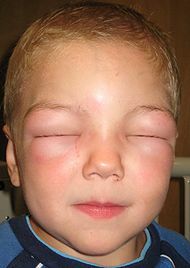
Atopic dermatitis in children
 Atopic dermatitis in children is a cutaneous, allergic disease that is caused by allergens, as well as toxins that affect the baby's skin. The disease is caused by a genetic predisposition to an excess of immunoglobulin E on contact with provoking allergens. Signs of atopic dermatitis in children include various allergic diseases. The term allergy is often used as a synonym for allergic diseases, and immunoglobulin E acts as a provocateur, but in some patients the level of immunoglobulin is normal and then the disease is caused by other factors. Atopic dermatitis is considered to be the most common of all vidovallergic diseases and is often called childhood eczema.
Atopic dermatitis in children is a cutaneous, allergic disease that is caused by allergens, as well as toxins that affect the baby's skin. The disease is caused by a genetic predisposition to an excess of immunoglobulin E on contact with provoking allergens. Signs of atopic dermatitis in children include various allergic diseases. The term allergy is often used as a synonym for allergic diseases, and immunoglobulin E acts as a provocateur, but in some patients the level of immunoglobulin is normal and then the disease is caused by other factors. Atopic dermatitis is considered to be the most common of all vidovallergic diseases and is often called childhood eczema.
Atopic dermatitis in infants
The onset of the disease occurs in the first six months of infants and quite often continues throughout adulthood. Most often this disease affects children under the age of 1, usually in families with hereditary cases of allergic diseases. The incidence of atopic dermatitis in infants is 10 cases per 1000 people. Often this disease is associated with such allergic diseases as allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma.
Atopic dermatitis in the baby can be caused not only by artificial feeding, but also by mother's milk, and the complexity of treatment is the possible joining of allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma( occurs in the absence of timely adequate qualified care) and other diseases of an allergic nature.
Usually the basis of atopic dermatitis in infants is their hereditary predisposition to the development of allergic reactions. Allergenic foods, constipation, drying out of the skin, excessive sweating, contact of the skin with certain chemicals( household chemicals, washing powders, etc.), direct contact with household allergens and synthetic fibers are the factors that trigger the onset of the disease.
Allergens that enter the body of the baby, act as a trigger mechanism in the development of atopic dermatitis. Medical research has shown that often the disease provokes an allergy to cow milk protein, but the reaction to egg, soybean, cereal and fish protein causes an allergy to a lesser degree, but a mixed allergic reaction is also possible.
The following causes of development in atopic dermatitis for infants are unbalanced nutrition of the mother during pregnancy, as well as complications caused by pregnancy. Under the risk factor fall and those children whose parents often overfeed their kids and they sort out weight.
An important role in the onset of atopic dermatitis is attributed to the state of the digestive tract in infants, since diseases such as intestinal dysbacteriosis, enterocolitis, helminthic invasions and gastritis contribute to an allergic disease.
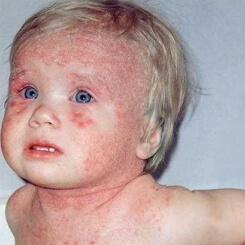
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis in the baby are rough cheeks, red buttocks, neuro-psychic manifestations, the tendency of all skin to dryness, the appearance of diaper rash, the scaling of the eyebrows, and the scalp. At the initial stage of the disease only the surface layers of the skin are affected, which are easily treatable. However, in the absence of timely treatment, atopic dermatitis in infants progresses, acquiring a protracted course with the defeat of new skin areas. The disease is aggravated by new symptoms: vesicles, ulcers, debilitating itching, redness of the skin extending to the limbs and trunk, attachment of bacterial flora, and also psychoneurological disorders.
How to cure an allergy? Treatment of atopic dermatitis in infants is often delayed because it is not an easy process. Methods of treatment are medicamentous and non-medicamentous. Consider non-drug, associated with improper eating of young mummy and aimed at eliminating the food allergen. Treatment includes a review, together with a doctor, of a diet during lactation and the removal of chronic constipation after childbirth in a woman. For the normalization of regular stools, women are advised to use drugs with lactulose, glycerin suppositories, observe a sufficient drinking regimen, enrich the diet with sour-milk products and fiber.
Diet for allergies on the artificial feeding of the baby includes soya mixes( Frisosa, Bona-soya, Soy-Soybeans), and cow's milk production is excluded, since the allergy to cow protein is the cause of the disease. If the condition does not change and the mixture remains allergic, mix the hydrolysers of cow's milk proteins( Alfare Nutramigen).In the event that the disease occurred at the time of introduction of complementary foods, it is likely that the allergens were in them, so by elimination( cereals, eggs, chicken, fish, etc.), we eliminate the cause of the allergenic reaction. We pay great attention to balanced nutrition, abundant drinking, prevention of constipation. We exclude from a food at an allergy carbohydrates, being in sweets. Pay attention to the environment of the stay of the baby: cool air, humidity 50%, in no case we are wrapping up the child, we maintain cleanliness in the room, we remove soft toys, animals, carpets, furniture with upholstery, washing with hot water all toys. All the laundry is washed with hypoallergenic agents and then rinsed well, but my dishes without detergents. Baby clothes should contain only natural fabrics( linen, cotton).Contact of smoking relatives should be minimized with the child.
Care of a child during an exacerbation of atopic dermatitis should be extremely attentive and include: daily bathing in the settled water, using herbs of nettle, yarrow, burdock root, birch buds. Use of neutral shampoos and soaps is permissible not more than 2 times a week. Each bath completes a gentle soaking in the towel and moistening with hypoallergenic agents. Well established itself lotion Excipial M, which includes urea. During the day, problem areas of the skin should not come into contact with water, and if necessary, use wet hypoallergenic wipes.
Medical treatment of atopic dermatitis in infants includes the use of ointments and creams from allergies, including steroids, hormones of the adrenal cortex, as well as drugs that restore the anti-inflammatory protective barrier of the skin( Exipial M).This lotion is prescribed to children in the second half of life. Excipial M effectively fights with atopic dermatitis in infants and does not allow the disease to develop further. Lotion is applied up to three times a day, and if necessary more often( and after water procedures).The severe course of atopic dermatitis in infants implies, in addition to the use of steroids and lotion, Exipion M, calcium preparations, antihistamines, antibacterial drugs, immunomodulators, antigen-specific therapy. For the removal of neuro-psychic processes, long walks, full night and day rest, positive microclimate in the family, medical therapy and physiotherapy procedures are necessary.
Atopic dermatitis in children - causes of
The causes of atopic dermatitis in children include hereditary factors, food allergens, exposure to chemicals, infections, extreme temperatures, stress, humidity. More than 10% of all atopic dermatitis in children occurs on food allergens of products such as eggs, cow's milk, peanuts, and also an allergic reaction can be caused by a tick of house dust, pollen, spores of mold fungi. Atopic dermatitis in children is aggravated in the summer, during a period of nervous tension and high humidity. Irritation acts as a secondary cause of atopic dermatitis, causing a change in the structure of the skin.
80% of cases are caused by a family history on the mother's side or on both sides of the parents. During the very first years of a baby's life, atopic dermatitis is manifested due to the presence of a food allergy. The most common cause are eggs, cow's milk proteins, cereals, fish and soy. The advantages of breastfeeding are known, but it is necessary to observe a hypoallergenic diet of a nursing mother. A special role is assigned to staphylococcus during atopic dermatitis in children, which is sown from 90% of the affected skin.
Atopic dermatitis in children - symptoms of
The following phases of atopic dermatitis in children: infant, child, adolescent and adult.
Infant form lasts up to two years and manifests itself on the face, extensor surfaces of the limbs, extends to the trunk. The disease is characterized by dry skin and the formation of crusts. Exacerbation of the disease occurs at the time of introduction of complementary foods and teething.
The pediatric form lasts from 2 to 12 years and is manifested in the form of skin eruptions on the folding surfaces, including the elbow and popliteal fossa of the extremities, the neck. This form is characterized by hyperemia, lichenification, papules, erosion, cracks, plaques, scratching, crusting and swelling of the skin. Disturb crack on the hands, as well as soles. There is hyperpigmentation of the eyelids, which is intensified due to scratching, and characteristic folds appear under the lower eyelid.
For the adult form, as for the adolescent, the alternation of the rash period with the period of their absence is characteristic. During the rash, the area of the face, neck, décolleté, wrists, hands and elbow fissures increases. For adult atopic dermatitis is characterized by a strong eruption of flexor surfaces, neck, face, hands, fingers and feet.
But for any phase of atopic dermatitis, dry skin, lichenification, itching, hyperemia, peeling, and rashes are characteristic.
Atopic dermatitis in children is expressed in a vicious circle, which starts with itching, followed by scratching, then rashes and itching. By external signs, allergic dermatitis is characterized by the nature of the rash. An allergic rash appears on the legs, on the arms, neck, underarms and in those places where there is moisture. The rash is often accompanied by itching, especially at night when the baby sweats. Rashes in atopic dermatitis in children for a very long time do not go away, even if the hypoallergenic diet is observed, and leave dark spots on the body.
Atopic dermatitis in children gradually disappears with age, which is caused by the maturation of liver cells. The degree of development of atopic dermatitis in children depends on the factor of bronchial asthma.
Atopic dermatitis in children - treatment of
How to treat and what does the prevention of sweating include?
First of all, do not allow sweats, diaper rash of the child. To do this, often change diapers, wet clothes, maintain the necessary humidity and temperature conditions to 21 degrees, remove the oilcloth from under the sheet, we do bathing in a solution of potassium permanganate or in the infusion of a string. Places affected by a rash, lubricated with baby cream, can be sterilized vegetable oil.
The early stage of atopic dermatitis in children is treated with an exception to the nutrition of those products that are capable of causing allergies. It is important for the mother to revise her diet if she is breastfeeding. Manifestations of the rash effectively lubricate the infusion of string or infusion of bay leaves, and large pimples to process green.
Atopic dermatitis in children is often a chronic disease and requires long-term treatment. Effective in the treatment of an integrated approach: diet compliance, the elimination of food allergens, the removal of inflammation of the skin and itching, the prevention of dryness, the use of preventive measures for the emergence of secondary infection. The leading doctor in the treatment of atopic dermatitis is the dermatologist with an allergist. Enterosgel, smecta, sorbogel are sorbents that will help in the fight against the absorption of toxins from the intestine.
Atopic dermatitis in children - diet
The treatment of the disease can be easily calculated from the causes of atopic dermatitis. For example, rashes provoked cherries, therefore, exclude from the diet this berry. And so much for the whole food. Exclude from the menu atopic dermatitis all red foods( vegetables, berries, juices, fruits), citrus fruits, greens, cereals, semolina, seafood. The diet should be fully observed by the mother while breastfeeding. Diet with atopic dermatitis consists of the mandatory exclusion of eggs, cow's milk, preservatives, fried foods, emulsifiers, smoked foods, sauces, food additives, chocolate, carbonated drinks, honey, cocoa. It is mandatory to limit the use of salt.
As soon as the food allergen is removed from the diet, the improvement of the child's condition immediately becomes noticeable.
Recommended food products: boiled beef is allowed;Vegetable, cereal, vegetarian soups;Olive oil and sunflower oil;boiled potatoes;Porridge( buckwheat, rice, oats);Lactic acid products;Cucumbers, parsley, dill, apples, tea, sugar;With bran or whole wheat bread;Apple compote, bio-yoghurt without additives, cottage cheese, yogurt.
Menu of a child with atopic dermatitis
Breakfast: buckwheat porridge with a small amount of oil 150 grams, whole grain bread 80 grams, tea with sugar
Lunch: vegetable soup( potatoes, cabbage, onions, tablespoon vegetable oil, beef 50 grams), bread with bran 200 grams, compote of apples
Snack: bio-yogurt without additives 200 grams
Dinner: oatmeal in vegetable oil 250 grams, Puree from varieties of green apples with sugar 200 grams.
. Adhere to such rules: do not overfeed a child, let him eat slowly and not in large portions.