Fracture of the malar bone

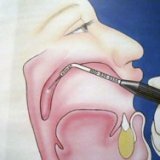
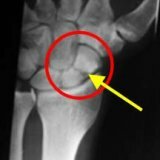
As a rule, radiographic equipment is used for optimal timely diagnosis, allowing to take a snapshot to check the integrity of the zygomatic bone, the fracture of which will be displayed. True, many experienced specialists say that it is extremely difficult to analyze the fractures of the malar bone on the X-ray. However, unidentified fractures can carry a number of negative consequences associated with the formation of certain pathologies. Experienced specialists performed endoscopy of the maxillary sinus in two dozen patients who underwent fractures of the malar bone and identified processes requiring surgical intervention.
Usually distinguish two types of fractures of the zygoma: with and without bias. Fractures with displacement are characterized by damage to the sinuses of the upper jaw. Fractures with displacement are of an open and closed type, as well as linear or comminuted. Damage, from the moment of fulfillment of which has passed to ten days, are fresh, and from ten days to one month from the date - obsolete. If more than one month has passed since the fracture, then such fractures are called incorrectly fused, or not at all fused.
Consider the symptoms that accompany the fracture with the displacement of the zygomatic bone:
- The formation of bleeding, swelling and wounds masking zapping in the cheekbone area.
- The edema of the eyelids is formed, which leads to the closing of the eye.
- In case of fracture of the zygomatic bone, bleeding from the nose, often from one nostril, is often observed.
- The patient can not open his mouth wide, and so move the lower jaw to the sides.
- Often there is a visual impairment, double vision in the eyes, which is associated with the displacement of the eyeball. Westing of the zygomatic bone, which when palpated causes painful sensations in a person.
The main task of specialists in the treatment of fracture of the malar bone is the restoration of integrity, which is carried out with the help of the correction of bone fragments, as well as their fixation. Zygomatic fractures with displacement are eliminated by surgical intervention, since they require the correction of bone fragments and fixation. Conventional fractures without displacement can be eliminated in a conservative way, which is accomplished by the use of medication and physiotherapy.
Technique of Limberg.
One of the most effective and widespread in our time is considered the method of repositioning the zygomatic bone by applying the technique of Limberg AA, which is made by the introduction of a special hook, introduced under the skin. For this, a small cut is made, which is placed exactly at the intersection of the two lines - horizontal and vertical. The horizontal line runs along the lower part of the zygomatic bone, and the vertical line runs from the corner of the eye to the bottom of the skull. The lines are perpendicular to each other. Then follows the repopulation of the bone with a hook inserted under the skin. The correct position of the bone can be judged by the click. If, for a long time of the operational process, it is impossible to fix the fragment, then it is necessary to apply the Kirschner needle, which is injected through the skin. If the special hook of Limberg is absent during the operation, you can apply a conventional single-tooth surgical hook.
Relatively long time ago, foreign scientists proposed a temporal method of fixing the deformities of the malar bone. This method was first used in 1927, which until now has not been changed. Produce a method by cutting the skin on the temple, somewhat retreating from the hair growth sites. The incision has a length of about two centimeters, and in addition to the skin, subcutaneous tissue is also cut. After that, various elevators are introduced there to promote the zygomatic bone and its repopulation.
Application of clamps and teeth.
Also known is the method by which in 1962 doctors NAZHANOV NN and JADOVSKY MN carried out an operation that consisted of cutting the skin, introducing a special wire loop into it. It served for reponation and correct fixation of debris of the malar bone. If more than ten days have passed since the fracture, then special tools with prongs and clamps are used. And in 1972, a well-known scientist invented an apparatus that served to fix and fix the obsolete fractures. The device consisted of a special hook with two teeth, a screw and support pads. The apparatus allowed to re-bone the cheekbone, while he needed a minimal surgeon's effort, and the bone was repositioned using two support pads. After that, a method was invented that allowed both old and fresh fractures to be introduced. The apparatus consisted of a hook, a support platform and a special lever with a handle.
All these methods were developed to reduce cosmetic defects after the operation, but each of them has a number of drawbacks. The most qualitative at the moment is the method of Linberg, but it requires cosmetic applications after the operation.
As for methods of conservative treatment, antibiotics are often used, and appropriate physiotherapeutic treatment is prescribed, which is prescribed by an otolaryngologist, neurologist and ophthalmologist. If the slightest signs of inflammation are observed, then the maxillary sinus is washed.