Hematomas on the head in newborns
Contents:
- Why do hematomas develop during labor?
- How does hematoma develop?
- Symptoms of
- Therapy
- Forecast
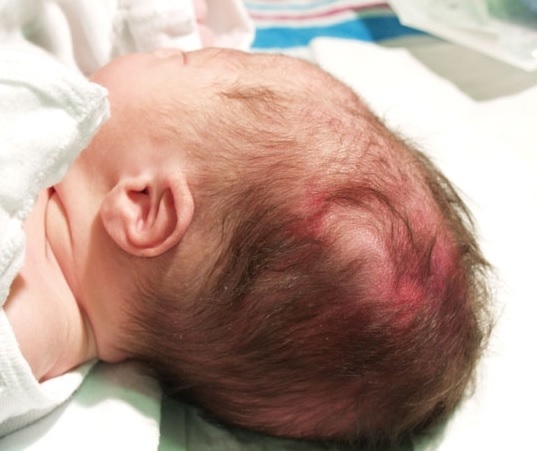 The child is a very fragile creature, however, in the process of its intrauterine development and birth, it is exposed to serious stresses. Not surprisingly, often the process of birth is accompanied by injuries and bruises. What hematomas on the head of newborns are dangerous, and which do not cause problems?
The child is a very fragile creature, however, in the process of its intrauterine development and birth, it is exposed to serious stresses. Not surprisingly, often the process of birth is accompanied by injuries and bruises. What hematomas on the head of newborns are dangerous, and which do not cause problems?
Why do hematomas develop during labor?
During pregnancy, most often the baby in the uterus is placed upside down, this is a normal physiological position that ensures the best course of labor.
When the baby starts to move outward, he traces the birth canal with his head. Even in the normal course of the process, it is squeezed by the tissues and bones of the pelvis, and on the crown or back of the baby a generic swelling is formed - swelling of the tissues. This is not a pathology, it passes by itself for a couple of days.
The risk of developing a hematoma on the head in a child after childbirth is increased if:
- The mother has a narrow pelvis.
- The fruit is too large.
- The baby is premature.
- The waters went away before the fights began.
- Birth first.
- Childbirth proceeds swiftly( for 1-1,5 hours).
- Prolonged delivery( more than a day).
- There is a pathology of the umbilical cord: a short, crook, bend.
How does the hematoma develop?
Risk factors have four types of effects on the head of the newborn:
- Mechanical - A strong contraction of the uterus during labor causes the baby's head to squeeze.
- The amniotic fluid protects the baby's head at birth, so early discharge of the head increases the risk of injury.
- In the uterus, the pressure differs from the atmospheric pressure. Their difference has a suction effect on body fluids, because of what they accumulate at the lowest point.
- In the pathology of the umbilical cord, the blood stagnates, because of which the risk of injury increases.
Any of them, and the more so combination, leads to the development of a hematoma on the head at birth.
Symptoms of
A generic swelling is an edema of the soft tissues of the head without clear outlines, located on the back of the head or the crown, that is, the lowest points of the head when passing through the birth canal. This is not a disease, it has no consequences, it dissolves itself.
Subaponeurotic hematoma is located between the muscle that covers the scalp and the skull bone. It often occurs when using a vacuum extractor during delivery. Damage looks like a patch of blood-soaked tissue with areas of voluminous blood accumulation. Small hemorrhages dissolve on their own within a week. Large are dangerous by the development of anemia, hypovolemic shock and infection of the area of trauma.
The area of periosteal stasis reflects damage to the periosteum of the skull, as a result of which its vessels dilate, burst, it becomes impregnated with blood. It looks like a bruise with clear boundaries.
If the effect on the head was stronger than normal, a cephalohematoma is formed - the accumulation of blood in the space between the skull bone and the periosteum. This is a much more serious problem requiring observation and timely treatment, since not only leads to frequent complications, but also is accompanied by a fracture of the skull bones.
It looks like an elastic tumor on the head, clearly delimited from the surrounding tissues. A few days later, a soft spot forms in the center, and borders, on the contrary, become denser.
The fact! The application of forceps to extract the fetus does not affect the development of the cephalohematoma.

In the vast majority of cases, it resolves itself on its own maximum in three weeks. In the case of an unfavorable course, the blood gradually replaces the connective and bone tissues - ossification of the hematoma occurs. If the body tries to "dissolve" unnecessary tissue, normal skull bones also suffer. In this case, a through hole is formed on the head in a remote period.
The extensive hematoma on the head of a baby has a negative effect on the entire body, worsening the course of the postpartum period. It causes prolonged jaundice and anemia in the newborn.
Therapy
There are no specific rules for the treatment of hematomas on the head in newborns, since the conventional classification of them has not yet been developed. Most often, her condition is observed for ten days. If during this time there are no positive changes, it is pumped out.
To this end, two needles are injected into the area of blood accumulation after local anesthesia. One removes the liquid, and the second maintains pressure, so that the cavity does not close before time. There are studies that indicate that hematomas need to be pumped out in any case, but so far it has not become widespread.
Forecast
Most often, the consequences of a hematoma formed during childbirth in a child does not remain on his head, since timely treatment, the body's own efforts do not leave room for them.
In the period closest to a trauma without adequate treatment, hematomas can get stuck, which is manifested by the child's high body temperature, he becomes restless, constantly crying, there is little to eat. If the infection spreads further through the vessels, meningitis or even sepsis may develop, which is very dangerous for the baby.
Extensive trauma leads to a deterioration in general condition, tearfulness, lethargy. Sometimes, in the absence of adequate drainage of the cephalohematoma in the distant period, through holes are formed in the bones of the skull.
write the question in the form below:



