How is laparoscopic surgery performed?

Advantages of laparoscopy.
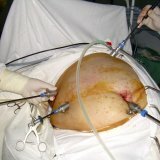
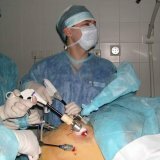
Laparoscopy can diagnose various diseases of internal organs, such as appendicitis and ovarian cyst. It is enough 3-4 puncture in the abdominal wall to perform the operation. Through one of the holes, which is located in the navel, a laparoscope is inserted. Laparoscope is a small telescope, equipped with a light source at the end. Thanks to a laporoscope, an image is displayed on the monitor via a digital video camera. On the monitor, the surgeon sees everything that happens inside the abdominal cavity in real time. Other punctures serve to introduce fine manipulators. Outwardly they resemble tubes with a diameter of 5 mm and a length of 40 cm. There is a handle for the surgeon from one side, and miniature scissors or forceps or a laser tool on the other.
There are times when a doctor can not accurately diagnose the disease of the pelvic organs and the abdominal cavity. Doctors then resort to the help of a unique in its kind endoscopic surgery, assigning the patient diagnostic laparoscopy. The main indicators for conducting diagnostic laparoscopy are pain in the abdomen, as well as the presence of a tumor-like formation.
The main advantages of laparoscopy, unlike cavitary surgery, appeared almost immediately after the introduction of this newest method in surgery. One of the main advantages is the absence of a cut of the skin on the anterior abdominal wall. As a rule, the incision heals for a long time and the patient has to endure painful sensations. After such an operation, the patient is discharged only for 10-15 days. After laparoscopy, the patient can get up after 2-3 hours. Literally the next day the patient's condition improves, and he can return to normal physical activity.2-3 days after laparoscopy a person can go to work. On the skin, the puncture marks heal fairly quickly. A few months they are almost invisible.
The technology of laparoscopy allows you to see on the screen of the monitor the smallest pathology that can not be noticed during the usual operation. Perhaps this is due to the fact that the image on the screen can be increased by 10 times. This allows you to see not only the foci of the pathology of the patient, but also gently remove them, while not affecting healthy organs and tissues.
How is laparoscopic surgery performed?
Laparoscopic surgery is performed according to a well-established scheme. Despite the fact that laparoscopy does not cut the abdominal wall in contrast to the cavitary operation, this method is also a surgery that is performed according to all the classical canons, requirements and established standards in the field of surgery.
Before the operation, the patient should refrain from eating for 8 hours.
Laparoscopic surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The patient is anesthetized during the operation. After he begins to act, and the anesthesiologist gives permission for the operation, the surgeon proceeds to the first stage, which is called "superimposing pneumoperitoneum."In the abdominal cavity, through a special thin cavity needle, called Veresha, carbon dioxide is injected. Carbon dioxide is considered the safest in the operation, so this option was chosen. Gas is supplied to the abdominal cavity until its pressure reaches 14-15 mm. Gt;Art. Determines the pressure of a special device whose name is endoflator. This device works throughout the operation and periodically pumps up carbon dioxide so that the pressure remains at the same level. What is gas for? Due to the gas pressure, the internal organs are compressed, which prevents them from being injured. The abdominal wall is raised, which allows the surgeon to work freely.
After the first stage comes the second - the introduction of a trocar intended for an optical instrument - a telescope( laparoscope).The laparoscope is inserted through a puncture located at the bottom of the navel. The surgeon carefully examines the abdominal cavity, as well as the diaphragm and liver. Further places are examined for better introduction of the following trocars, which are necessary for additional manipulators. Punctures are made along the line of pubic hair growth, one puncture to the left of the middle line, the other to the right.
After the introduction of manipulators, the surgeon examines the internal organs of the abdominal cavity strictly clockwise, marking all the pathologies, then the removal of the detected pathological formations begins.
Laparoscopy, despite its delicacy and effectiveness is a full-fledged surgery. The patient experiences less discomfort and pain. Laparoscopy can reduce the risk of postoperative complications, has a cosmetic effect, the scar does not remain after the operation. But laparoscopy, like a normal operation, can also be accompanied by various complications. For example, complications can arise from anesthesia, from infection, from direct surgical intervention. Surgical complications include such diseases as subcutaneous emphysema, injuries of the intestine and vessels. Subcutaneous emphysema is formed when carbon dioxide enters the subcutaneous fatty tissue, but within 1-2 days it passes. When injuring the intestine or vessels during laparoscopic surgery, it is necessary to suture the wounded organ.