotracheitis), and respiratory syncytial infection leads to complications such as bronchial obstruction and bronchiolitis. Symptoms that may indicate the development of complications are :
- prolonged( more than 5 days) fever;
- fever arising after a brief abatement of symptoms;
- headache in the forehead.
Prevention of acute respiratory diseases is reduced to measures to strengthen the body's defenses.Great attention should be given to hardening, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and consuming as many vitamins as possible.In the period of epidemics, it is recommended to take prophylactic drugs - immunomodulators, as well as antiviral agents in the recommended dosages for prevention.It is necessary to avoid hypothermia, minimize contact with sick people and strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene.
ARI in children: symptoms and treatment
 In children, the immune system is not completely formed, and therefore the probability of infection and development of complications is higher for them than for adults.The incubation period in children is shorter, and the development of the disease is more rapid.
In children, the immune system is not completely formed, and therefore the probability of infection and development of complications is higher for them than for adults.The incubation period in children is shorter, and the development of the disease is more rapid.
Symptoms of ARD in a child are the same as for any adult patient, but often they are more pronounced.Antiviral drugs( Rimantadine and others) should be given to the child in the first 24-36 hours after the appearance of the first symptoms. The 5-day course is shown, and the dose is calculated as follows:
- from 3 to 7 years - 1.5 mg per 1 kg of weight per day( divided into 2 doses);
- from 7 to 10 years - 50 mg twice a day;
- from 10 and older - 50 mg 3 times a day.
Babies under 3 years old for the treatment of acute respiratory disease are shown containing rimantadine syrup Algirem 10 ml per day.The effectiveness of the antiviral agent increases in combination with antispasmodics( Drotaverin), which give 0.02-0.04 mg per reception.With a virus infection, Arbidol will also help.It can be given to children from 2 years older.To lubricate the nasal mucosa, you can use oxolin ointment, which also has antiviral activity and is effective in adenovirus infection.To facilitate the course of the disease and accelerate recovery allows interferon, a solution of which is instilled in the nasal passages 4-6 times a day.In the treatment of colds and suspected bacterial etiology, antibiotics should be given to children with extreme caution.Antibiotic therapy is justified in the development of complications.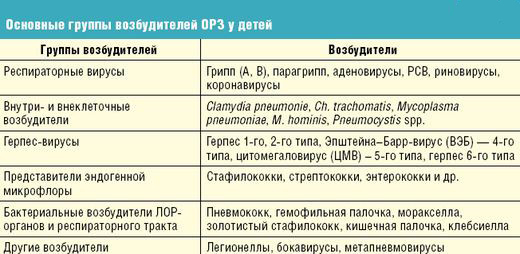 Important: use of acetylsalicylic acid( Aspirin) for the treatment of symptoms of acute respiratory disease and influenza in children and adolescents under the age of 15 can lead to complications such as Ray's syndrome.When it develops brain damage( encephalopathy) and fatty liver disease, provoking in turn a marked hepatic insufficiency.
Important: use of acetylsalicylic acid( Aspirin) for the treatment of symptoms of acute respiratory disease and influenza in children and adolescents under the age of 15 can lead to complications such as Ray's syndrome.When it develops brain damage( encephalopathy) and fatty liver disease, provoking in turn a marked hepatic insufficiency.
Cold during pregnancy
 ARI during pregnancy are observed quite often.Natural physiological changes in the body of a pregnant woman often cause a more protracted course of these diseases.Viruses can become the direct cause of impaired development of the fetus.In addition, with the development of symptoms of ARI in a pregnant woman, there is a possibility of a sharp decrease in blood flow in the placental system, which will lead to hypoxia of the fetus.A certain danger may be presented by some medicines taken by a future mother, therefore preparations for treating ARI should be selected with extreme caution.
ARI during pregnancy are observed quite often.Natural physiological changes in the body of a pregnant woman often cause a more protracted course of these diseases.Viruses can become the direct cause of impaired development of the fetus.In addition, with the development of symptoms of ARI in a pregnant woman, there is a possibility of a sharp decrease in blood flow in the placental system, which will lead to hypoxia of the fetus.A certain danger may be presented by some medicines taken by a future mother, therefore preparations for treating ARI should be selected with extreme caution.
The use of antibiotics, as well as most synthetic drugs of systemic action, should be avoided whenever possible.Any medication should be taken only as directed by the doctor.
ARI during first trimester pregnancy
The first trimester is the most dangerous period, because the fetus is not sufficiently protected.Various viruses can lead to the formation of malformations, sometimes even incompatible with life.With ORT in 1 trimester, the risk of spontaneous abortion( miscarriage) is increased
Cold during pregnancy in the second trimester
In the second trimester the placenta is already a reliable barrier to the path of infectious agents.Nevertheless, the likelihood of serious complications exists, and it is especially great when the mother has comorbidities or with gestosis.Up to the middle of the 2nd trimester, viruses can adversely affect the process of forming the baby's nervous system.There is also the possibility of intrauterine infection of the unborn child and fetal nutrition.
Cold during pregnancy III trimester
The third trimester can be considered a relatively safe period, but a number of disorders can cause miscarriage and premature birth.Pregnant women with ARI should regularly measure body temperature.It is believed that if it is less than 38 ° C, then it should not be knocked down, but it is dangerous to overheat the fruit for more than two days.To bring down the temperature should not take acetylsalicylic acid - preference during pregnancy should be given to an analgesic antipyretic, like paracetamol.
Konev Alexander Sergeevich, the therapist



