Operative treatment of ovarian cysts
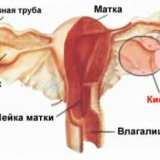
One of the most common gynecological diseases is the ovarian cyst. Ovarian cyst is a benign neoplasm and belongs to the category of tumors. Cyst is a cavity filled with liquid. Previously, according to medical statistics, this disease occurred mainly in women after fifty years of age, but now it has significantly grown younger and appears even in the nulliparous category of women.
Ovarian cysts come in different types, such as:
- cyst of the yellow ovary body;
- follicular;
- dermoid;
- paraovarian;
- endometrioid;
- is mucinous.
Each of the above cysts has its own etiology, symptoms and causes. The most common causes of this tumor on the ovaries include: early onset of the menstrual cycle, abnormalities in follicle maturation, disruption of the endocrine system, multiple abortions, and much more. Diagnosis is very important when diagnosing an ovarian cyst. First of all, it is an examination of the gynecologist and finding out the presence of symptoms of the disease. Further, ultrasound is performed and preferably intravaginal, which will show the real results of the examination. Sometimes a procedure is performed to puncture the posterior vaginal vault, which will help determine whether blood or fluid is contained in the abdominal cavity. But the most successful as a method of diagnosis, and the method of surgical treatment of ovarian cysts is laparoscopy. Along the way, a blood test is carried out by means of oncomarkers, which will show the level of malignancy of this tumor. Also use the procedure CT( computer tomography) and MRI( magnetic resonance imaging), which will help to determine the size of education, location, contouring, will show the contents of the cyst and much more.
So, what kind of surgical treatment of ovarian cysts? Of course, the treatment of the ovarian cyst depends on a large number of factors, it can be a certain severity of the symptoms, the risk that a process of degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant, age qualification, and the preservation of reproductive function may occur. Of course, it is better when treatment of ovarian cysts will be limited only to conservative treatment, but this can only be said and advised by a gynecologist who conducted all necessary examinations and made an accurate diagnosis. Unfortunately, conservative therapy is possible only in those cases when there are no complications in the functionality of the ovaries such as suppuration, rupture of capsules and the like.
Operative treatment is fundamental in the treatment of ovarian tumors. Before the beginning, which necessarily carries out a histological study to clarify the nature of the tumor( if there is no malignancy).To date, the most progressive and successful method is laparoscopy. It consists in producing two small incisions in the abdominal cavity afterwards, into which air is injected. And directly into one of the notches, a laparoscope( a thin tube with a lens at the end) is inserted, and in another cut a so-called manipulator is inserted, through which the doctor will be able to carefully inspect the organs. In this case, the laparoscope is used as a diagnostic method to establish an accurate diagnosis. However, surgical treatment of the cyst can be performed by means of laparoscopic removal of the ovarian cyst. For carrying out this kind of operation, careful differential diagnostics, as well as mandatory dynamic ultrasound with Doppler function, is very important. It is also necessary to use additional studies, such as hormone tests, biochemical analyzes and oncomarker readings.
Operative laparoscopic intervention lasts for twenty to forty minutes. For this operation, the day is selected when the woman does not have menstruation and preoperative preparation is mandatory. The so-called "hospital complex" of preoperative preparation includes:
- blood test - clinical;
- establishment of blood type and Rh factor;
- analysis for coagulation;
- ultrasound;
- electrocardiogram;
- all gynecological smears;
- inspection and anesthesia consultation.
The essence of the operation is that a hole is made in the abdominal cavity of 5 mm in size, into which the instruments are inserted. And in the monitor located in the operating room is transferred the image of the whole process of the operation. Laparoscopy of ovarian cysts is done both under general and under local anesthesia. This type of operation allows not only to carry out the necessary diagnostics, but also to avoid cancer in patients.
Laparoscopic ovarian cyst removal operations are divided into:
- cyst removal operation with mandatory preservation of healthy ovarian tissue called a cystectomy;
- oophorectomy with adnexectomy, that is, the process of removing the ovary or uterine appendages;
After laparoscopic intervention, only two or three scars remain on the patient's body for a length of not more than one and a half centimeters, which eventually heal successfully. After the operation, as a normal phenomenon, there are small pains in the lower abdomen, which are blocked by taking painkillers or injections. A few hours after the operation, the patient can already get up and walk. The extract is usually held for 3-4 days. In the district polyclinic, the treatment of sutures and the use of strengthening and antibacterial therapy are prescribed.
Laparoscopic treatment is a great and effective chance for our women to avoid terrible malignant diseases. Therefore, it is always necessary to remember to women that if any pain or other symptoms occur, you should immediately seek medical advice from a gynecologist.


