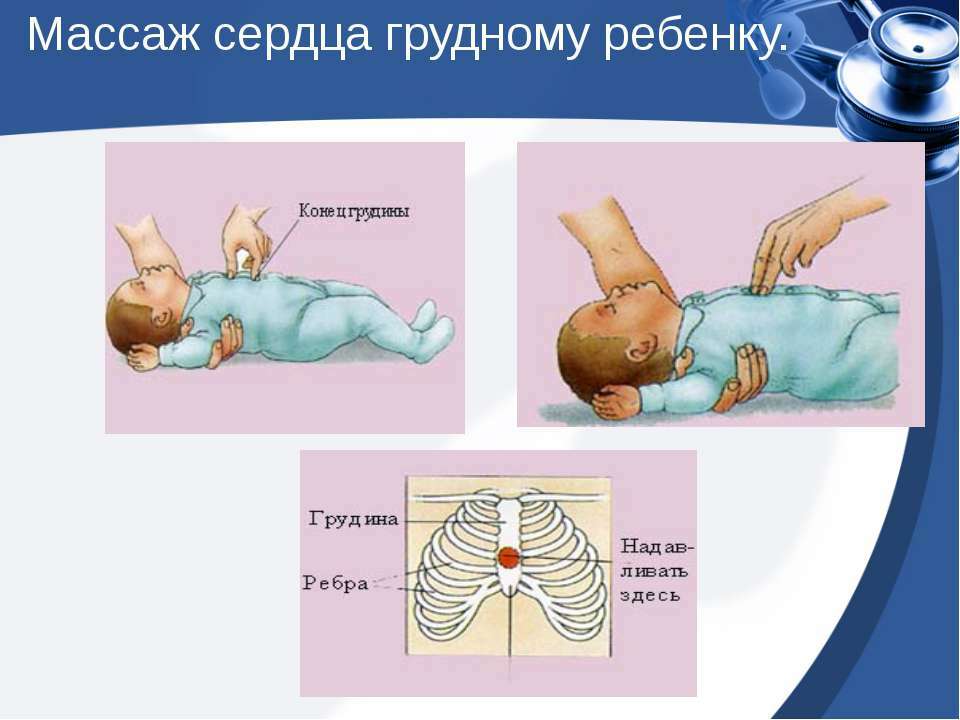
Emergency care for cardiogenic shock

What is cardiogenic shock? If a person has heart failure complicating myocardial infarction, the arterial pressure drops critically, the pulse becomes fast and weak, the patient falls into an unconscious state - this is called cardiogenic shock.
This condition is considered to be the most severe for a person who is likely to die. It develops in acute periods of a heart attack, usually in the first hours - and not only in the presence of extensive infarction, but also with small focal. Shock can also occur when a person has an embolism of the pulmonary artery, and sometimes in the state of an acute myocardium.
There are four types of development and course of this sudden disease, especially the following:
- reflex - the body's response to a severe pain attack;
- true cardiogenic - a sharp decrease in the contractility of the myocardium;
- reactive shock - one of the most difficult options;
- arrhythmic shock - occurs when a violation of the heart rate.
Symptomatic
- arterial blood pressure drops sharply;
- characteristic of the appearance of the patient - facial features are sharpened, the skin turns pale, possibly the onset of cyanosis, the appearance of a spotted-marble pattern on the skin;
- sticky and cold sweat;
- quickening of breathing, wet wheezing, occasionally small bubbles;
- pulse is frequent and weakly palpated, heart tone is deaf;
- anuria or olygia;
- pulmonary edema, possible loss of consciousness;
Mortality from cardiogenic shock occurs in 85% of cases, as blood supply to the brain, liver, kidneys is impaired, coronary blood flow deteriorates. In this case, emergency measures are required. Before the arrival of an ambulance, you should provide the patient with complete peace, urgently call emergency care or take him to the hospital.
Diagnose cardiogenic shock in case of infarction, taking as a basis a characteristic clinical picture - history and objective research, including the results of electrocardiographic and laboratory studies.
Emergency care
- provide the patient with complete peace of mind;
- is urgently hospitalized, however, if there has come a cardiogenic shock of 2 or 3 degrees, first it is necessary to take measures for withdrawal from it;
- for transportation to the intensive care unit to use a special machine, to provide support to the cardiac emergency team that will carry out resuscitation along the way.
Special events and medical care
- introduction of analgesics of the drug group;
- intravenously 1% mezatone solution, concurrently with subcutaneous or intramuscular injection of cordiamine, 10% caffeine solution, or 5% solution of ephedrine - these drugs are desirable to be administered every two hours;
- introduction of a long intravenous dropper - 0.2% noradrenaline solution;
- administration of an intravenous drip - hydrocortisone, prednisolone or urbazone;
- relieve pain with nitrous oxide;
- application of oxygen therapy;
- with blockade of the heart, bradycardia to enter ephedrine, atropine;
- if established ventricular extrasystole - enter intravenous;A dropper of 1% lidocaine
- solution to conduct electrical defibrillation of the heart if ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation are established; if cardiac blockade is observed, electrical stimulation;
- connect to the device of artificial ventilation and artificial circulation;
Only one list of the measures listed above makes it clear how serious this situation is. The account goes literally for a minute. Human life depends on the speed of decision-making.
These measures are aimed at stopping the pain syndrome, which is the main cause of cardiogenic shock. They are carried out with the aim to normalize the heart rhythm, to enhance the contractile ability of the myocardium. It also happens that it is possible to reduce the area of the infarction.