Hemolytic disease of newborns( HDN)

In seven out of ten children born in the hospital, maternity hospitals detect jaundice of the skin.Some babies are already born with jaundice, while others turn yellow after hours or even days after birth.
In 90% of cases all ends safely: the diagnosis of physiological jaundice of newborns is confirmed.But in 10% of cases, doctors are forced to ascertain the fact that the baby has a congenital or acquired, often severe disease, which has caused the skin and mucous membranes to turn yellow.One of these diseases is hemolytic disease of newborns.
Table of contents: Concept and mechanism of HDN development Causes of hemolytic disease development Forms of hemolytic disease of newborns Hemolytic disease: consequences and complications Pre- and postnatal diagnosis of HDN Hemolytic disease of newborns: treatment Recommended:CONCEPT OF HEMOLITIS DISEASE OF NEWBORN)
Hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn is a congenital disease that can manifest itself and when the baby is still in the morningBoth mothers, and when he was born.
In its essence, this is an immunological confrontation between two related organisms - the mother's organism and the child's organism.The cause of this conflict, paradoxically, is the incompatibility of the mother's blood with fetal blood, which results in the destruction of the baby's red blood cells.
Development mechanism of the ASN23ASD
The human erythrocyte envelope is "populated" with various antigens( AG), more than 100 species.Scientists have grouped all AH into erythrocyte systems, of which more than 14 are known( AB0, Rh, Kid, Kell, Duffy, etc.).
Rh( Rh) includes AG, responsible for the Rh rhesus blood: Rh( +) or Rh( -).In the system AB0 - AG, determining the group membership of human blood: B and A. Antigens of both these systems are able and ready to instantly trigger an immune response when they meet with the appropriate antibodies( AT).In blood in norm or rate AT to AG their native erythrocytes are absent.
What happens with hemolytic disease of the fetus and the newborn?In the blood of the child through the placenta from the blood of the mother penetrate AT, suitable, as a key to the lock, to the antigens of red blood cells of the fetus.Their meeting gives rise to an immune reaction, the result of which is hemolysis( destruction) of the baby's erythrocytes.But where did the blood in the mother come from the AT to the child's erythrocyte AH?
CAUSES FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF HEMOLITICAL DISEASE
Hemolytic disease: causes for a rhesus system conflict
This form of HDN develops if a sensitized woman with Rh( -) blood is pregnant with a fetus with Rh( +) blood.
What does the term "sensitized" mean?This means that at least once Rh( +) red blood cells have entered the blood of the woman, for example, in previous Rh( +) pregnancies, which resulted in childbirth, abortion or miscarriage.Erythrocytes of the fetus penetrate the placenta into the bloodstream of the mother and during pregnancy( especially active at 37-40 weeks), and during childbirth.Sensitization could occur with blood transfusion, organ transplant.
The table shows the likelihood of Rh-conflict between the mother and the fetus.
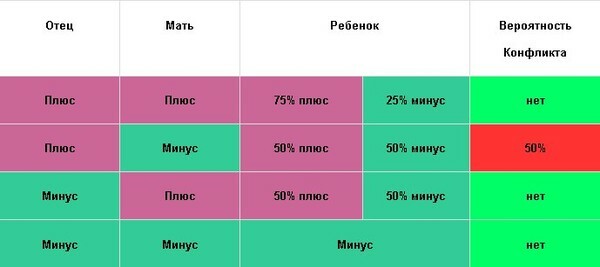 For the first "acquaintance" with foreign erythrocytes the mother's organism reacts by producing the corresponding antibodies.From this moment, the antibodies circulate in the mother's blood and "wait for a new encounter" with foreign Rh( +) red blood cells.And if the first meeting of antibodies with antigens could have ended quite safely, then the second and all subsequent ones will represent an aggressive, aggravated with each time confrontation that affects the child.
For the first "acquaintance" with foreign erythrocytes the mother's organism reacts by producing the corresponding antibodies.From this moment, the antibodies circulate in the mother's blood and "wait for a new encounter" with foreign Rh( +) red blood cells.And if the first meeting of antibodies with antigens could have ended quite safely, then the second and all subsequent ones will represent an aggressive, aggravated with each time confrontation that affects the child.
Hemolytic disease: causes of conflict in the system AB0
Conflict in the AVO system occurs much more often than the Rhesus-conflict, but it is usually easier than the latter.

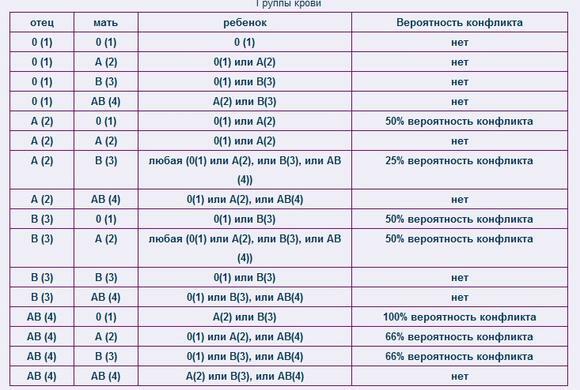
In the table: agglutinogens are group antigens( in erythrocytes), agglutinins are group antibodies( in blood plasma).The blood of each group is a specific set of AH and AT.Note, if antigens A are present in the blood, there is always no antibody α, and if there is B, then there is no β.Why?Because their meeting triggers an immune reaction of agglutination( adhesion) of erythrocytes with their subsequent destruction.This is the conflict over the ABO system, in which hemolytic disease of the blood of newborns develops.
The sensitization of a woman in the ABO system can occur both during pregnancy and before her, for example, when the food ration is saturated with animal proteins, when vaccinated, in case of an infectious disease.
The table shows the likelihood of a conflict between the mother and the fetus in the blood group.
FORMS OF HDN AND THEIR CLINICAL FEATURES
Based on the severity of the course in 50% of cases, hemolytic disease of the neonatal blood proceeds easily, in 25-30% of cases its course is regarded as of medium severity, in 20-30%How heavy.
By the type of conflict there are HDN by the Rh system, by the ABO system and by antigens belonging to other erythrocyte systems.Clinical forms of hemolytic disease of newborns are largely determined by the type of conflict that has arisen.
Fetal calyx
If Rh is in conflict, and at 20-29 weeks of gestation, antibodies are massively attacking the unripe fetus, fetal hydrops develop.
With this form of hemolytic disease of the newborn, the baby is born without jaundice, but with marked swelling of the body and all internal organs.The child has signs of immaturity, reduced muscle tone, weak reflexes, he moves little.Skin pale, it can be hemorrhages.Breathing disorders and signs of acute heart failure are recorded.
In the analysis of blood - severe anemia and very low total protein content.
If antibodies begin to attack a baby after the 29th week, the clinical form of HDN and then, whether it is congenital or acquired, depends on how much and when( in utero and / or in labor) the mother antibodies penetrated the baby.
Jaundice form
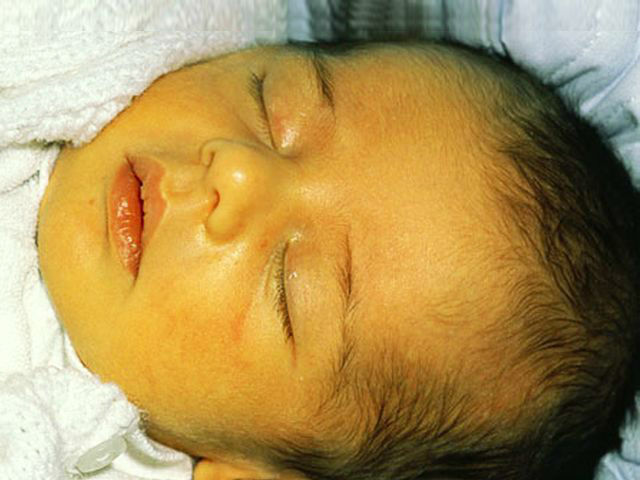 This form is the result of a massive hit of the Rh antibodies of the mother to the baby from the 37th week before the birth( congenital) and during labor( acquired).A distinctive feature of the most frequent( 90% of all cases) icteric form - the early( in the first hours or days) the appearance of jaundice.It reaches its maximum to 2-4 days, is accompanied by a mild anemia, some swelling of the tissues, an increase in the liver and spleen.The earlier jaundice appears, the heavier the course of the disease.
This form is the result of a massive hit of the Rh antibodies of the mother to the baby from the 37th week before the birth( congenital) and during labor( acquired).A distinctive feature of the most frequent( 90% of all cases) icteric form - the early( in the first hours or days) the appearance of jaundice.It reaches its maximum to 2-4 days, is accompanied by a mild anemia, some swelling of the tissues, an increase in the liver and spleen.The earlier jaundice appears, the heavier the course of the disease.
Anemia form
This form is diagnosed in 10% of all children with hemolytic disease, the reason for it is a prolonged effect on the fetus, starting from the 29th week, of small "portions" of Rh antibodies.The child is born very pale, jaundice or not, or it is very weakly expressed.There are gradually increasing signs of bilirubin intoxication( adynamia, lethargy, "bad" reflexes).
Edema
If, after the 29th week of pregnancy, Rh antibodies begin a massive fetal attack, edematous form of HDN develops.Clinical manifestations of it are similar to the symptoms of hydrocephalus of the fetus.
HDN according to the AB0 system: clinical features:
- late( on day 2-3) jaundice appears;
- rarely increases liver and spleen;
- extremely rarely develop congenital icteric and edematous forms;
- often takes the acquired icteric-anemic forms;
- is approaching zero the incidence of severe complications.
Why is the AV0-conflict less common than Rh -conflict, results in a manifest heavy GBN form?
- For AVO-sensitization, a woman needs to have much more fetal blood in her bloodstream than with Rh-sensitization.
- In contrast to Rh antigens, group AHs are found in addition to erythrocytes in all other fetal tissues, in the placenta and in the amniotic fluid.At a meeting with maternal antibodies the immune "blow" is necessary not only on erythrocytes, but is distributed on all these tissues.
- In the mother's body, there are own group antibodies that can cope with the red blood cells of the fetus that have entered the blood.
HEMOLITIC DISEASE: CONSEQUENCES AND COMPLICATIONS
- The syndrome of disseminated intravascular coagulation or DIC syndrome develops as a result of a sharp increase in blood clotting.In small and large vessels blood clots are formed, infarcts and necrosis of organs, hemorrhages to organs occur.The reason - a massive entry into the blood of tissue thromboplastin from hemolytic erythrocytes.
- Hypoglycemia is a reduction in blood glucose.
- Bilirubin encephalopathy is the result of nuclear jaundice, in which extremely toxic indirect bilirubin "impregnates" the structures of the brain, destroying neurons.It is manifested by neurologic symptoms and the formation of bilirubin encephalopathy( paralysis, deafness, etc.).
- Syndrome of bile thickening, in which the bile ducts are clogged with mucous and bilious corks.
- Secondary lesions of the heart muscle, liver, kidneys.
- Secondary immunodeficiency - develops because of damage to components of the immune system by indirect bilirubin and immune complexes.
Prenatal diagnosis of is aimed at identifying women at high risk of developing fetal hemolytic disease, the consequences of which are no less dangerous than herself.
Therefore obstetrician-gynecologist carefully and accurately in terms of GBN asks the patient, finds out the necessary details of anamnesis( abortions, number of pregnancies, etc.).Throughout pregnancy, women at risk of GBN are monitored by antibodies in blood and in amniotic fluid, ultrasound of the fetus and placenta, CTG of the fetus, dopplerometry.
Postnatal diagnosis of implies the detection of newborns who are at high risk of developing HDN and those who already have HDN.For this purpose, the neonatologist regularly inspects all newborns for jaundice, edema and other signs of illness.
Laboratory tests are the control of the level of bilirubin and glucose in the child's blood in the dynamics, the determination of the blood group and Rh factor, immunological tests for the presence of antibodies in the blood of the child, in the blood and milk of the mother.
Hemolytic DISEASE OF NEWBORNS: TREATMENT AND PREVENTION
With hemolytic disease of newborns, treatment can be operative and conservative.When choosing therapeutic tactics, doctors are guided by the severity of the baby's condition and the level of hyperbilirubinemia.
Operative treatment is a replacement blood transfusion operation.Appointed in the presence of a newborn signs of severe HDN, a history of anamnesis, when symptoms of intoxication with bilirubin.Used hemosorption and plasmapheresis.
Conservative treatment is primarily phototherapy, irradiation with a special lamp, whose beams of toxic bilirubin are made non-toxic.
Assignable infusion therapy( albumin, physiological solution, glucose solution) is aimed at removing bilirubin intoxication and prompt removal of bilirubin from the body.
The medications( zixorin, etc.), which activate the enzyme system of the liver, are used.Adsorbents( carbolen, agar-agar, etc.), cholagogue( by means of electrophoresis), vitamins( E, ATP, A), stabilizing cell membranes, hepatoprotectors( essenciale, etc.), antihemorrhagic agents( adroxone, etc.) are used.
Zaluzhanskaya Elena, pediatrician