Pulmonary edema: symptoms, causes and emergency treatment
 Pulmonary edema is not an isolated disease, but rather a complication of a number of pathologies.Its essence lies in the excessive accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the lung, its swelling into the lumen of the alveoli, which leads to a deterioration in the functions of breathing and the death of the patient.
Pulmonary edema is not an isolated disease, but rather a complication of a number of pathologies.Its essence lies in the excessive accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the lung, its swelling into the lumen of the alveoli, which leads to a deterioration in the functions of breathing and the death of the patient.
Anatomy and physiology of the pulmonary gas exchange system
Lungs representA set of hollow tubes of small diameter, at the end of each of which there are alveoli - saccule thin-walled formations filled with air.All these structures are shrouded in filaments consisting of connective tissue.These strands form a kind of framework that forms the lung itself and is called interstitium.Part interstitium are interalveolar septa permeated with capillaries.
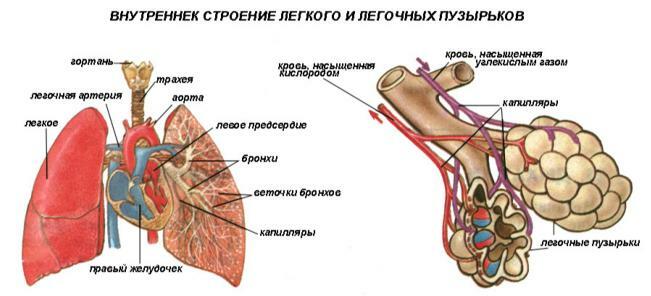 The wall of the alveolus and capillary together with the interstitial tissue form an alveolar capillary membrane( AKM) 0.2-2 microns thick, through which oxygen and carbon dioxide are diffused into and out of the blood.
The wall of the alveolus and capillary together with the interstitial tissue form an alveolar capillary membrane( AKM) 0.2-2 microns thick, through which oxygen and carbon dioxide are diffused into and out of the blood. Mechanism and causes of development of pulmonary edema
There are many reasons for the appearance of pulmonary edema( AL), but regardless of the factor that caused the complication, the mechanism of its development is the same - the accumulation of excess fluid in the tissues interstitium, thickening as a result of alveolar capillaryMembranes and reducing the diffusion of gases( primarily oxygen).As a result, tissue hypoxia( oxygen starvation of all tissues) and acidosis - a shift in acid-base balance, leading to the inevitable death of the patient, if he does not receive emergency care.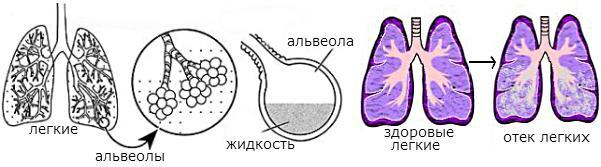 There is no single classification of pulmonary edema, however, according to the pathogenetic mechanism, it can be divided into:
There is no single classification of pulmonary edema, however, according to the pathogenetic mechanism, it can be divided into:
- AL due to increased capillary pressure resulting from:
- acute myocardial infarction;
- cardiac arrhythmias;
- cardiomyopathy;
- myocarditis;
- of exudative pericarditis;
- hypertensive crisis;
- stenosis of pulmonary arteries;
- heart defects;
- massive infusion of blood-substituting solutions;
- renal failure in the anuria phase.
- AL due to increased capillary wall permeability with:
- acute respiratory distress syndrome;
- intoxications( eg, drugs);
- anti-cancer chemotherapy;
- application of X-ray contrast preparations;
- inhalation of toxic substances;
- Allergies.
- OL due to impaired lymph flow in cancerous lesions of lymphatic vessels.
- AL due to changes in intrathoracic interstitial pressure during caisson disease and evacuation( removal) of fluid from the pleural cavity.
- OL due to a decrease in the protein content in the blood plasma.
- Mixed AL:
- is neurogenic;
- postoperative;
- with eclampsia;
- in the syndrome of ovarian hyperstimulation;
- for high altitude sickness.
Formerly, a classification was used that includes such types of pulmonary edema as the interstitial and alveolar ones.At present, it was abandoned, since these two types of AL are in fact only stages of the development of the syndrome.In addition, in terms of diagnosis and treatment, this division does not have any useful function.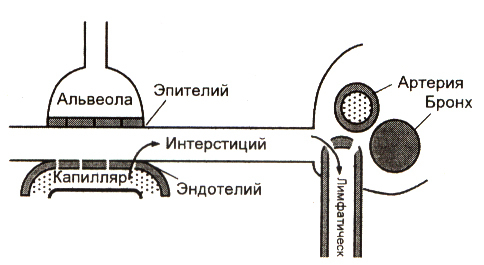 Normally, only a small amount of fluid from the interstitium penetrates into the alveoli.Almost all of it is absorbed into the blood and lymphatic capillaries and is removed from the alveolar capillary membrane.However, if the permeability of the AKM fluid is disrupted, it becomes too much and it does not have time to move all into the vessels.In this case, it impregnates the interstitium, increasing its thickness, and in the most neglected situation it begins to enter the lumen of the alveoli, further worsening the gas exchange.
Normally, only a small amount of fluid from the interstitium penetrates into the alveoli.Almost all of it is absorbed into the blood and lymphatic capillaries and is removed from the alveolar capillary membrane.However, if the permeability of the AKM fluid is disrupted, it becomes too much and it does not have time to move all into the vessels.In this case, it impregnates the interstitium, increasing its thickness, and in the most neglected situation it begins to enter the lumen of the alveoli, further worsening the gas exchange.
Symptoms of pulmonary edema
Symptomatology of pulmonary edema depends little on the factors that led to its development.The difference between AL caused by disturbances in the cardiovascular system and edema not associated with cardiac causes is only the rate of development of pathology.
AL associated with circulatory disorders
With cardiogenic pulmonary edema( caused by circulatory disturbances), the first symptom is cardiac asthma, manifested by dyspnea at rest, increased respiratory movements, a feeling of severe air shortage, suffocation.Most often, the attack begins at night, the patient immediately wakes up and takes a sitting position in which it is easier for him to breathe.At the same time he drops his legs from the bed, resting his hands on its edge.This is the position of orthopnea, which almost every patient takes.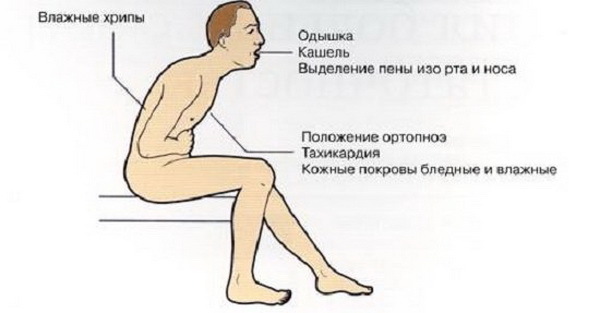 For the beginning of a pulmonary edema it is characteristic to desire to approach a window, to breathe a fresh air.In this state, the patient does not speak much, but his face clearly shows emotional tension.According to the expression of doctors "the patient is completely given to the struggle for air". The skin becomes pale, the nasolabial triangle acquires a cyanotic color( acrocyanosis).This indicates an increase in hypoxia.Perhaps the appearance of cold sticky sweat is a sign of impending cardiogenic shock, which is an exceptionally serious complication of any cardiac pathology.With further development, the patient's breathing becomes noisy, even at a distance the bubbling in his chest is heard, it is possible to extract pink foamy sputum in large volumes.At this stage, the amount of liquid already far exceeds the capillary capacity for its removal, and the liquid part of the blood begins to penetrate into the alveoli.
For the beginning of a pulmonary edema it is characteristic to desire to approach a window, to breathe a fresh air.In this state, the patient does not speak much, but his face clearly shows emotional tension.According to the expression of doctors "the patient is completely given to the struggle for air". The skin becomes pale, the nasolabial triangle acquires a cyanotic color( acrocyanosis).This indicates an increase in hypoxia.Perhaps the appearance of cold sticky sweat is a sign of impending cardiogenic shock, which is an exceptionally serious complication of any cardiac pathology.With further development, the patient's breathing becomes noisy, even at a distance the bubbling in his chest is heard, it is possible to extract pink foamy sputum in large volumes.At this stage, the amount of liquid already far exceeds the capillary capacity for its removal, and the liquid part of the blood begins to penetrate into the alveoli.
Non-cardiogenic edema of light
In this case, the phenomena of pulmonary edema arise due to damage to the alveolar capillary membrane by various factors( microbial toxins, chemicals, mediators of allergy, etc.).Unlike cardiogenic, this type of OL appears only after a relatively long time after exposure to the damaging agent( up to 48 hours).The symptomatology of non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema is completely the same as the cardiac form of the lung.The only difference is that cardiogenic AL is much easier to treat and is resolved faster, completely disappearing in 2-4 days.Non-cardiogenic edema has to be treated for 1-3 weeks, very often( up to 80% of cases) it ends with a lethal outcome.But even in case of successful treatment this form of OL is accompanied by persistent residual phenomena.
Diagnosis of pulmonary edema
For the diagnosis of pulmonary edema, anamnesis is very important.And although sometimes they can not be obtained, but it is information on existing diseases that can lead the doctor to think about the causes of the complication.After finding out an anamnesis, the patient is examined and auscultated.At this moment, changes in the color of the skin and mucous membranes are revealed, profuse sweat, attention is drawn to the patient's breathing posture, his behavior.When listening to the lungs, there are rales, hard breathing, listening to the heart - muffling its tones, the rhythm of "gallop", noise.The main indicator of pulmonary edema is a reduction in the saturation of blood with oxygen.For its detection, pulse oximetry is used, a method available to any ambulance team.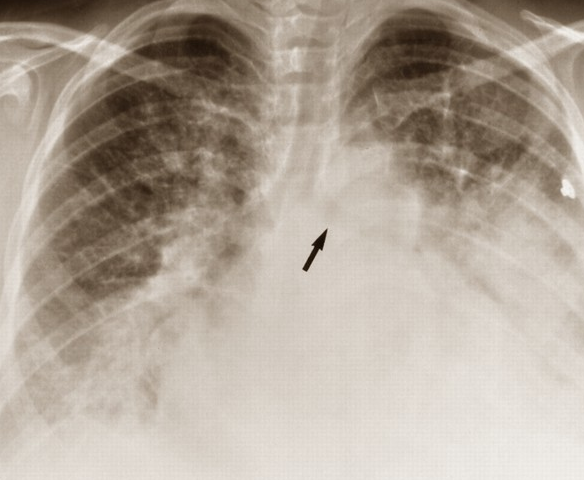 Hemodynamic disorders are detected by measuring blood pressure and counting the heart rate.It is mandatory to conduct emergency electrocardiography taking into account the patient's condition - this method allows to identify the causes of cardiogenic form of edema and to develop optimal treatment tactics.In a hospital, chest X-ray is additionally performed, which reveals signs of pulmonary edema and some pathologies that led to it.With the help of this study, the causes of the disease can be relatively accurately differentiated. Other diagnostic pathology methods are used:
Hemodynamic disorders are detected by measuring blood pressure and counting the heart rate.It is mandatory to conduct emergency electrocardiography taking into account the patient's condition - this method allows to identify the causes of cardiogenic form of edema and to develop optimal treatment tactics.In a hospital, chest X-ray is additionally performed, which reveals signs of pulmonary edema and some pathologies that led to it.With the help of this study, the causes of the disease can be relatively accurately differentiated. Other diagnostic pathology methods are used:
- echocardiography, which allows to identify abnormalities or pathology of heart valves leading to hemodynamic disturbances;
- catheterization of the pulmonary artery to detect changes in pressure in this vessel;
- transpulmonary thermodilution, which allows to determine the degree of edema;
- biochemical blood test, with the help of which some pathological conditions that can lead to OL are revealed;
- The gas composition of the blood is the most important analysis, giving information about the saturation of blood with oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Treatment and emergency aid for pulmonary edema
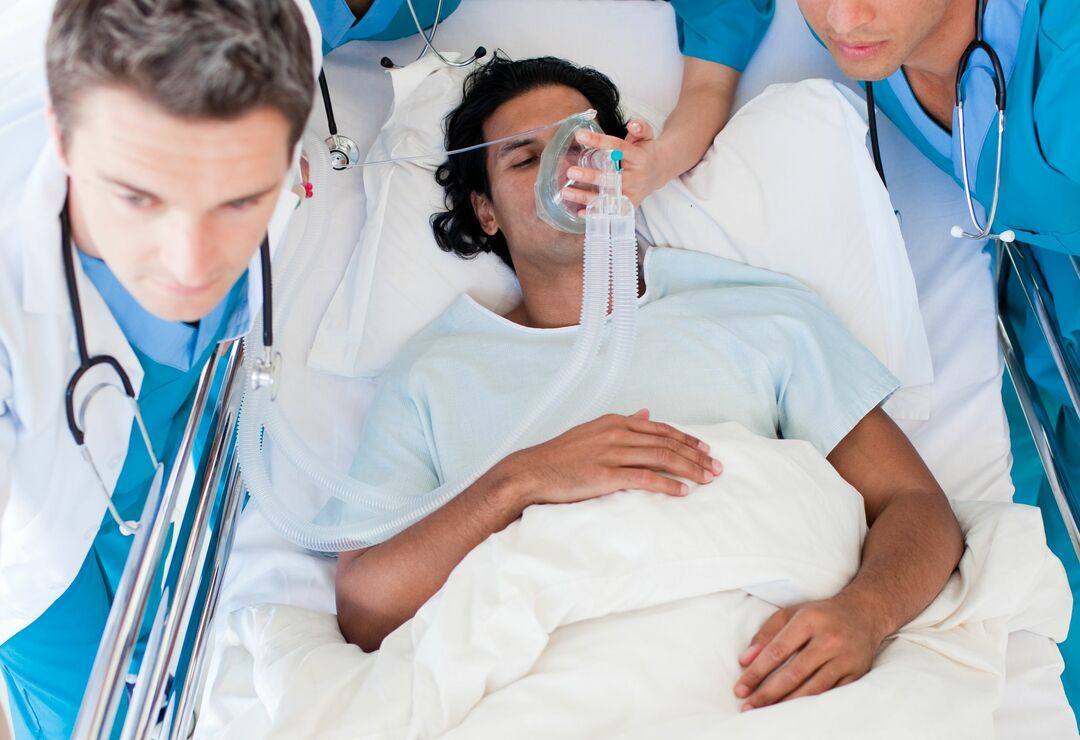 The first thing to start treating OL is oxygen therapy.Inhaling to patients with pure oxygen can reduce the degree of hypoxia, dilute the alveoli and improve the transport of gases into the blood.This gives doctors the necessary time to introduce medications that can eliminate pathology.In the presence of hemorrhagic foam, oxygen is passed through a water-alcohol solution, since ethanol is capable of destroying bubbles.In the absence of the effect of standard oxygen therapy, oxygen is transferred to the respiratory mask under pressure.In particularly severe cases, tracheal intubation and artificial ventilation may be required. Drug therapy depends on the pathology leading to the development of pulmonary edema:
The first thing to start treating OL is oxygen therapy.Inhaling to patients with pure oxygen can reduce the degree of hypoxia, dilute the alveoli and improve the transport of gases into the blood.This gives doctors the necessary time to introduce medications that can eliminate pathology.In the presence of hemorrhagic foam, oxygen is passed through a water-alcohol solution, since ethanol is capable of destroying bubbles.In the absence of the effect of standard oxygen therapy, oxygen is transferred to the respiratory mask under pressure.In particularly severe cases, tracheal intubation and artificial ventilation may be required. Drug therapy depends on the pathology leading to the development of pulmonary edema:
-
 with myocardial infarction appoint nitroglycerin, aspirin, clopidogrel, heparin, and with severe heart pain - narcotic analgesics;
with myocardial infarction appoint nitroglycerin, aspirin, clopidogrel, heparin, and with severe heart pain - narcotic analgesics; - for arrhythmias - antiarrhythmics - verapamil, digoxin, metoprolol, atropine;
- for hypertensive crisis intravenously injected drugs from the group of nitrates and furosemide;
- for a variety of infectious diseases - antibiotics;
- for the allergic nature of edema - antihistamines, glucocorticosteroids;
- for hypoalbuminemia - intravenous administration of albumin solutions, etc.
Reduced systolic blood pressure below 90 mmHg.Art.Is an unfavorable sign.In this case, nitrates are contraindicated even in the presence of a heart attack, dopamine preparations are prescribed instead.A frequent "companion" of cardiogenic pulmonary edema is bronchospasm.When this syndrome is detected, bronchodilators are prescribed.
Prevention of pulmonary edema
 As most often this syndrome occurs in people with chronic diseases, timely treatment of them can reduce the likelihood of pulmonary edema.Completely to exclude its occurrence is impossible, especially with long-term arrhythmias, ischemic heart disease, heart defects and heart failure.However, careful monitoring of the condition by the doctor and strict implementation of all medical recommendations helps to avoid decompensation of these diseases, and hence the development of their complications, including pulmonary edema. Bozbey Gennadiy, medical reviewer, ambulance doctor
As most often this syndrome occurs in people with chronic diseases, timely treatment of them can reduce the likelihood of pulmonary edema.Completely to exclude its occurrence is impossible, especially with long-term arrhythmias, ischemic heart disease, heart defects and heart failure.However, careful monitoring of the condition by the doctor and strict implementation of all medical recommendations helps to avoid decompensation of these diseases, and hence the development of their complications, including pulmonary edema. Bozbey Gennadiy, medical reviewer, ambulance doctor