Liver abscess: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
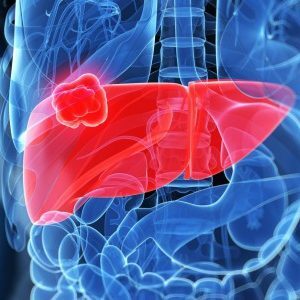 Liver abscess is a purulent inflammation of the liver tissue, which leads to its death, destruction of the organ and the appearance of a purulent cavity in it.10-20 years ago, liver abscess in most cases arose again - as a consequence of inflammatory disease and the formation of abscess in other organs and tissues.Now the trend is that more often there are primary abscesses of the hepatic tissue, catching up on the statistics of secondary lesions.
Liver abscess is a purulent inflammation of the liver tissue, which leads to its death, destruction of the organ and the appearance of a purulent cavity in it.10-20 years ago, liver abscess in most cases arose again - as a consequence of inflammatory disease and the formation of abscess in other organs and tissues.Now the trend is that more often there are primary abscesses of the hepatic tissue, catching up on the statistics of secondary lesions.
Causes of liver abscess development
The immediate cause of inflammation in the liver tissue, which then flows into the formation of pus, is infection - in most cases it is:
- bacteria;
- parasites( unicellular organisms of amoeba).
Pathogens can penetrate the liver tissue in a variety of ways:
- is hematogenic - through the blood vessels( , thus the infection can enter the liver tissue even from distant organs - for example, from the lower extremities of with any of their inflammatoryOr inflammatory-purulent diseases);
- contact - with the breakthrough into the liver of pus from the bile ducts or gallbladder, afflicted with a purulent-inflammatory process( most often this happens with the empyema of the gallbladder - the presence of pus not only in its cavity, but also impregnating the purulent contents of its walls);
- for injuries - can penetrate into the liver tissue as with closed abdominal injuries( such abscesses are also called ischemic, because the oxygen supply of the liver suffers), and with penetrating wounds with violation of the integrity of the liver caused by the contaminated object.
In some cases, doctors can not find out where and how the infectious agent has entered the hepatic parenchyma - such liver abscesses are called cryptogenic.
Hematogenous skid infection in the liver happens :
- portal - by branches of the portal vein;
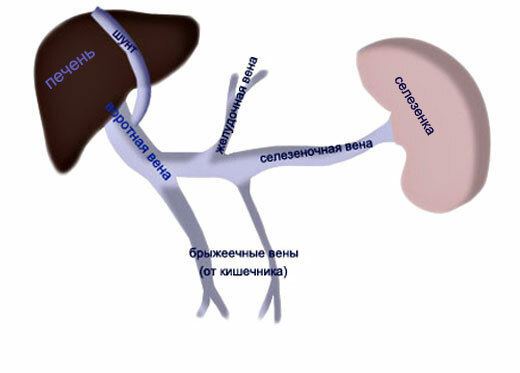
- arterial - on the hepatic artery( the main vessel of the liver, thanks to which the liver receives oxygen and nutrients).
Abscesses of the liver arise:
- "from scratch" - in absolutely healthy people in a completely healthy liver tissue;These are primary abscesses;
- due to another, previously developed liver pathology;These are secondary ulcers.
The most common secondary liver ulcers occur in pathological conditions such as:
- suppuration of cysts of nonparasitic origin( cavities in liver tissues filled with liquid contents);
- infection of echinococcal cysts( if there is a flat echinococcus in the liver);
- suppuration of foci of destruction( necrosis and decay) of benign and malignant neoplasms of the liver;
- infection of tuberculous granulomas - accumulations of liver cells killed due to the tuberculosis process and surrounded by blood cells and Kokh sticks causing tuberculosis;
- infection of syphilitic granulomas - accumulations of dead hepatic cells with scar tissue around and treponema, causing syphilis.
Factors contributing to the occurrence of liver abscess
No liver abscess occurs in every person in whom the causative agents of are located. There are a number of factors that contribute to the penetration of pathogens into the liver and the appearance of an abscess in the hepatic parenchyma.If they are present, you should be especially vigilant so that there is no provocation for infection of the liver and the formation of an abscess in it.
The ingestion of microorganisms into the liver via the bile ducts is facilitated by diseases such as:
- cholelithiasis( formation of sand and stones in the gallbladder and bile ducts);
- acute cholecystitis and acute cholangitis( inflammation of the gallbladder and bile ducts);
- different types of cancer of the intrahepatic bile ducts.
The penetration of infection into the liver by the hematogenous pathway occurs most often by:
- portal vein( vessel that brings blood to the liver from the organs of the abdominal cavity);
- by the hepatic vein( vessel carrying blood from the liver).
