Dysbacteriosis in infants: why is it developing and should it be treated?
 Dysbacteriosis of the intestine in the baby is due to a change in the qualitative and quantitative composition of the microflora( i.e., its eubiosis or microbiocenosis). This is not a disease, but one of the manifestations of a wide variety of diseases and pathological conditions.
Dysbacteriosis of the intestine in the baby is due to a change in the qualitative and quantitative composition of the microflora( i.e., its eubiosis or microbiocenosis). This is not a disease, but one of the manifestations of a wide variety of diseases and pathological conditions.
Why do we need bacteria in the intestines?
All areas of the body, one way or another communicating with the environment( oral cavity, nasopharynx, intestines, vagina), are normally populated with microflora.In these areas there is always not one species of bacteria, but a combination of colonies of different microbes.

In the intestine of a healthy person, there are always intestinal rods, lacto- and bifidobacteria, and a number of other microorganisms.Many of them are needed to maintain a high level of immunity.
The main functions of the intestinal microflora:
- participate in the process of biosynthesis of vitamins( K, PP, and group B);
- regulation of gas exchange in the lumen of the intestine;
- is involved in the synthesis of certain acids;
- stimulation of mucosal cell renewal;
- activation of intestinal enzymes;
- stimulation of lymphoid cells;
- is involved in the metabolism of urinary, bile and fatty acids.
Bacteria are capable of indirectly blocking the development of tumor processes.In addition, they are involved in maintaining the energy, exchange and ionic constancy of the internal environment.Without some microorganisms, normal digestion and absorption of nutrients are impossible.
What affects the intestinal microflora?
Both properties and composition of the intestinal microflora depend on a number of factors.
Microbiocenosis is affected by:
- age;
- general condition of the body;
- power supply;
- presence of acute and chronic diseases;
- reception of pharmacological preparations;
- time of the year.
Note: almost any pathology is capable of provoking a dysbacteriosis, expressed to a greater or lesser extent.Even if the microflora can not change the disease as such, the qualitative and quantitative composition of the bacteria is influenced by the medications taken or the forced change in the nature of the diet.
Than the dysbacteriosis for the baby
 is dangerous. If the division of epithelial cells is disturbed, the permeability of the mucous membrane changes.As a result - allergens and toxins, which must remain in the lumen and gradually leave the body naturally, are actively absorbed and enter the blood.Thus, allergization and the general intoxication of an organism are quite often caused by infringements from eubiosis.
is dangerous. If the division of epithelial cells is disturbed, the permeability of the mucous membrane changes.As a result - allergens and toxins, which must remain in the lumen and gradually leave the body naturally, are actively absorbed and enter the blood.Thus, allergization and the general intoxication of an organism are quite often caused by infringements from eubiosis.
On the background of dysbacteriosis of the intestine, the synthesis of lysozyme and immunoglobulins by lymphoid cells is disrupted.A direct consequence is a sharp decrease in immunity, because it is these substances that provide protection from various infectious agents - viruses and bacteria.
What should parents know about the intestinal dysbiosis in infants?
 Note: in newborn infants in the absence of pathologies colonization of the intestine by lacto- and bifidobacteria is completed as early as 3-5 days after birth.Colonies of these beneficial microorganisms are much more active in babies who are breastfed, not artificial mixtures. In infants of the first year of life receiving breast milk, up to 98% of the intestinal microflora is bifidobacteria.
Note: in newborn infants in the absence of pathologies colonization of the intestine by lacto- and bifidobacteria is completed as early as 3-5 days after birth.Colonies of these beneficial microorganisms are much more active in babies who are breastfed, not artificial mixtures. In infants of the first year of life receiving breast milk, up to 98% of the intestinal microflora is bifidobacteria.
It is important for parents to remember that intestinal dysbacteriosis is not a disease, but a consequence of pathologies.Elimination of the problem does not affect the cause of its occurrence.It is necessary first of all to eliminate the possible etiologic factor, and not try to treat dysbacteriosis as such.
The concept of "normal microflora" is relative.During the diagnosis feces are analyzed, and the number of bacteria in the feces does not allow to judge objectively the state of microbiocenosis in the intestine.Samples give an idea of the microbes present in the lumen of the intestine, and digestive processes occur in the near-wall region.In addition, the digestion and assimilation of nutrients is predominantly in the small intestine, and stool analysis roughly reflects the state of eubiosis in the thick sections.
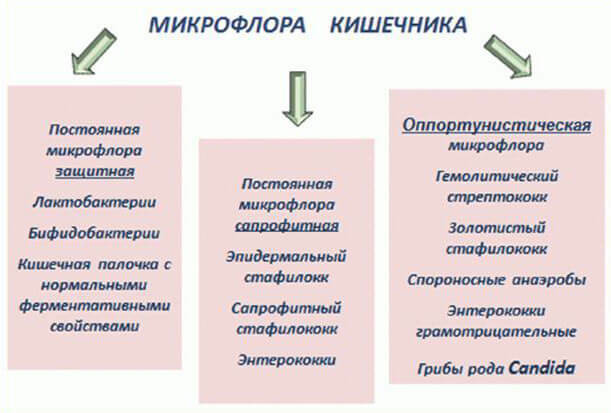
Most experts now believe that routine bacteriological research is irrational and informative .Eubiosis in each child is purely specific, and depends on many factors.The results of the analyzes are characterized by instability - fecal samples taken at different times of the day can be very different.
A much more informative study is a biopsy specimen taken from the jejunum, but this study is rarely done.
Important: only in very rare cases in the results of laboratory studies can you see the "norm", since the number of at least one species of bacteria usually goes beyond the limits set by official medicine.
There are a number of symptoms that babies often write off for dysbiosis.
Among them:
- general lethargy;
- change in stool frequency;
- frequent regurgitation;
- flatulence( bloating);
- change in consistency, color and odor of stool;
- disorders of appetite;
- bad breath;
- is an allergic dermatitis.
In practice, dysbacteriosis is the same symptom of a certain pathology as all of the above clinical signs.
Measures to correct intestinal dysbacteriosis in the baby can be considered as "pseudo-therapy", as standard laboratory tests do not give an idea of the true state of the microflora.
Now the concept "dysbiosis" is considered more correct.It implies certain violations in the mechanisms of interaction of the organism with its own eubiosis and environmental factors.
Only an experienced specialist can identify a disease or disorder that provoked a change in the composition of the intestinal microflora, as well as other symptoms.Prebiotics and probiotics are, of course, quite effective means, but they can be given to a baby only if the pediatrician finds such a measure necessary.
Popular questions about dysbiosis and the advisability of his treatment are answered by a pediatrician, Dr. Komarovsky:
Plisov Vladimir, medical reviewer