Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection
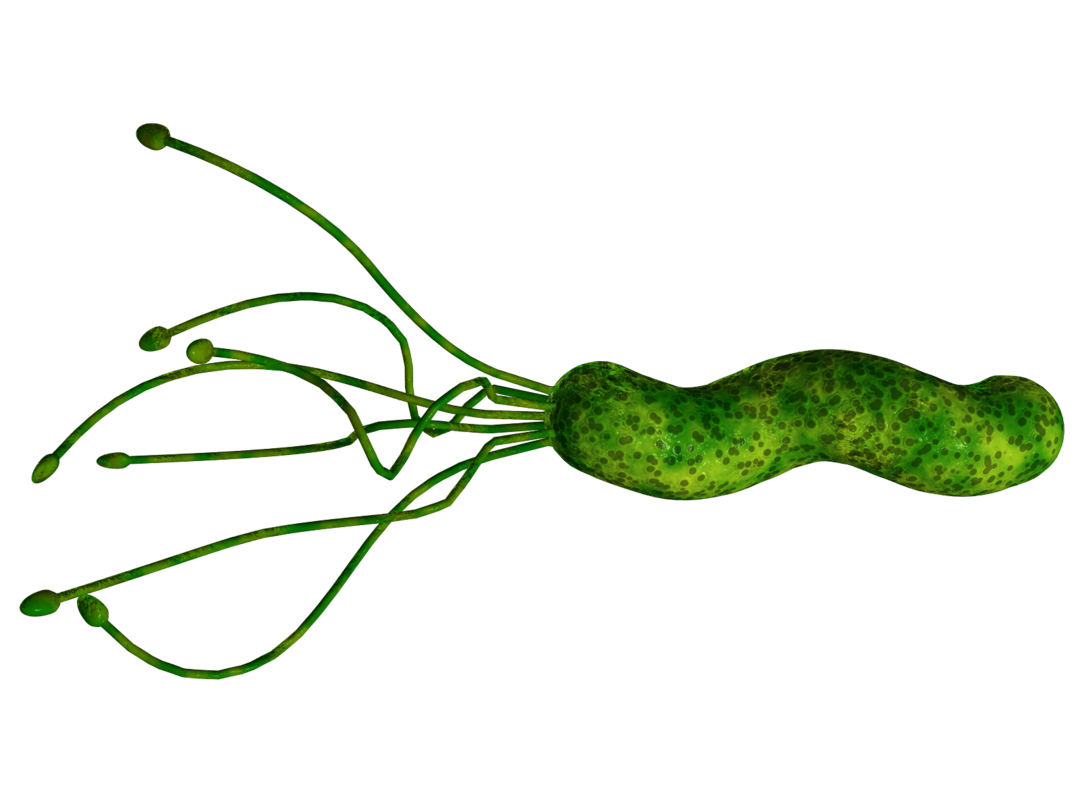
Helicobacter pylori( Helicobacter pylori) is a gram-negative bacterium that is capable of colonizing and damaging various zones of the stomach and duodenum.Some cases of gastritis, duodenitis and even malignant tumors of the stomach are associated with this microorganism, but the overwhelming majority of carriers of these diseases have not been found.
According to R. Warren and B. Marshall, most cases of gastritis and gastric ulcers are due to Helicobacter pylori.Previously, leading role in the pathogenesis of these pathologies was given to acute food and stress factors.
Table of contents: What diseases can cause a microorganism?Methods for detecting the bacterium Helicobacter pyloriWhat diseases can cause a microorganism?
Interesting! The scientific community doubted that the bacterium could live and develop in a sharply acidic stomach content, but Barry Marshall drank a Helicobacter pylori culture and contracted gastritis, which was confirmed by endoscopic examination.At the next stage of the experiment, the researcher cured gastritis, taking metronidazole-damaging bacteria and bismuth compounds.In 2005 R. Warren and B. Marshall were awarded the Nobel Prize for their discovery.
There are a number of pathologies of the digestive system, if the gastroenterologist is suspected of having to take tests for Helicobacter pylori:
- chronic and acute gastritis;
- gastric ulcer;
- malignant neoplasm in the stomach;
- chronic and acute duodenitis;
- combined gastric ulcerative lesion.
Important: bacteria belonging to the genus Helicobacter are the only microorganisms discovered so far that not only survive long in a sharply acidic gastric environment but are also capable of multiplying there by colonizing the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Methods for detecting the bacterium Helicobacter pylori
Methods for the detection of a pathogenic bacterium are conventionally divided into:
- invasive;
- non-invasive.
The invasive diagnostic procedures are:
- histological method;
- Helpel test( rapid urease analysis);
- bacteriological method;
- molecular genetic method( PCR in biopsy taken material).
Non-invasive detection methods for bacteria:
- serological method;
- enzyme immunoassay for the presence of a specific antigen;
- urease respiratory test with 13C-urea.
Invasive techniques suggest a biopsy( taking a section of the gastrointestinal organ) through fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy( FEGDS).Then a laboratory analysis of the biopsy taken during the procedure is carried out.
Non-invasive studies do not imply endoscopic intervention.
Note : according to the latest medical statistics, bacteria of this species are less than half of patients with gastrointestinal diseases.
Invasive tests for Helicobacter Pylori
Histological method
The histological method of the study is based on microscopic examination of print smears after preliminary staining with "classical" methods.The analysis helps to identify the level of atrophy, the presence of inflammation and the general dissemination of the biopsy specimen Helicobacter pylori.The technique allows to establish intestinal metaplasia.
Rapid urease test
Helpel test is based on the fact that HP synthesizes urease, and under its action urea hydrolyses with the release of ammonium ions.Acidity is shifted to the alkaline side, which is determined by means of an indicator.The material is placed in a liquid containing the desired indicator and urea.If the color changes, this can indicate the presence of a pathogenic microorganism.
Molecular genetic method;PCR determination in biological material
A fragment of the mucosa is permissible to be examined by PCR.The method makes it possible to reveal cultures of different degrees of pathogenicity.
Bacteriologic method
The bacteriological method of studying the biopsy specimen allows carrying out the culture analysis and establishing the susceptibility of the strain to antibiotics.The study is conducted, starting antibiotic therapy of the "first line".The method is especially relevant in areas where the population has a low susceptibility to such a common drug as clarithromycin.It is also used if standard eradication therapy is to be performed.The bacteriological method is also relevant if the "second line" therapy is ineffective.
Non-invasive detection methods Helicobacter Pylori
Serological method
The serological method, also based on enzyme immunoassay, consists in the detection of immunoglobulin G against Helicobacter pylori.The material for the study in this case is serum.Since IgG persists in the blood for a long time, it is not advisable to apply a method to monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
Study of feces for the presence of Helicobacter pylori antigen( ELISA)
The most sensitive method for determining the characteristic antigen is the enzyme immunoassay using monoclonal antibodies.It is used both for initial diagnosis and for determining the effectiveness of the therapy.
Ureasic respiratory test with 13C-urea
 The urease respiratory test is based on the study of the patient's exhaled air after a preliminary intake of the urea solution.The solution is preliminarily labeled with the carbon isotope( 13C).If there is Helicobacter pylori in the stomach of the patient, a chemical reaction is under way - under the action of bacterial urease, urea passes a chain of reactions, the result of which is CO, which exits the patient's lungs and is fixed by an expiratory spectrometer.This test is used both for the detection of pathology, and for determining the effectiveness of the therapeutic measures being carried out.
The urease respiratory test is based on the study of the patient's exhaled air after a preliminary intake of the urea solution.The solution is preliminarily labeled with the carbon isotope( 13C).If there is Helicobacter pylori in the stomach of the patient, a chemical reaction is under way - under the action of bacterial urease, urea passes a chain of reactions, the result of which is CO, which exits the patient's lungs and is fixed by an expiratory spectrometer.This test is used both for the detection of pathology, and for determining the effectiveness of the therapeutic measures being carried out.
Norm
If the body lacks Helicobacter pylori strains, all tests, both invasive and non-invasive, will give negative results.
Important: isolated strains of the genus Helicobacter have been identified in the liver of some mammals.They can cause liver disease in humans.
Vladimir Plisov, medical reviewer