Spleen rupture: causes, symptoms, effects
 Any organ of the human body is equally important for the life of the body as a whole.The spleen is of a special category.It performs several completely different functions, and if it is damaged, the quality of life of a person will significantly worsen, or it will not be able to live because of the massive bleeding that occurs when this organ is damaged.
Any organ of the human body is equally important for the life of the body as a whole.The spleen is of a special category.It performs several completely different functions, and if it is damaged, the quality of life of a person will significantly worsen, or it will not be able to live because of the massive bleeding that occurs when this organ is damaged.
Causes of rupture of the spleen
 The spleen is located inside the human body, that is, it is protected by the musculoskeletal framework from the effects of environmental factors.But itself does not possess a particular strength, and there is no need for super-efforts to damage it.The internal "filling" of the spleen is the so-called pulp( translated as "pulp"), which is a gentle structure.
The spleen is located inside the human body, that is, it is protected by the musculoskeletal framework from the effects of environmental factors.But itself does not possess a particular strength, and there is no need for super-efforts to damage it.The internal "filling" of the spleen is the so-called pulp( translated as "pulp"), which is a gentle structure.
But even the presence of a protective case is not able to protect the spleen from damage. Under the action of the traumatic factor, the pulp is broken subcapsularly.This means that the connective tissue membrane remains intact, and the soft tissues of the spleen are damaged.
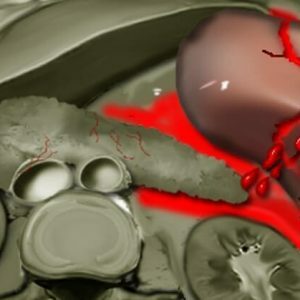
A rupture of the spleen is a violation of the integrity of its parts, which is due to a traumatic effect on that area of the abdomen in which the spleen is projected - the lower part of the thorax to the left or the left hypochondrium. The most common causes of rupture of the spleen in patients who were brought to the clinic are
-
 falling from a height when a blow to the ground or other hard surface occurred on the left hypochondrium and the left half of the abdomen;
falling from a height when a blow to the ground or other hard surface occurred on the left hypochondrium and the left half of the abdomen; - various catastrophes - auto, railway, industrial( blows by bulky production equipment, collapses in the mine), natural( collapses due to earthquakes, tree trunks in hurricanes);
- deliberate infliction of physical injuries( both sharp objects and blunt ones, even clinical cases are described, when the rupture of the spleen was diagnosed after a fist in the side);
- sports injuries( kick of a boxer in the left hypochondria of the opponent, fall on a gymnastic projectile);Often rupture of the spleen in such cases is observed in beginners who are trying to set some records, but in the absence of general sports training overestimated their capabilities and aimed at too high a bar of achievements.
Risk Factors
Most often, the splenic rupture occurs in the working age of 30 to 55 years.In men it is diagnosed more often than in women. Categories of people most at risk of getting a rupture of the spleen:
- persons whose work activity is associated with severe physical exertion or extreme conditions;
- residing in a socially unfavorable environment, in which the practice of assault is often used to find out the relationship;
- Dysfunctional families in which, with an educational purpose, they do not shun beatings;
- families, built on the principles of patriarchy and authoritarianism, as a result of which a woman often suffers assault by her husband.
Why do some people suffer from a traumatizing of the abdomen without risking damage to the spleen, while others who have the same physical fitness, with similar anatomical features of the chest and abdominal wall, have a splenic rupture even with uncritical mechanical action? There are a number of factors that contribute to the rupture of the tissues of this organ:
-
 Failure of connective tissue capsule( congenital or due to spleen diseases);
Failure of connective tissue capsule( congenital or due to spleen diseases); - is the fullness of the organ due to the fact that it deposited a large amount of blood;
- disease of the spleen, which causes splenomegaly( increase in size), resulting in the spleen being projected below the edge of its protector - the costal arch;
- looseness of spleen tissues due to hereditary factor or acquired diseases;
- low position of the organ directly at the time of injury;
- respiratory phase - on exhalation to injure the spleen is easier, because due to the excursion of the ribs it is closer to the anterior abdominal wall of the ;
- a small filling of the intestine at the time of injury, because of which its loops cease to be a life-saving cushion in case of a stomach injury on the left.
Spleen ruptures can be:
- isolated, without damage to other internal organs;
- in combination with trauma of one or more internal organs( so-called polytrauma).
In polytrauma, rupture of the spleen is most often accompanied by:
-
 rib fractures;
rib fractures; - lesions from the chest - in particular, pneumo- and hemothorax( resp. Air and blood in the pleural cavity, which are normal there);
- liver damage;
- rupture of the mesentery( a thin connective tissue film with which the intestine is attached from the inside to the abdominal wall);
- fractures of the spine in the thoracic and lumbar spine.
Classification of spleen injuries
In terms of the degree of damage to the fragments of the spleen, its ruptures occur( in terms of the degree of increase in severity):
- concussion - it breaks a small section of the spleen's parenchyma, the capsule( case) remains intact;
- rupture of the case with insignificant damage( at the level of microrusions) of the parenchyma of the spleen;
- one-stage gap - simultaneously, the capsule case and inner contents of the spleen are torn;
- a two-stage rupture - the tender parenchyma first tears, macroscopically the capsule remains intact, but has microscopic damage of a linear character, which causes a visible( macroscopic) violation of the capsule integrity after a while;
- imaginary two-stage rupture - the parenchyma ruptures, but the blood clot blocks the source of bleeding, it stops, but after a while the clot is washed out, the bleeding is resumed;
- imaginary three-moment rupture - there is a two-moment rupture at which bleeding is suspended, as the clot again tamponizes( blocks) its source, after which it is again washed out, the bleeding continues.
According to the national statistics, most often occur momentary spleen ruptures, accompanied by heavy bleeding into the abdominal cavity and rapidly developing blood loss, which is a danger to life. The time taken from the moment of injury to the critical level of bleeding due to bleeding is 4-6 hours.
But there are also atypical cases when, with a small rupture of the spleen, it is closed by a huge clot of blood, the bleeding stops and can resume as much as 7-20 days, when the clot is shifted. Reasons for resuming bleeding:
- cough;
- loud sneezing sneeze;
- spitting;
- awkward turn of the trunk( for example, uncontrolled in a dream in bed);
- act of defecation - especially with constipation, when the patient, in order to recover, tuzhitsya, like a woman during childbirth;
and a number of other circumstances that provoke an increase in pressure in the spleen.
Symptoms of rupture of the spleen
 The clinical manifestations of spleen injuries accompanied by its ruptures are diverse on the one hand, and is quite typical on the other.Therefore, making the diagnosis purely due to symptoms without using additional survey methods is not difficult . Help in diagnosis is the collection of anamnesis( information from the patient about the development of the condition) - in the anamnesis a traumatic factor( fall, fight) is clearly traced.
The clinical manifestations of spleen injuries accompanied by its ruptures are diverse on the one hand, and is quite typical on the other.Therefore, making the diagnosis purely due to symptoms without using additional survey methods is not difficult . Help in diagnosis is the collection of anamnesis( information from the patient about the development of the condition) - in the anamnesis a traumatic factor( fall, fight) is clearly traced.
In the first hours after the trauma of the spleen, a pain complaint in the upper left part of the abdominal wall and in the lower part of the chest on the left is characteristic( the symptom is characteristic in the first hours after the injury).
From the side of the abdominal cavity organs,
- paresis of the intestine( absence of peristalsis) has already been observed for some time: its internal contents "freeze" in place and do not move in the direction of the anus, as is normal;
- gas retention, their accumulation in the intestines and because of this bloating( as the surgeons say, "belly is a mountain");
- inability to recover( although the final segment of the large intestine may be overcrowded).
Without fail shows signs of acute blood loss:
- marked paleness;
- cold sweat, sticky in consistency;
- sharp deterioration in general condition;
- marked general weakness;
- drowsiness up to the state of prostration( lack of orientation in space, place and time);
- dizziness, accompanied by a darkening in the eyes, sometimes - a subjective sensation of "sparks from the eyes";
- in neglected cases with critical blood loss - twilight consciousness bordering on syncope;
- vomiting( even in the absence of any contents in the stomach);
- increased heart rate and decreased blood pressure;
- shortness of breath;
- tinnitus, sometimes with variations - clinking, easy to ring.
With critical blood loss, general weakness and lethargy is replaced by an excitement that at any time can be replaced by syncope.
Signs of hemorrhage are valuable for diagnosis, as they make it clear that a "leak" of blood has occurred, that is, a pronounced organ damage.But, on the other hand, they are nonspecific, since they can develop at any catastrophe in the abdomen, and not only when the spleen ruptures.
When percussion( tapping fingers) of the anterior abdominal wall, blunting( deafness) of sound is observed due to the accumulation of fluid( blood) in the sloping areas of the abdomen. When auscultation( listening with a phonendoscope or stethoscope) peristaltic intestinal noise will be weakened.Respiration in the left half of the thorax will also be relaxed. Diagnosis of rupture of the spleen in most cases can be made on clinical grounds, without resorting to additional methods of examination - trauma in history( history of development of the condition), pain in the left side of the abdomen and rapidly growing signs of blood loss in the firstTurn allows you to suspect a rupture of the spleen. Of the additional methods of examination informative is the radiography of the abdomen. The main radiologic signs of rupture of the spleen are:
 is characterized by the following characteristics: about 80-85% of the affected patients take a characteristic posture - they lie on their left side, bent and pulling their knees to their stomachs;
is characterized by the following characteristics: about 80-85% of the affected patients take a characteristic posture - they lie on their left side, bent and pulling their knees to their stomachs; Diagnosis of rupture of the spleen
 From modern diagnostic methods, a 100% result in the correct diagnosis is provided by
From modern diagnostic methods, a 100% result in the correct diagnosis is provided by
The MRI method will help to estimate the degree of blood loss due to the presence of blood in the abdominal cavity.
Blood test may not be informative : blood counts in the first hours of acute blood loss remain unchanged due to compensatory mechanisms( the body understands that the blood transporting nutrients and air has become scarce and gives away some of it from the depot).
Therapeutic tactics for rupture of the spleen
 The biggest danger in rupturing the spleen is bleeding, which leads to blood loss, which in turn is life-threatening. Bleeding from a damaged spleen can stop by itself thanks to a blood clot that swabs the damaged area.But in the vast majority of cases showed urgent surgical intervention to stop bleeding.
The biggest danger in rupturing the spleen is bleeding, which leads to blood loss, which in turn is life-threatening. Bleeding from a damaged spleen can stop by itself thanks to a blood clot that swabs the damaged area.But in the vast majority of cases showed urgent surgical intervention to stop bleeding.
Due to the fact that the inner contents of the spleen is a spongy substance, it is simply impossible to apply seams to it if damaged, to the point that it is simply impossible to impose them and tighten the full surgical junction - they cut through the tissues.Therefore, even with spongy injuries of the spleen, surgeons are forced to remove it. Direct indications for removal of this organ without attempted suturing:
- extensive gaps;
- gaps in the area of the so-called gate( the place where the artery enters the organ and where the vein comes from);Through and ruptured damage to the
- .
A victim who has a ruptured capsule with intact parenchyma is lucky: in this case, the damage is sewn unproblematically.But after the operation, a careful observation is carried out, since after rupture of the capsule, a parenchyma rupture may occur after a while.
The sooner a surgical operation is performed, the sooner the hemorrhage stops, the less blood loss there is. For its reimbursement, blood products and blood substitutes are poured.Practice also reinfusion: the blood that has poured out into the abdominal cavity from the injured spleen is collected, filtered and immediately, during surgery, injected into the bloodstream of the patient.
Damaged spleen: to be or not to be?
Until recently, surgical tactics in the rupture of the spleen were reduced to the removal of this organ.But practical practitioners do not stop disputing whether it is advisable to perform reconstructive( resuming integrity) operations on the spleen when it is damaged.
The significance of the spleen for the human body can not be overestimated, knowing its role. She begins to work actively on early terms of fetal development - inserts a weighty 5 kopecks into hematopoiesis: up to 9 months of intrauterine fetal development is one of the organs of the whole blood system of the future little man, which produces red blood cells and leukocytes.
Before the birth of the baby, the hemopoiesis mission transmits the spleen to the bone marrow, but becomes attached to the immune system - it starts producing lymphocytes and monocytes.Nevertheless, he does not forget his hemopoietic role: in case of some blood diseases, hearts of hematopoies appear in it again.
The functions of the spleen after childbirth and its growing are as follows:
-
 organ is the main "factory" for the production of circulating lymphocytes( cells that fight with bacteria, protozoa and foreign objects penetrated into the body), as well as antibodies( structures that prevent the reproduction of bacteria and viruses and the formation of protein poisons);
organ is the main "factory" for the production of circulating lymphocytes( cells that fight with bacteria, protozoa and foreign objects penetrated into the body), as well as antibodies( structures that prevent the reproduction of bacteria and viruses and the formation of protein poisons); - spleen serves as a "cemetery" of some blood cells - old, unsuitable, diseased and damaged red blood cells and platelets;Without such function, the obsolete blood cells would long wander around the body, introducing it into confusion( the cells are present, but do not bring any benefits);
- organ takes part in the exchange of iron and the production of bile - after the destruction of red blood cells and platelets in them, their residues are sent to the liver, where they are disposed of.Thus, erythrocytes and platelets, having completed their "blood" life, thanks to the spleen begin to exist in the bile excretory system ;
- parenchyma of the spleen is capable of depositing( accumulating) blood, and also accumulates "for a rainy day" platelets( about a third of all platelets of the human body) and gives them in case of need( for example, in acute or chronic hemorrhage, destruction of diseased platelets).
Even a brief overview of the functions of the spleen gives an understanding that it is necessary to revise the surgical tactics in its ruptures, which now amounts to the removal of this body .It must be taken into account that the role of the spleen has not yet been fully studied. If scientists prove that it performs endocrine( hormone-forming) functions, in particular, it performs hormonal regulation of the bone marrow - its significance for the human body will grow at times. And this means that practitioners will need to think carefully about the development of surgical methods that ensure the preservation of the spleen when it is damaged.
Forecasts after removal of the spleen
Since the functions performed by the spleen are not only performed by it, after the removal of this organ, a person due to correct and full rehabilitation measures can return to the usual way of life. But the possible consequences:
- weakened immunity;
- changes from the blood;
- signs of dyspepsia( disorders of the digestive system);
- formation of large and small blood clots in the blood vessels of the liver;
- lung atelectasis - the collapse of some of their sites.For the rest of his life, the person who suffered the removal of the spleen must adhere to certain recommendations:
- beware of infectious diseases - for this purpose it is timely to be vaccinated during epidemics, to avoid gathering places( queues, celebrations, public transport),Before going to exotic countries to do vaccinations, carefully observe the rules of sanitation and hygiene;
- colds, do not engage in self-medication at home, and immediately consult a doctor;
- Avoid countries where you can get malaria;
- first two years once a year to do a control ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, then, if there are no changes due to splenectomy - every two years;
- all medicines should be used only as prescribed by the doctor or after consulting with him;
- to engage in physical education( but not sports - the difference with physical education is in the severity of physical activity), observe the correct mode of rest, work, nutrition, sex, quit smoking, do not use narcotic substances, do not abuse alcohol( but use it minimized)That is, to lead a healthy lifestyle.
With careful adherence to these simple rules, the patient with a remote spleen will not feel a change in general condition.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, consulting physician