Syndrome of intracranial pressure in a newborn
Contents:
- Causes of increased intracranial pressure
- How to determine intracranial pressure in infants
- Diagnosis
- Treatment
 In the cranium, the brain takes up to 86% of the volume, blood is 8.5%.At 7.5%, the subarachnoid space is filled with liquor produced in the ventricles from the blood plasma. Cerebrospinal fluid circulates through the spinal canal, filling the sub-pits. Then it penetrates into the veins and partially into the lymph, exits through the venous sinuses. Moving under pressure, the substance supplies the CNS with nutrition and oxygen.
In the cranium, the brain takes up to 86% of the volume, blood is 8.5%.At 7.5%, the subarachnoid space is filled with liquor produced in the ventricles from the blood plasma. Cerebrospinal fluid circulates through the spinal canal, filling the sub-pits. Then it penetrates into the veins and partially into the lymph, exits through the venous sinuses. Moving under pressure, the substance supplies the CNS with nutrition and oxygen.
With large accumulation( hypertension), insufficient outflow, the characteristic symptoms of intracranial pressure in infants develop. In case of a decrease in the number of cerebrospinal fluid( hypotension) - after trauma, taking diuretics, there is a reduction in ICP.
Pressure values are constantly fluctuating, but variability is not a sign of the disease. In a calm state, the indices are normal, but it costs the baby to scream, and the units rush upward. However, there are a number of typical signs indicating an existing pathology.
Causes of increased intracranial pressure
With increased intracranial pressure, in 90% of infants, hypertension-hydrocephalic syndrome is detected. The pathology arises because of:
- hypoxia;
- cerebral hemorrhage;
- g of the apoplectic meningitis;
- of arachnoiditis, encephalitis;
- tumors.
There are less frequent anomalies of cerebrospinal fluid. An increase in ICP without congenital disorders is a sign of perinatal encephalopathy, which develops in the pre-natal phase( before birth) and in the first month of life. The main factors provoking an anomaly during pregnancy and childbirth:
- infectious diseases in the mother;
- severe toxicosis;
- placental abruption;
- taking medication.
Important! Babies can be born healthy, but external factors lead to impairment of outflow( abscess, trauma, tremors, swelling).
How to determine intracranial pressure in infants
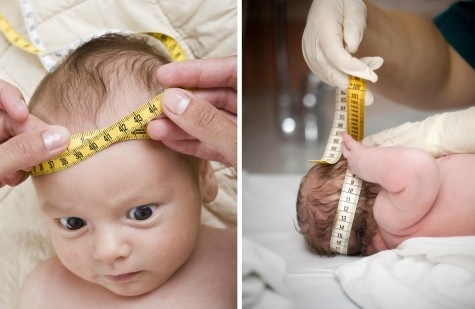
If a small swollen fontanel is visible in the baby, signaling a possible hydrocephalus, it's time to be alert. Hypertension occurs when there is insufficient absorption of the CSF, which leads to its accumulation. The substance presses on the ventricles of the brain, progressing in volume. At the kid for 1 month the circle increases on some centimeters. Anomaly is noticeable in the first postnatal week. Signs of intracranial pressure in the infant:
- the kid's eyes are lowered downwards, the sclera( Gref's symptoms) are visible, strabismus;
- the boundaries of the fontanel diverge;
- a venous mesh is visible;
- present anxiety, irritability, disturbed sleep;
- tremor, increased limb tone;
- a disproportionate head, an altered shape of the frontal part;
- frequent regurgitation;
- development delay.
Because the intracranial pressure in the infant is not enough for individual symptoms, complex studies are being conducted.
Diagnostics
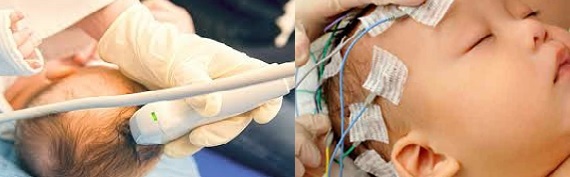 A pediatric neurologist determines reflex violations, directs to an ophthalmologist for examination of the fundus. With increased intracranial pressure, new veins are dilated in the newborn, there is a spasm of the arteries, edema of the optic nerve.
A pediatric neurologist determines reflex violations, directs to an ophthalmologist for examination of the fundus. With increased intracranial pressure, new veins are dilated in the newborn, there is a spasm of the arteries, edema of the optic nerve.
Neurosonography, ultrasound of the brain are carried out. Foci of lesion, hemorrhage are detected, the degree of ICP is determined. The most accurate method is the indications of axial, computed tomography. If symptoms of intracranial pressure in a newborn are difficult to detect, puncture is performed by inserting a needle into the spinal canal. Based on the testimony, the doctor confirms or ignores the preliminary diagnosis.
Treatment of
What should I do if my baby has intracranial pressure? With the appointment of adequate therapy, pathology can be cured. Not taken in time, the measures will lead to complications:
- severe headaches;
- to vegetative-vascular disorders;
- delayed mental and physical development;
- to psychomotor disorders.
The choice of treatment regimen depends on the cause of ICP.With hydrocephalus prescribe drugs that prevent the accumulation of liquor, contributing to the removal of excess fluid( Diakarb + preparations with potassium and magnesium), neuroprotectors. If there is no persistent dynamics, vascular drugs that enhance cerebral blood flow are prescribed.
Nootropics are prescribed for treatment of intracranial pressure in infants with perinatal encephalopathy. Massage, physical education, baths with soothing herbs help.
In case of severe hypertension-hydrocephalic syndrome, shunting is performed to correct the outflow. Quickly solve the problem allow minimally invasive endovideosurgical technologies. With the help of tubules from the holes in the abdominal cavity or in the atrium, excess fluid is excreted.
Neuroinfections are cured by complex schemes with an emphasis on antibiotic therapy. In all cases, the forecast is favorable. Attention to alarming symptoms, timely access to a doctor will save you from serious problems in the future.
write the question in the form below: