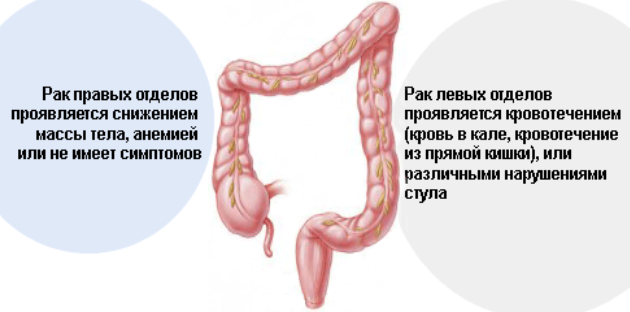
Colon adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of malignant colon tumors.This neoplasm develops from degenerated glandular cells of the epithelial lining of the mucous membrane.
Note: is the fourth most frequent oncological disease among women, and the third among men.
Table of Contents: Risk Factors Classification Symptoms of adenocarcinoma Diagnosis Prognosis for colon adenocarcinoma Treatment of glandular tumorsThe risk of colon adenocarcinoma increases significantly in patients older than 50 years.In the early stages of the disease, as a rule, occurs almost asymptomatically, or the erased clinical manifestations of can be observed.As the tumor grows, patients begin to complain of pain in the abdominal region, general weakness, a feeling of incomplete liberation of the bowel after defecation, and frequent tenesmus.The patient's appetite is usually absent, and the body weight decreases sharply.The general body temperature rises to low-grade figures, and in laboratory analysis, blood and mucus are found in the excrement.Often fixed intestinal obstruction, caused by the closure of the lumen of the colon with a bulky neoplasm.
The prognosis of the disease depends on the volume of the cancer, the presence of secondary foci( metastases), as well as the depth of the lesion and the stage of differentiation( revealed during the cytological study of the biopsy). The basis of treatment is an operative intervention, during which adenocarcinoma of the large intestine is excised.Risk Factors
The cause of the formation of malignant tumors is the degeneration( malignancy) of normal cellular elements.
The likelihood of developing adenocarcinoma increases:
-
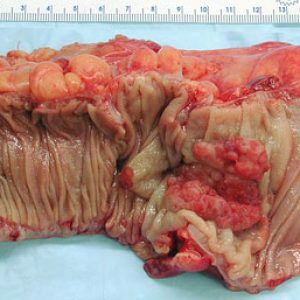 chronic intestinal diseases( inflammatory genesis);
chronic intestinal diseases( inflammatory genesis); - ulcerative colitis;
- granulomatous enteritis( Crohn's disease);
- polyps of the intestinal wall;
- influence of some types of household chemicals;
- impairment of blood supply to the intestine( ischemic changes);
- disorders of peristalsis( chronic constipation and fecal matter formation);
- lack of fiber in the diet;
- high level of consumption of meat products( red meat);
- lack of exercise( sedentary lifestyle);
- occupational hazards( including sedentary work);
- age factor( advanced age).
Note: it is believed that in a number of patients the risk of developing glandular tumors is genetically determined.
Classification, stages of colon adenocarcinoma
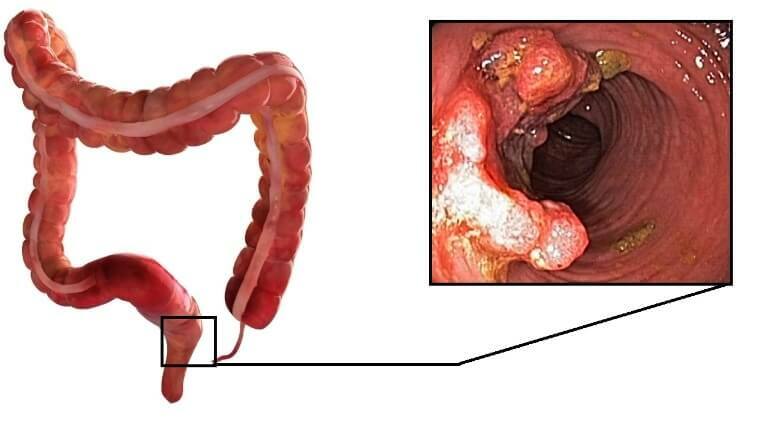
Note: almost 40% of the case affects the caecum.
Normal and malignant cells have a number of differences.On how much they are expressed, the outcome of the disease largely depends.
Species of adenocarcinomas:
-
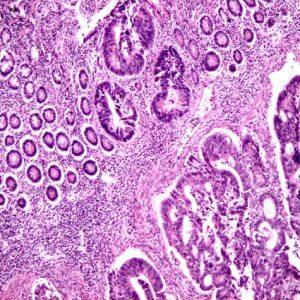 highly differentiated colon adenocarcinoma;
highly differentiated colon adenocarcinoma; - moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma of the large intestine;
- is a low-grade adenocarcinoma of the large intestine;
- is mucinous;
- is a cyst-celled cell;
- squamous cell;
- is tubular.
The highly differentiated adenocarcinoma of the colon is characterized by the preservation of an almost normal cell structure( only an increase in nuclei is noted).Cellular elements retain their functions;The tumor in elderly patients practically does not expand and does not metastasize. The prognosis for this form of cancer is the most favorable. In young people, the risk of recurrence and development of secondary foci even after a successful operation is quite significant.Diagnosis presents certain problems due to the slow development of pathology and the high degree of similarity of altered cells to normal ones.
The moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma is much more dangerous.The proliferation of altered cells often provokes intestinal obstruction.Volumetric neoplasm can disrupt the integrity of the intestinal wall, and lead to bleeding or inflammation of the peritoneum( peritonitis).It is also possible to form fistulous passages.Surgical treatment is necessarily complemented by chemotherapy and radiotherapy, which increases the patient's chances of recovery.
The most aggressive variety of adenocarcinoma of the large intestine is low-grade( diagnosed in 20% of cases). It is characterized by pronounced cellular polymorphism, rapid growth, lack of clear boundaries and the formation of secondary foci in the early stages.The prognosis is usually unfavorable, but with the timely initiation of complex therapy it is possible to achieve a long-term remission.
Mucinous adenocarcinoma consists of epithelial cells and mucin.The mucosal tumor is characterized by fuzzy boundaries;It has the property of giving metastases to nearby lymph nodes.The probability of recurrence is very high, since this type of malignant neoplasm is resistant to radiotherapy.
The ring-shaped tumor, more common in young people, is particularly aggressive.This adenocarcinoma usually grows into the inner layers of the intestinal wall. Most patients at the time of diagnosis already have metastases in the regional lymph nodes and liver .
The squamous adenocarcinoma differs in high degree of malignancy, which most often develops in the anal canal zone.The new growth sprouts into the prostate, urethra and bladder.3-year survival with such a tumor is low, and relapses occur very often.
The tubular adenocarcinoma , diagnosed in half of patients with glandular colon cancer, is characterized by fuzzy boundaries and relatively small dimensions.It is based on specific tubular structures.
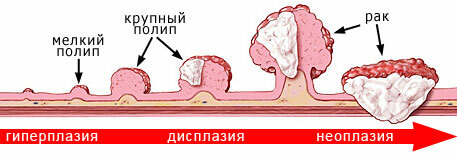
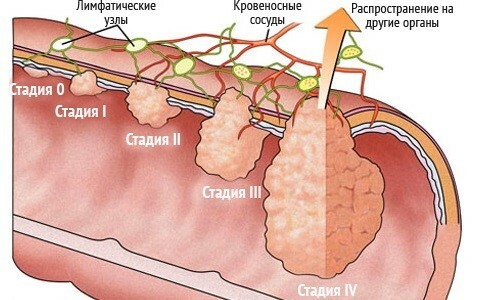
According to the classification accepted in the Russian Federation, 4 stages are distinguished:
- The tumor is localized within the mucosa boundaries.
- New growth sprouts deeper layers of the wall, but lymph nodes are not affected.
- Intestinal wall and lymph nodes are affected.
- Remote metastasis was diagnosed.
Symptoms of adenocarcinoma
In most cases, this type of cancer develops slowly enough.For a long time the patient does not notice any changes in his condition.
Important : adenocarcinoma is often a consequence of a chronic inflammatory process in the intestinal wall, and the first manifestations are often mistaken for exacerbation of long-existing pathology.
Unfortunately, the neoplasm is usually diagnosed at later stages, when single or multiple secondary foci have already formed. This circumstance substantially complicates the treatment and reduces the patient's chances of a full recovery.
Early clinical signs:
- pathological admixtures in feces( blood and mucus are detected in 90% of cases);
- Irregular bowel movement( constipation).
Later symptoms:
- pain in the abdominal area( character - blunt, aching);
- increased fatigue;
- general weakness;
- decrease in body weight on a background of normal nutrition;
- loss of appetite;
- subfebrile temperature for no apparent reason;
- alternation of diarrhea and constipation;
- change in stool character and appearance of putrefactive odor during defecation;
- frequent tenesmus( false urge to empty the intestines);
- jaundice( with metastases in the liver and gallbladder).
The intensity and duration of pain attacks increases as adenocarcinoma proliferates.On the background of intoxication and chronic bleeding anemia appears.
Important: if the lower sections are affected, then the blood on the surface of the fecal matter has a bright scarlet color.With a higher tumor location, the blood is dark.If the neoplasm is located on the right side of the intestine, the bleeding is hidden.
Weight loss is caused by a violation of the intake of digestive enzymes in the lumen of the intestine and a decrease in the absorption of nutrients.
The cause of hyperthermia( within subfebrile values) is the response of the immune system to a pathological neoplasm.The process of decay of adenocarcinoma can be accompanied by a rise in temperature to 38 ° C and higher.
If the tumor closes the lumen of the gut, there is a delay in the feces, which is accompanied by the appearance of nausea and vomiting( against the background of a general poisoning of the body).In this case, there is also an increase in the intensity of the pain syndrome.
Wastes react with the tumor, leading to its ulceration and infection.A sign of such a complication are impurities of pus and dark blood in the excrements.
With the involvement of the retroperitoneal tissue of the retroperitoneal region, a symptom such as tension and intense pain in the muscles of the lumbar region appears.
In the late stages of adenocarcinoma development, "abdominal dropsy"( ascites) and hepatomegaly( enlargement of the liver in size) can be detected.
Diagnosis
 The sooner the correct diagnosis is made, the higher the patient's chances of survival and even a complete cure.
The sooner the correct diagnosis is made, the higher the patient's chances of survival and even a complete cure.
Note: in the structure of colon cancer is more than 80% of adenocarcinomas.
To assess the state of the caudal part of the large intestine, palpation is practiced.An area of about 30 cm behind the anal opening is inspected by means of a special instrument - a sigmoidoscope.Colonoscopy is indicated for the visualization of the entire colon.
During the endoscopic examination, if a pathologically altered zone is detected, a tissue sample( biopsy) can be taken for subsequent histological and cytological analysis in the laboratory.
To clarify the localization of adenocarcinoma and verification of the diagnosis, irrigoscopy is used - one of the fluoroscopy methods.
During the diagnosis, ultrasound scanning of the abdominal organs, urine, blood( including biochemical) and stool( for occult blood) tests are mandatory.
The most informative, safe and atraumatic way to detect cancer is MRI.Tomography allows you to make the correct diagnosis in the presence of obvious contraindications to endoscopy( bleeding or diverticula).
A biopsy specimen is needed to detect differentiation of the glandular tumor, which allows for a treatment plan and a prognosis.
Prognosis for colon adenocarcinoma
Important: one of the features of this disease can be considered the almost simultaneous or sequential formation of several tumors.
Radical treatment is possible if cancer is detected in the early stages of development.At the first stage of highly differentiated carcinoma, the survival rate of patients is 90%, but in the second stage it decreases to 80%.
If secondary foci are found in regional lymph nodes, 5-year survival is reduced to 50% or less.
The probability of cure is significantly lower in patients with a low-grade tumor. If there are multiple metastases in the liver( they can form already in the early stages), the life span is reduced to 6-12 months.
Important: active metastasis is more common in young people, but in elderly patients the percentage of operational mortality is higher( especially in secondary foci in the lungs).
Treatment of glandular tumors
In adenocarcinoma of the large intestine, a complex treatment involving radical excision of the neoplasm within the healthy tissues, removal of metastases, chemotherapy and irradiation is practiced.
Note: preoperative preparation includes the implementation of cleansing enemas and the appointment of so-called."Slagless" diet and laxatives.
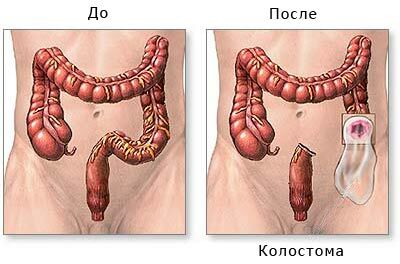
The affected intestinal tract is subject to resection with the formation of anastomosis( anastomosis), restoring the integrity of the digestive tract department .If radical intervention is not possible, the colostomy is shown to divert the waste products.
In the postoperative period, patients are subject to compulsory dispensary supervision.They need to regularly take tests and undergo an endoscopic examination of the lower gastrointestinal tract.Once every six months an ultrasound examination is performed to detect possible metastases.
The combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy as an independent treatment method is practiced in inoperable tumors.His task is the overall temporary improvement of the patient's condition and a decrease in the level of total intoxication of the body.
Palliative treatment involves the appointment of strong( including narcotic) analgesics.
Vladimir Plisov, medical reviewer