In case of diseases of the abdominal cavity, infection of the liver most often occurs in such pathological conditions as:
-
 acute or chronic appendicitis( including at the stage of infiltration, when there are no changes in the appendix yet, but microorganisms have already spreadFor its limits - primarily in the liver tissue);
acute or chronic appendicitis( including at the stage of infiltration, when there are no changes in the appendix yet, but microorganisms have already spreadFor its limits - primarily in the liver tissue); - diverticulitis of the large intestine( inflammation of the saccular protrusions of the wall of the large intestine);
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis( inflammation of the mucous membrane of the colon, which occurs with immune disorders).
Injury to the liver is the third most common factor in which pathogens are most likely to enter the liver and provoke the formation of an abscess in it:
- medical - during surgery on the abdominal organs when the liver is inadvertently damaged;
- household - for example, falling on objects with sharp fragments;
- criminal - most often stabbed liver.
Less frequent occurrence of liver abscess is facilitated by:
- liver cyst;
- hematomas( blood accumulation in the hepatic tissue with blunt abdominal trauma).
In the presence of contributing factors, liver abscess was most often observed in patients with acute appendicitis;
- ;
- cholelithiasis( especially with stratification of signs of acute inflammation of the gallbladder or bile ducts).
Genetic predisposition of liver tissue to suppuration is not proven, but as for the sexual factor, liver abscess occurs more often in men.
There are also age differences as to which pathogens most commonly cause liver abscess:
- in the 20 to 35 age group - amoeba;
- is older than 35 years - bacterial pathogens.
The most common liver abscess is found in middle and old age.
Disease development
 Liver abscess is a classic purulent process.Bacteria or amoebas penetrate the hepatic parenchyma, secrete proteolytic enzymes that destroy hepatocytes( liver cells).
Liver abscess is a classic purulent process.Bacteria or amoebas penetrate the hepatic parenchyma, secrete proteolytic enzymes that destroy hepatocytes( liver cells).
When the process is started, the biological toxins released poison the whole organism.In far-reaching cases, there may be a septic-bacterial shock.
Liver abscesses are:
- single( more often);
- multiple( less often).
The right lobe of the liver is twice as likely to be affected as the left one.
Symptoms of liver abscess
All signs of this disease can be divided into two groups:
- local - manifest on the part of the liver;
- general - are manifested in the form of changes from the whole body.
Local signs develop from the first day of the formation of the abscess in the hepatic parenchyma.These are:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- enlargement of the liver( hepatomegaly);
- feeling of heaviness under the right rib( often the patient characterizes him like this: "It's like a stone that crushes").
The pain in the right side has the following symptoms:
- blunt and aching;When the abscess progresses, the patients complain that something is bursting under the rib in the stomach;
- long, uninterrupted;Sometimes there is a decrease in the pain syndrome, but it does not completely disappear throughout the entire disease, the patient can feel pain even through sleep;
- giving to the right forearm, sometimes( depending on the characteristics of the peripheral nervous system of the patient) can give in the right scapula, collarbone and right half of the neck;Less often with the increase of pain syndrome, the patient can complain that he "pulls" completely his right arm.
General signs from the whole body can:
- directly indicate liver disease or at least pathology on the part of the gastrointestinal tract;
- be nonspecific, characteristic of diseases of many organs and systems.
The first group of common symptoms include:
- jaundice - it is more common for multiple small and medium liver abscesses;
- ascites - the presence of free fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Jaundice manifests by staining to a characteristic yellow color:
-
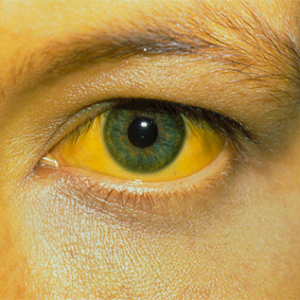 whole-body skin;
whole-body skin; - skin appendages - in particular, nail plates;
- of visible mucous membranes( conjunctiva, tongue, oral cavity);
- sclera;
- biological fluids and secretions( saliva, tear fluid, in rare cases - secretions from the upper respiratory tract).
The second group of common characteristics include:
- increase in body temperature from 38-39 degrees Celsius and above;Hyperthermia keeps at this level throughout the time of day, sometimes there can be a sharp increase in temperature to 40-41 degrees and a sharp decrease again to 38-39 degrees;
- periodic chills - a feeling of cold that arises from the spasm of the blood vessels of the skin;The patient is trembling and covered with "goosebumps"( it arises from the contraction of the muscle fibers that go to the hair follicles - therefore, when the "goose-skin" phenomenon occurs, the hairs on the skin integrate literally become a rack).With a liver abscess, the chill correlates with the temperature and can increase with its increase;
- sharp deterioration of appetite;
- weight loss( doctors observed rare cases when the patient's thinning was the only clinical sign of liver abscess);
- rarely occurs splenomegaly - an increase in the spleen.
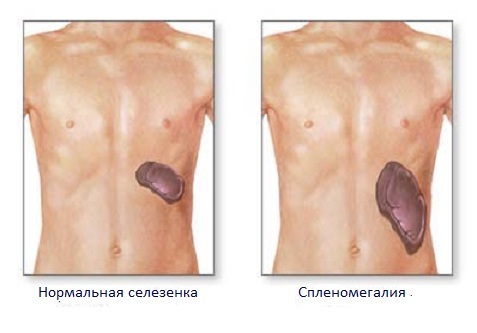
Splenomegaly with abscess of the liver is a bad sign because it indicates its progression and the consequences of this process , namely :
- of so-called portal hypertension, when the pressure in the portal vein system that increasesPurification of blood from all organs of the abdominal cavity to the liver;
- acute thrombophlebitis portal vein - its clotting with a blood clot.
Complications
Not only the liver abscess, but also its complications worsen the patient's condition and the quality of his life.The most common complications of hepatic abscess are:
- breakthrough abscess;
- bleeding from the liver vessels;
- subdiaphragmatic abscess on the right;
- septic shock.
A breakthrough in the hepatic abscess happens in:
- abdominal cavity, resulting in the development of peritonitis - inflammation of the peritoneum;
- nearby abdominal organ( loops of small or large intestine, stomach).
- pleural cavity, followed by the development of purulent lesions of the pleura;
- pericardium( pericardial bag).With a large amount of pus, a cardiac tamponade can develop - a violation of his work due to squeezing;
- bronchus with the development of purulent endobronchitis.
Bleeding from the liver vessels occurs when a purulent process "corroded" them.
Subdiaphragmatic abscess develops when abscesses are found on the surface of the liver that is attached to the diaphragm.
The manifestations of liver abscess are not specific( typical only for this disease).Therefore, the diagnosis can be made based on a complex of symptoms, as well as data in the history of the disease.
The most indicative for the diagnosis of liver abscess is the simultaneous manifestation of such symptoms:
-
 persistent pain and heaviness under the right rib;
persistent pain and heaviness under the right rib; - stable increase in body temperature immediately to 38-39 degrees Celsius;
- chills, the manifestations of which are directly proportional to the temperature figures;
- lack of appetite and not very fast, but increasing weight loss;
- presence in the history( history) of life of chronic diseases of the abdominal cavity, especially with the inflammatory component, and septic diseases;
- when examined in case of a long-gone process the stomach may not take part in the act of breathing due to severe soreness in the right hypochondrium;Also, due to severe soreness under the right rib, the patient can not lie on his right side.
Diagnosis will also be assisted by the inspection data.Such a patient with a look:
- dull;
- sluggish( intoxication affects);
- skinny;
- with further development of the disease exhausted, reacts sharply to the feeling in the right hypochondrium.
With a pronounced process( untreated abscess and late treatment in the clinic, as well as with multiple abscesses), a visual contrast can appear due to the patient's large stomach( due to enlarged liver and ascites) and thin, thin arms and legs.
In order to confirm the diagnosis of liver abscess and exclude similar in appearance of the disease, it is necessary to conduct additional research methods - instrumental and laboratory.
The patient must undergo: X-ray examination - in a number of cases( but not always) the image shows a sign of the hepatic ulcer, namely the cavity( or several cavities with multiple abscesses) with a horizontal level of contents( pus); In more complex cases, resort to such research methods as: Before the era of laparoscopy in complex diagnostic cases, a diagnostic laparotomy was performed - an abdominal incision with a diagnostic purpose.This is the most traumatic method of diagnosing the diseases of the abdominal cavity of , therefore it is used in extreme cases( including in the absence of necessary diagnostic equipment). Laboratory methods of investigation: All treatment methods for liver abscess are divided into two large groups : Conservative treatment is not an alternative to the invasive methods of . It is used: Conservative therapy of liver abscess includes the following measures: Principles of dietary nutrition in liver abscess: MedicationTreatment is as follows: Invasive but non-operative method involves percutaneous drainage of the abscess: Surgical treatment is used: During an operation through a cut in the right upper quadrant( sometimes a cut along the middle line of the abdomen), the abscess is opened, its cavity is sanitized and drained. If liver abscess develops due to infection of the biliary tract, then drainage is performed. In general, any preventive measures, thanks to which a person protects himself from infection, will automatically be protected from liver abscess. In the presence of diseases that are capable of provoking a secondary liver abscess, these diseases should be fully treated as a secondary prevention. Especially should be on check with: The elementary observance of personal hygiene has a powerful preventive value - first of all it is: Also important: With timely diagnostics and properly prescribed treatment of , the prognosis of liver abscess is generally favorable - if the abscess is single or two or three, then most patients recover without consequences.Multiple abscesses and late circulation cause a high degree of lethality. Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, consulting physician
Treatment of liver abscess

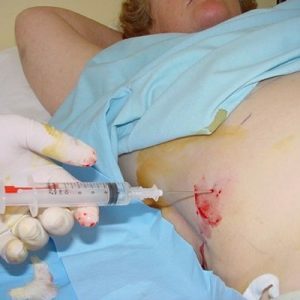 through the anterior abdominal wall inThe abscess cavity is penetrated by a needle;
through the anterior abdominal wall inThe abscess cavity is penetrated by a needle;
Prevention of liver abscess
Forecast