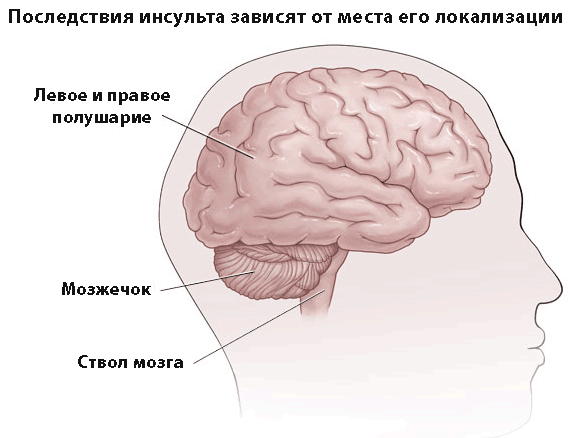
Pulmonary artery stenosis

Stenosis is a narrowing of the pulmonary artery and is considered a congenital heart disease. Among the various types of heart defects, stenosis occurs in six to ten percent of cases. There are three types of narrowing: Valve, Valve and Valve. Most often there is a valvular type of constriction, approximately, in eighty to ninety percent of cases.
Symptomatic of stenosis
If the degree of narrowing of the pulmonary artery is easy, then in most cases the disease does not cause any symptoms. With a more severe course of the disease, dyspnea and fatigue appear, chest pain with physical exertion, dizziness, cyanosis, fainting. Dyspnea appears in this disease as a result of inadequate perfusion of working muscles, which eventually causes reflex ventilation of the lungs. Cyanosis with stenosis can be of two types: central origin( as a result of a discharge through an open oval window of blood) and peripheral( as a result of low cardiac output).
Diagnosis of the disease
Heart auscultation
With a light and moderate course of valvular stenosis, the second tone is not altered or can be slightly weakened as a result of less involvement of the pulmonary component in its formation. With severe stenosis and a significant increase in pressure in the ventricle, the second tone can completely disappear. When nadklapannom or infundibular stenosis, a second tone does not change.
With valvular stenosis in the second intercostal space in the left region of the sternum, the early systolic "click" can be heard at the moment of the greatest opening of the valves of the artery valve. This systolic "click" increases with exhalation. With other types of stenosis( subvalvular and supra-valvular), systolic "cliques" are not listened to.
The main auscultative manifestation of the disease is expressed in coarse systolic murmur in the second intercostal space on the left side of the sternum with spreading to the back and under the left collarbone.
Electrocardiogram for stenosis
With a small stenosis of the pulmonary artery, no changes are detected on the electrocardiogram. With moderate and severe stenosis, signs of dilatation of the right ventricle and auricle are found. In addition, sometimes there is supraventricular arrhythmia.
Echocardiography with stenosis
The area of the healthy valve opening of the pulmonary artery is two square centimeters. In the two-dimensional regime with valvular stenosis, specialists identify a dome-shaped protrusion of the thickened valves of the artery valve at the time of contraction of the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery trunk. Also characteristic of stenosis is the thickening of the wall of the right ventricle. In addition, there are other levels of pulmonary artery obstruction. Doppler mode provides the ability to determine the degree of obstruction by the pressure gradient between the pulmonary trunk and the right ventricle. A moderate degree of disease can be diagnosed with a peak systolic gradient less than fifty millimeters of mercury. With moderate stenosis, the pressure gradient is fifty to eighty millimeters. Heavy stenosis corresponds to a pressure gradient of more than eighty millimeters. With such a course of the disease, the gradient can reach values of one hundred and fifty millimeters and even more.
Treatment of stenosis in adults
Valve stenoses of mild to moderate severity usually occur quite favorably and do not require particularly severe interventions in treatment. With podklapannom muscle stenosis the situation is different - the disease has already a more significant progression. Progression nadklapannogo stenosis is slow. As the pressure gradient between the pulmonary artery and the right ventricle increases and reaches a value of more than fifty millimeters, valvuloplasty is necessary for valvular stenosis. It should be noted that after this procedure, more than half of the patients develop a failure of the pulmonary artery valve. If heart failure occurs, then it is treated. It is recommended to carry out actions for the prevention of endocarditis of infectious nature, since the probability of its development is high.