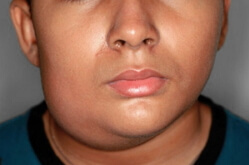
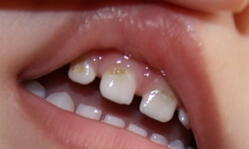
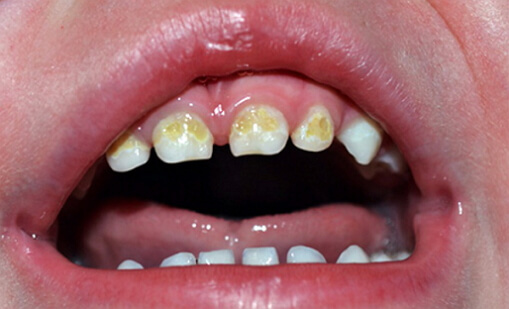
Cyst of lower jaw

The jaw cyst is a pathology, because of which a void forms in the jawbone, which in turn fills the fluid. The problem is complicated by the fact that this liquid formation can for a long time not manifest itself in any way and does not disturb, but at the same time increase. You can see the maxillary cyst only through an X-ray, but it is done when inflammatory pains already occur. The appearance of inflammation of the cyst is accompanied by redness, swelling and swelling of the gums. This is a rather dangerous problem, the jaw cyst leads to a number of complex diseases: osteomyelitis, periostitis, moreover, often the disease results in sinusitis or fistula, and sometimes even ends with a jaw fracture. In this case, this pathology affects both the lower and upper jaw. It can be cured only by an operative method.
Classification of
The jaw cyst can be of three types: keratokist( primordial), follicular and radicular.
Keratokist, it is also primordial - this cyst is formed in the lower jaw in the very corner, often occurs in the place where the so-called wisdom tooth should appear. This cyst can be single-chambered or multi-chambered, it contains the substance of cholesteatoma, the cyst itself has very thin fibrous walls with a thin epithelium. The problem is complicated by the fact that after removal, this cyst can be restored because of existing jaw tissue disorders.
The follicular jaw cyst - it forms and develops from the enamel of the teeth, which could not erupt, the cyst is located in the aveolar part of the jaw. This is the place where the upper and lower canines are located, the medical terminology calls them the second premolar and the third molar. The cyst is internally covered with multilayered flat epithelium, and in the follicular cyst, several unformed or even formed teeth can often be located.
Radical cyst is the most common cyst, it occurs in 80% of cases, as a rule, it is formed near the root. Near-root cyst, can be formed due to prolonged periodontitis, it can appear from complex granulomas in the area of any tooth. The upper cyst is much more common than the lower cyst, the diameter of such a cyst can be up to 2-3 cm, although the usual size is 2-9 mm. The walls of the cyst are thin-layered, fibrous, the surface is covered with multilayer epithelium and does not undergo keratinization in any way, they consist of plasma cells and lymphocytes. When the cyst is inflamed, the plasma cells are hyperlazed, expanded and directed into the wall, which leads to painful inflammatory processes. Given the location of the radicular cyst, it is able to penetrate with growth and inflammation in the maxillary sinuses, from which the chronic sinusitis develops.
Manifestations and symptoms of cyst
When the jaw cyst is only developing, right up to the first inflammation, there are no symptoms. But when the cyst is fully formed, hardly noticeable dense roundness appears, it does not hurt and the person does not suspect anything. If you scan the cyst on the x-ray, you will see the plane of the cyst in the form of a sphere and the root of the tooth, which is affected by peridonitis. In the case of the follicular cyst, the image clearly shows teeth that are not cut and contained in the cyst. Often there are purulent complications, for all the symptoms they look like an osteomelitis.
Methods of treatment
If timely cystectomy and cystostomy, you can do without surgery and autopsy. However, most often an autopsy is needed, mainly removal of suppuration and fluid is required, the cyst cavity needs to be completely cleaned.
These actions allow you to save the teeth located in the cyst area, as well as, if possible, restore those functions that were lost. Such a process as cystectomy allows not only to work with the cavity, but also to cut the root of the tooth, but this is done only when the root is in the cyst no more than a third of the length. If the tooth has gone deeper, then there is no sense in cutting, as well as treating it, for a long time it will not survive. This operation is quite painful, often afterwards infection, such teeth become very weak. The cavities that remain from the cyst create a problem for the jaw, the bone becomes less firm. But modern technologies are constantly developing new materials that can fill the cavities of the cyst, this makes it possible to block the cavity of the cyst in advance and prevent it from developing. Biological material is able not only to fill the cavity of the cyst, but also to restore the correct functionality of the teeth, and also strengthens the jawbone.