Puncture of the breast
Nowadays, gland punctures or biopsies are used to diagnose the mammary gland, such as aspiration fine-needle, incisional, excision, stereotaxic and thick-needle. Puncture specialists recommend when finding nodules in the chest, seals and other neoplasms. When visual changes reveal changes in the structure of the skin, ulcers, discharge from the breast of a yellow, transparent or bloody color, this type of diagnosis is mandatory, because there is a possibility of cancer.
Positive actions of puncture of the mammary gland
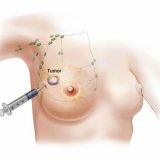
To determine the nature of tumor formation, a procedure is performed to puncture( biopsy) the mammary glands. To identify a malignant tumor or benign. In the case of breast cancer symptoms, only after a biopsy a final diagnosis is made. Puncture of the gland is performed surgically or with a needle. Methods of needle puncture( non-operative methods) have less stress on the patient and are associated with the least risk of complications. But, non-surgical methods of puncture of the breast can not always give a complete reliable answer. For the puncture of non-palpable tumors, glands are used with a stereotactic biopsy or ultrasound. Most often( 80% of cases) the results of a puncture of the mammary gland reject malignant processes.
Fine needle aspiration puncture of this gland
This method of research is used to perform puncture of palpable( which are probed) breast tumors. When performing breast biopsy, the patient is in a sitting position. On the skin of the breast, specialists mark the place of puncture. The mammary gland is treated with an antiseptic. After that, enter into the thickness of the mammary gland a thin long needle on the syringe. Then the plunger of the syringe is drawn several times. Such a technique in the needle and syringe, as a rule, absorbs a small amount of glandular tissue. If a biopsy of the cyst is being performed, the liquid that was in it is sucked into the syringe. After pumping out the entire fluid cysts, the painful sensations that she caused the patients completely disappear.
Conduction of incisional puncture of the breast
An incisional biopsy consists in the excision of a small piece of tumor tissue. But this method of puncture is more like surgical intervention. An incisional breast biopsy is performed under local anesthesia. Very often such a method of puncture is performed when the results of an aspiration biopsy are not reliable enough. Also incisional and aspiration punctures can sometimes give false results, but their advantage can be called their speed.
Excisional puncture of the gland
A mini operation is performed during excision biopsy of the mammary glands, during which the specialist part or the entire tumor. Such a procedure can not be considered therapeutic in any way, because in the case of detection of cancer cells, in addition to the tumor itself, removal of lymph nodes is required, even more extensive intervention may be required. When performing an excision puncture, the tumor formation is less than 2.5, then the excision of the entire tumor is performed by specialists, and only a part of the tumor is removed if the tumor size is large.
Stereotaxic fine needle puncture
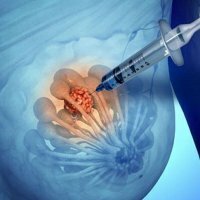
This method of puncture the breast is as follows. From several places of the tumor, several samples of tissue are taken with the help of a needle. If the tumor is located deep in the tissues of the breast and can not be probed, ultrasound or mammography is used to perform the puncture. The patient lies on a special table on her back. After a few pictures of mammography or ultrasound at different angles are taken to form a three-dimensional image and determine the exact location of the fine needle.
Thick-needle biopsy of the mammary gland
Thick-needle puncture of the gland makes it possible to obtain a portion of the breast tissue somewhat larger in size. To conduct this biopsy, use a thick needle equipped with a cutting device. The advantage of this method of breast biopsy is that a larger area of the tissue in terms of the size for histological examination can more reliably determine the exact diagnosis.