Convex forehead and eyes in the child: is it worth worrying?
Contents:
- What are the causes of the convex forehead
- Anatomical feature of
- Rickets
- Hydrocephalus
- Convex eyes: causes of
- Is it worth worrying about changing the facial skull?
 Every person is special, therefore the body structure norms for an adult person are conditional. In childhood, the body is arranged differently, so parents are concerned about some features of the child. Convex child's forehead is a frequent reason for parents to see a doctor. Let's try to understand the reasons for the convex forehead and find out whether this is the norm or pathology.
Every person is special, therefore the body structure norms for an adult person are conditional. In childhood, the body is arranged differently, so parents are concerned about some features of the child. Convex child's forehead is a frequent reason for parents to see a doctor. Let's try to understand the reasons for the convex forehead and find out whether this is the norm or pathology.
What are the causes of the convex forehead
? At the time of the birth of the child, the size of the head is one of the defining factors of childbirth, since the head of the first passes through the birth canal. On its volume depends on how the birth will proceed. The head of the child in relation to the proportion of the body is larger than that of the adult, which sometimes can alarm his parents. Therefore, let us consider the most frequent causes of the convex forehead of a newborn.
Causes of convex forehead in a child:
- physiological feature;
- signs of rickets;
- hydrocephalus.
 Find out when there is an asymmetry in the lateral ventricles of the brain in adults.
Find out when there is an asymmetry in the lateral ventricles of the brain in adults.
Did you know that ventriculomegaly in a fetus is a pathological condition of the brain? Each person differs from each other in some ways. The size of the head and facial skull play one of the main roles. If the child visually enlarged forehead, head or other part of the skull, then the child should be shown to the doctor. Visual inspection, measurement of the size of the head, carrying out ultrasonic diagnostics will answer the question of whether this case is the norm. If pathology is not revealed during the study, then this feature should not be taken into account. With age, the bones of the skull will change, and everything will return to normal.
Rickets
Rickets is a common cause of the change in the facial part of the skull. This is a serious disease that occurs quite often among children under the age of three, due to the lack of vitamin D. Rickets are found in all countries of the world, but most of all in the northern regions where there is a lack of sunlight.
Vitamin D enters the body with food of the animal or is produced under the influence of ultraviolet. The main task of vitamin D is to regulate the absorption of calcium and phosphorus and to store these microelements in bone tissue.
In the first months of vitamin D deficiency, the symptoms of rickets are not specific and can pass the attention of parents. The baby appears:
- tearfulness;
- sleep disorders;
- excessive irritability;
- sweating;
- baldness of the occiput;
- indigestion.
If the deficit continues, then the following symptoms appear in a month:
- muscle hypotension;
- later teething;
- bone deformation;
- later closure of the fontanel.
Bone deformities are the main symptoms that are characteristic of rickets, and they remain for life, even if compensating for a deficiency of vitamin D.
Bone deformities:
- wheel-shaped or X-shaped changes in the lower limbs;
- changes in pelvic bones;In girls with age this will affect the course of childbirth;
- ribs thicken - rachitic "rosary";
- convex forehead: parietal and frontal tubercles grow;
- head resembles the shape of a square and becomes disproportionately large;
- thicken carpal joints - "bracelets".
These symptoms appear during the height of the disease and are associated with excessive osteogenesis. In adulthood, bone deformations remain and are manifested in the form of a disorder of posture, deformation of the lower limbs, narrowing of the pelvis.
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalic syndrome is the excessive production and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid( cerebrospinal fluid) in the ventricles of the brain. In children, the syndrome is manifested by an increase in the head and swelling of the fontanel. The main diseases that lead to hydrocephalus:
- intrauterine infection;
- congenital malformations of the brain;
- infectious diseases( meningitis, encephalitis);
- neoplasm of the brain.
Hydrocephalus has the following symptoms:
- decreased muscle tone;
- appearance of pathological reflexes;
- convulsive syndrome;
- strabismus or the "setting sun" syndrome;
- lethargy or, conversely, a child's anxiety.
The main manifestation of hydrocephalus is a disproportionate increase in the volume of the head and a circumference increase of 1 cm or more for each month.
Due to increased production of cerebrospinal fluid, the cerebral ventricles expand. The liquid penetrates into the circumferential space, causing damage to the brain tissue. As a result of increased intracranial pressure, there is a thinning of the bones of the skull, an expansion of the gap between the bones. The spring swells and pulsates, the scalp stretches, the veins of the head swell. The photo shows a convex forehead in the child as a consequence of rickets( hydrocephalus).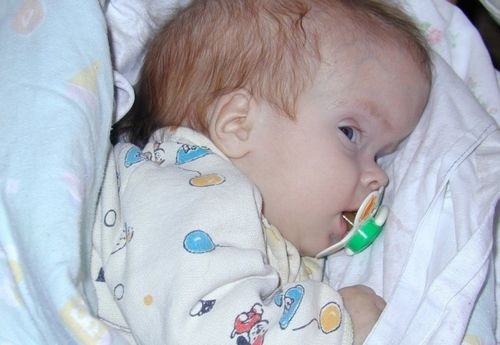
Convex eyes: causes of
Convex eyes in medical practice are called exophthalmos. This can be both a variant of the norm( anatomical feature) and a consequence of the disease. The main cause of bulging eyes is thyroid disease.
Basedova's disease is an autoimmune thyroid disorder that leads to increased production of hormones. An excess of thyroxin leads to the following symptoms:
- pulse acceleration over 90 beats per minute( sometimes over 120);
- weight loss;
- tremor of hands;
- insomnia, anxiety, headaches, changes in blood pressure;
- menstrual irregularities in women and spermatogenesis in men;
- increased eyes due to subcutaneous tissue.
Eye changes in thyrotoxicosis: become wide open, swollen, due to this convex. Over time, vision weakens due to edema of the optic nerve. The disease requires consultation and treatment from the endocrinologist.
 Read why there is microcephaly in a child, how is it manifested and what predictions for the baby and his parents?
Read why there is microcephaly in a child, how is it manifested and what predictions for the baby and his parents?
Do you know which hematomas on the head of newborns are dangerous, and which do not cause problems?
Find out why there is tremor in infants: the causes, manifestations, the connection with other pathologies.
Is it worth worrying about changing the facial skull?
You have examined the main causes of changes in the face in children: increased forehead and eyes. This may be either an individual characteristic, or an illness. And only the doctor, when examining and conducting the necessary examinations, will be able to deliver or remove the diagnosis. Therefore, any change in the shape or size of the head requires a doctor.
write the question in the form below: