Breast biopsy
Mammary glands.
The thoracic gland consists of a special glandular tissue and includes from fifteen to twenty parts, which in turn consist of lobules. The composition of the lobules includes cells that produce milk.
The lobes of the breast extend from the nipples along the radii.
The mammary gland is covered with a very delicate and thin skin. Under the skin are hidden fat and connective capsules, giving the breast form. In the mammary gland there is no muscle tissue.
The so-called mammary ducts connect the nipples and different groups of lobes. A total of fifteen or twenty canals come to the nipple.
Cooper ligaments( formed by connective tissue septum separating the lobules) fix the mammary glands on the chest.
Mammary glands play an important role in the process of childbearing, therefore they are strongly influenced by sex hormones progesterone and estrogen. In their production, mainly the ovaries participate.
Biopsy.
Biopsy is a laboratory study under a microscope of samples of tissue or fluid taken from the breast. The method is based on the difference in mammary gland cells in various types of tumors.
Breast biopsy facilitates the establishment of a correct diagnosis or its clarification, detection of malignant formation at an early stage, recognition of a tumor, inflammatory or hormonal process. Repeated biopsy helps control the effectiveness of treatment.
Biopsy is indicated in the diagnosis of inflammatory processes in the mammary gland, suspected of having a tumor, mastopathy.
Types of biopsy.
To determine the nature of the tumor process - benign or malignant - incision, aspiration and puncture biopsy types are used.
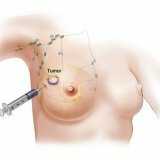
Puncture biopsy is done on an outpatient basis without anesthesia. In the mammary gland in the place of the neoplasm the surgeon inserts a syringe and sucks out a small amount of tissue. After the procedure, a bruise may remain on the skin.
The sample is stained with a special dye and subjected to microscopic examination. Histological examination of tissues is the most accurate method of diagnosing cancer. The error here is excluded, because the tissue of the malignant tumor has a very peculiar structure. However, in the case when a cancer tumor after breast biopsy is not established, the diagnosis "oncology" can not be completely ruled out, since the tissue sample could be taken from an unaffected node. In case of doubt, it is recommended to remove the node operatively and to examine the surgical material.
The procedure for aspiration biopsy is the intake of fluid from the cyst with a special syringe with a thin needle. This requires a high accuracy of the material. Aspiration is usually repeated three to four times, each time pulling the plunger of the syringe to failure, removing the syringe from the needle and releasing air from it.
Taken sample is examined under a microscope for the purpose of detecting malignant cells.
If the malignant character of the tumor can not be excluded, an incisional biopsy is performed. The procedure requires anesthesia. A surgical oncologist performs the removal of a suspicious neoplasm. If the patient is in advanced age, incisional biopsy can be prescribed without a preliminary aspiration biopsy, since at an older age, benign tumors are a rarity.
Presence of a tumor.
Sometimes a woman is very worried about the presence of a tumor, although all studies deny cancer. To normalize the mental state of the patient, the doctor can prescribe an operation. Most often, however, the state of the node is simply observed.
The tissue of the remote node is sent to a laboratory study. If the results of the analysis are obtained immediately, the tissue sample is subjected to a quick freeze and sent to the laboratory while the patient is still on the operating table.
You should never abandon your biopsy, which is the right way to diagnose cancer at the very beginning of a tumor.