Urinalysis: types, decoding, rules of preparation and delivery
Urine analysis is important in the diagnosis of pathological changes in the kidneys, heart disease.Valuable additional information due to a general analysis of urine can also be obtained if other organs are impaired.Virtually all the painful processes in the body affect the properties of urine.Repeated study of laboratory indicators allows to evaluate the stages of pathological processes, the effect of drug therapy.
The result of a poor urine test should be the reason for the patient to consult a doctor.
Table of contents: What are the rules for collecting and delivering urine How to collect urinalysis What are the indicators evaluated in the general analysis of urine Organoleptic and physicochemical properties assessed by the general analysis of urine Biochemical characteristics of the general urine analysis Urine analysis by Nechiporenko Norms urine tests in the childWhat are the rules for collecting and delivering urine
Not all people know how to properly pass urinalysis, what are the requirements for collection, minimizing distortionsGOVERNMENTAL data.
Biochemical composition of urine directly depends on the amount of fluid being supplied to the body, climatic conditions of living, physical activity.Before analyzing it is important to observe the rules of delivery and storage of the investigated biomaterial, which allows obtaining reliable data.
Before collecting urine for analysis, doctors recommend not overdoing the day, especially not to abuse fatty, floury and sweet.It is necessary to refrain from smoked and spicy food.It is also important not to subject yourself to physical overload.
How to assemble the urine test
 The urine is collected in clean and dried utensils.It is best to take an average "portion" of morning urine.Women should be aware that during the period of menstruation should refrain from conducting the analysis.In an emergency, it is better to apply the urine output through a soft catheter.To catheterization also resorted to the impossibility of self-emptying the bladder due to existing diseases.
The urine is collected in clean and dried utensils.It is best to take an average "portion" of morning urine.Women should be aware that during the period of menstruation should refrain from conducting the analysis.In an emergency, it is better to apply the urine output through a soft catheter.To catheterization also resorted to the impossibility of self-emptying the bladder due to existing diseases.
The analysis should be carried out within a few hours after the material is collected.If this is not possible, the urine should be stored in a cool place.Preservatives can also be used that do not distort the results of the study.
On dishes with material it is necessary to put the name and age of the patient.
Important: decoding of the urinalysis is performed only by a doctor who examines the patient and knows all the subtleties of the existing disease.It must be remembered that the results of urinalysis without examination can be interpreted incorrectly.
Urine test rates in adults, table:
| RATE INDICATOR | REJECT | |
|---|---|---|
| amount of urine in the morning portion | 100-300 ml | least 100 ml |
| 300 ml | ||
| Transparency | full | cloudy at the time separation |
| flakes and threads | ||
| Color | straw yellow | orange-red |
| kind of meat slops | ||
| brown | ||
| black | ||
| bright yellow | ||
| transparent light yellow | ||
| pH | acidic | neutral |
| alkaline | ||
| osmolarity | 600-800 mmol /l | less than 600 mmol / l |
| more than 800 mmol / l | ||
| Relative density( specific gravity) | 1,018-1,025( 1018-1025) | above 1,025( 1025) |
| Below 1.018( 1018) | ||
| Acetone | no | have |
| protein | no( or trace amounts) | have |
| Glucose | no | have |
| Ketone bodies | no | have |
| leukocytes | men: 0-3 in sight, women 0-5 in sight | 5-20 in sight |
| over 20 in sight | ||
| Red blood cells | no( or single) | less than 100 in sight |
| more than 100 in sight |
Which indicators are evaluated in the general urine analysis
Clinical laboratories allow assessing the physical properties of urine, its chemical composition and microscopic diagnosisUrinary sediment.In addition to general clinical analysis, the Nechiporenko method is used.With his help, additional clarification of kidney diseases is carried out.
Organoleptic and physico-chemical properties assessed by the general analysis of urine
The organoleptic properties of urine include color, odor, and amount of secreted fluid.To the physicochemical - density and chemical reaction.
The color of urine varies depending on its concentration and the presence of coloring substances.In this case :
-
 It becomes pale or colorless after taking diuretics, in the case of existing diabetes mellitus.Dark color( color of beer) is typical for diseases accompanied by the release of bile pigments into the urine.Usually this occurs with hepatitis.
It becomes pale or colorless after taking diuretics, in the case of existing diabetes mellitus.Dark color( color of beer) is typical for diseases accompanied by the release of bile pigments into the urine.Usually this occurs with hepatitis. - Tumor processes, traumatic injuries of the kidneys due to the appearance of erythrocytes in the urine give different shades of red, reminiscent of the color of meat slops.
- The increased turbidity of urine is observed in the presence of a large number of salts, epithelial cells, mucous secretions, fatty substances, pathogenic bacteria.
The odor of urine is determined in the event of a prolonged presence in the container.The speed of its development depends on the temperature of the room.
In the presence of certain diseases, various shades of urine odor may appear, for example:
- infection with E. coli promotes the development of odor feces in the urine;
- ketonuria - an acetone smell;
- isovaleric and glutaric acidemia - the smell of sweaty feet;
- trimethylaminuria - a shade of decaying fish;
- tyrosinemia - rancid fish stench;
- phenylketonuria - mouse odor;
- fistulas between the intestine or purulent cavities and urinary tracts - putrefactive smell;
- cystitis - odor of ammonia vapor;
For sugar diabetes, a fruity hue is characteristic, due to the appearance of acetone in the urine.
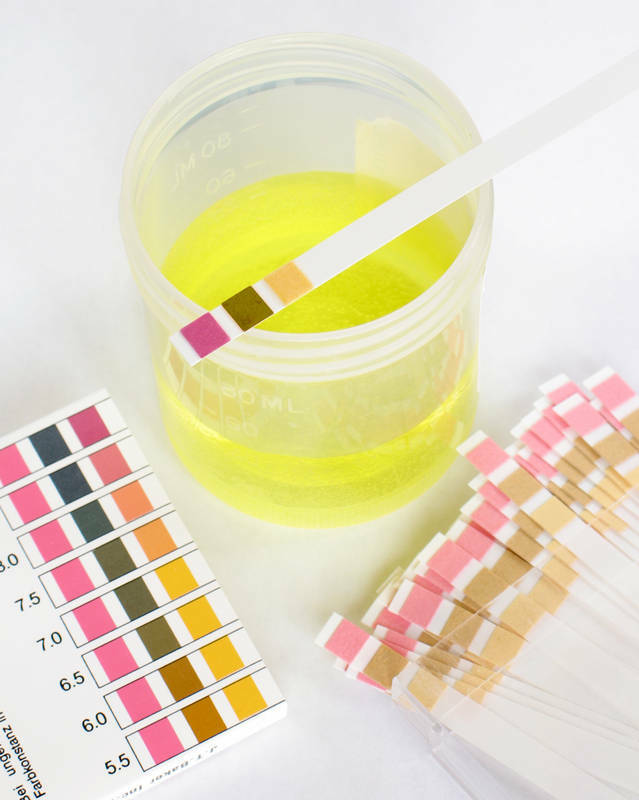 The chemical reaction of depends on the prevailing nature of the patient. It is usually weakly acidic or neutral . Diabetes mellitus, chronic heart failure , kidney problems, pregnancy can give an acidic reaction.The pronounced acid reaction, taking place against the background of the acidosis of the body, is typical for severe infectious diseases accompanied by fever, with diseases of the intestinal tract, starvation.
The chemical reaction of depends on the prevailing nature of the patient. It is usually weakly acidic or neutral . Diabetes mellitus, chronic heart failure , kidney problems, pregnancy can give an acidic reaction.The pronounced acid reaction, taking place against the background of the acidosis of the body, is typical for severe infectious diseases accompanied by fever, with diseases of the intestinal tract, starvation.
Alkalosis - a satellite of chronic rapid breathing in diseases of the lungs, the heart provokes an alkaline reaction of urine.Similar changes occur with indomitable vomiting, some kidney diseases, pathology of the endocrine system, the use of diuretics, transfusions of a large number of carbonate solutions for intravenous administration.Alkaline urine can also give some food.
The adult urine is in the range of 1,001 - 1,040 g / l . It is determined by the total concentration of physical compounds and organisms dissolved in it.These include proteins, pigments, glucose isomers, bacteria, uniform elements of blood.
The amount of excreted urine per day in a healthy person ranges from 1 liter to 2 liters, depending on the drinking load, air temperature.Diabetes mellitus is the main pathology, in which the patient can allocate about 8 liters and more per day.
Note: at night the excretion of urine slows down normally.If there is a reverse trend, you should suspect a chronic process in the kidney tissue or a possible mental pathology.
Biochemical characteristics of general urine analysis
Important information that helps the physician in the diagnostic process is data on the content of protein components, products of bile pigment exchange, glucose isomers, acetone and other substances.
Protein in the analysis of urine
In the urine of a healthy person, the protein is not determined.
The cause of its appearance( proteinuria) can be:
- renal - in case of ingestion of protein from the blood plasma in inflammatory diseases of the kidneys, severe external stimuli( severe cold, stress, physical overload);
- extracellular - the protein enters the urine from the urinary tract.
Urine analysis for protein is a very important and valuable diagnostic indicator.
Urine test for sugar
Normally, urine does not contain sugar .Finding it can indicate the intake of a large number of carbohydrates in food.Then we are talking about physiological glucosuria.
Pathological glucosuria can cause:
- diabetes mellitus;
- pituitary disease;
- pathology of the adrenal glands.
It is worth considering if in the general analysis of urine there are ketone bodies :
- acetone;
- acetoacetic acid;
- Batta-hydroxybutyric acid
Their presence confirms the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, acute inflammatory processes of kidney and liver tissue.For diabetes mellitus, the presence of ketone bodies is a formidable sign of the development of one of the species of coma.
Microscopy of urine sediment in general urine analysis
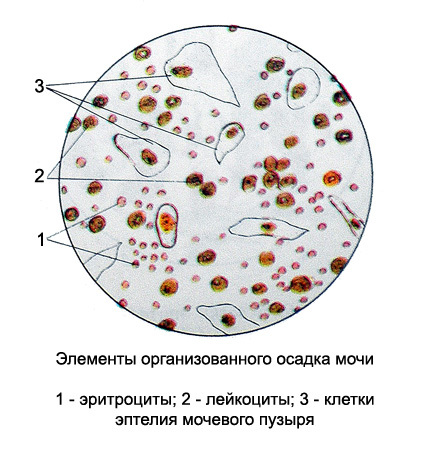
This method evaluates the appearance of blood elements in the urine.
Urinalysis for red blood cells
The presence of erythrocytes in the urine, both unchanged( with contained hemoglobin) and altered( freed from hemoglobin, colorless) is called hematuria.
There are two types of this condition:
- macrohematuria - erythrocytes are in the urine in large quantities, because of what it acquires a reddish hue( meat slops);
- microhematuria - erythrocytes are defined only in the field of view of the microscope.
The appearance of unmodified red blood cells is characteristic of:
- of kidney infarcts;
- presence of stones;
- tuberculosis process of kidney tissue;
- traumatic lesions;
- malignant tumors;
- inflammation of the bladder and urethra.
The level of the erythrocyte source is determined by a three-stage breakdown:
- if the blood in the first portion means that the blood source is the urethra;
- if the blood is in three portions - there is a kidney pathology;
- if the blood is only in the last dose, then it is about inflammation of the bladder or the tumor process.
Urine analysis for the contents of cylinders and epithelial cells
Cylinders are globulin structure molds that repeat the shape of the renal tubules.
Two kinds of cylinders can be detected in urine:
- hyaline - indicators of chronic nephritis;
- epithelial-cellular cells of the renal tubules.Among them there are: granular cylinders, waxy cylinders( flat homogeneous structures).
The increase in the number of cylinders( cylindruria) occurs with pathological processes in the tubules of the kidneys.Especially the number of these cells increases with nephrosis.
Epithelial cells in the general analysis of urine can be:
- flat( rounded with a small nucleus).In the urine appear from the mucosa of the genitals;
- transitional - lining the mucosa of the bladder and renal pelvis;
- renal( irregularly shaped with a yellowish tinge) - characteristic markers of kidney damage in infectious diseases and poisonings.
Urinalysis for leukocytes
Urine of healthy individuals may contain in a single quantity of white blood cells .When the lab assistant discovers white blood cell clusters on the whole field of view of the microscope, the doctor has every reason to suspect the patient of pyuria - pus in the urine.This condition can be observed in severe forms of inflammatory diseases of the kidneys - pyelonephritis, with a purulent pathology of the bladder and urinary tract.
You can understand where the source of pyuria is located, thanks to a three-glassed sample, similar in determining the source of blood in the urine.
Urinalysis by Nechiporenko is an additional and more precise method of determining the degree of white blood cells in the urine( leukocyturia).
Urinalysis by Nechiporenko
 Urine is collected with the morning portion, after preparation and carrying out the procedure of the toilet of external urinary organs.The average portion of morning urine is taken.For analysis, 5 ml of material is used, which is subjected to centrifugation for 10 minutes.
Urine is collected with the morning portion, after preparation and carrying out the procedure of the toilet of external urinary organs.The average portion of morning urine is taken.For analysis, 5 ml of material is used, which is subjected to centrifugation for 10 minutes.
After this part of the analysis, the liquid contents are drained and the concentrate is placed in the Goriaev chamber to count the number of red blood cells, leukocytes and cylinders.The resulting number of elements is multiplied by 250.
If the number of white blood cells exceeds 2000 in 1 ml, then the patient can be suspected of inflammation of the bladder, the presence of prostatitis, nephrolithiasis, pyelonephritis.
If the number of erythrocytes is more than 1000 in 1 ml, then the patient, if there are other signs, can confirm glomerulonephritis, a kidney infarction.
The appearance of cylinders also confirms kidney pathology, depending on the predominance of certain forms - hyaline, granular, waxy, erythrocyte and epithelial.
Norms of urinalysis in a child
Rates of urinalysis in a child, table:
| Indicators | results |
| Color | From straw to dark yellow |
| smell | blur |
| Appearance | Transparent |
| Relative density | from 1,010 to 1,025 |
| pH | 5 to 7,0 |
| protein | 0,00 - 0,14 g / l |
| Glucose | 0,00 - 1,00 mmol /l |
| Ketone bodies | 0 - 0.5 mmol / l |
| Bilirubin | 0 - 8.5 mmol / l |
| Urobilinogen | 0 - 35 pmol / l |
| Hemoglobin | No |
| Bacteria( nitrite test) | None |
| erythrocytes | 0 to 2 in view |
| Leukocytes | 0 to 5 in the field of view |
| Epithelial cells | 0 to 5 in the field of view |
| cylinders | None except1-2 hyaline cylinders |
| crystals | Detected |
| Bacteria | No |
| yeasts | No |
| Parasites | No |
on collecting urine analysis in children and deciphering urineThe child in the video review tells Dr. Komarovsky: