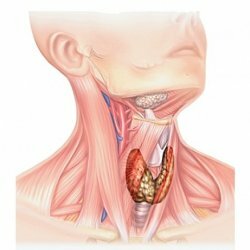
Thyroid cancer is not a death sentence
 One of the most unpleasant and exciting moments of a person's life is the day when your doctor, sometimes quite straight or hints, tells you that the facts at his disposal indicate that you have a malignant education.
One of the most unpleasant and exciting moments of a person's life is the day when your doctor, sometimes quite straight or hints, tells you that the facts at his disposal indicate that you have a malignant education.
Remember, first of all, that the information you have been told is not your death sentence, but merely a signal that further treatment should include surgical intervention, which must be performed in the near future.
As for the results of treatment, for the vast majority of patients( more than 95%) a timely operation means a complete cure and a fairly good quality of life over the next decades.
Some scientific information about thyroid cancer
Thyroid cancer is a widespread disease in the world. Groups of cancer cells are found in about 6% of all people. However, in the overwhelming majority, it remains in a latent( latent) form, without causing clinical manifestations, and is a finding of the pathologist. However, even if the cancerous tumor begins to progress, then in the vast majority of cases this process is slow, so it is called "lazy" cancer. In general, as one of the authors with a peculiar sense of humor wrote, "If you had the opportunity to choose the form of cancer, you should choose this one."
What causes the appearance of cancer cells in the gland or the transition of it from the inactive latent form to the active is still not known. Precisely established provoking effect of penetrating radiation, especially external irradiation on the gland region. There is information about the unfavorable effect of radioactive substances trapped inside the body, which took place in children after the Chernobyl accident. However, our data on a survey of the population of the Leningrad Region in the zone of radionuclide deposition 10 years after the Chernobyl accident did not confirm an increase in the incidence of thyroid cancer in the population living there.
There are several types of thyroid cancer that differ in the characteristics of cells and tumor growth rates, treatment options and prognosis.
This division is based on the degree of differentiation of cancer cells.
The highest degree of differentiation has papillary carcinoma, this type of cancer accounts for more than 70% of all thyroid tumors. Fortunately, this form of cancer is the least aggressive.
Here are its main characteristics:
- is rarely observed spreading beyond the neck;
- is most often diagnosed at the age of 30 to 50 years;
- in women occurs three times more often;
- occurrence is often associated with exposure to penetrating radiation;
- accumulates radioactive iodine;
- is more aggressive in old age;
- in young people proceeds more favorably and rarely leads to death.
Follicular cancer also belongs to differentiated tumors. It is somewhat more aggressive than the papillary, but nevertheless has a relatively favorable current. Its main features resemble papillary:
- is more often detected at the age of 40-60 years;
- is three times more common in women than in men;
- absorbs radioactive iodine;
- gives germination to the blood vessels and can spread along the bloodstream;
- is more aggressive in the elderly.
Sometimes a tumor can have a mixed follicular-papillary structure. The cure rate for these forms of cancer is close to 100%.
In the thyroid gland there are so-called "C" cells that produce not thyroid hormones, but a hormone calcitonin involved in the regulation of calcium levels. Malignant tumors can arise from these cells - medullary cancer, which accounts for about 5% of all cancers of the thyroid gland. The main features of medullary cancer are the following:
- is more common in women than in men;
- occurrence is not associated with exposure to radiation;
- produces calcitonin;
- is more aggressive than papillary and follicular cancers, metastases to the lymph nodes of the neck, bones, liver;
- has a tendency to spread within individual families. Therefore, if the cancer is detected in one of the family members, it is necessary to examine the level of calcitonin in the remaining blood relatives. If someone's hormone level is elevated, he should remove the thyroid gland, because even if there is no malignant tumor at that moment, it will necessarily appear in the future;
- if the level of calcitonin in family members is normal, it is advisable nevertheless to perform a special genetic testing to determine those who have a genetic predisposition for the emergence of medullary cancer;
- after the removal of the thyroid gland requires periodic examination of calcitonin for the timely detection of recurrence of the disease.
More than half of patients who underwent surgery for thyroid cancer live more than ten years.
Less than 2% of all thyroid cancers are low-grade tumors that do not produce hormones and do not absorb radioactive iodine. This is an extremely aggressive form of cancer, all of whose treatment methods to date have been unsuccessful.
Diagnosis of thyroid cancer
Unfortunately, the clinical signs that indicate the malignancy of the thyroid tumor appear too late. This usually occurs when the tumor extends beyond the gland and grows into the nearby structures of the neck. Then the patients have breathing and swallowing disorders, and with the involvement of the laryngeal nerves, the voice changes. Often the first sign that makes one suspect a malignant character of the tumor is the appearance of metastases in the lymph nodes of the neck.
Instrumental methods such as ultrasound, computed tomography, as well as radioisotope study and thermography of the thyroid gland, reveal only indirect signs that indicate the possibility of a malignant tumor.
The main diagnostic method is a morphological study of tumor cells that are currently being obtained by performing fine needle aspiration biopsy under ultrasound guidance. This method allows you to establish the correct diagnosis in 95-96% of cases. But even among the remaining 4-5%, the overwhelming majority is the so-called "false positive" results, when the cytologist can not completely reject the presence of a malignant tumor during the study. The patient is offered surgery, after which the study and the remote drug are reported that the tumor was benign."False negative" results, when an experienced cytologist does not recognize the malignant nature of the tumor, are extremely rare. So, on more than 5 thousand biopsies performed in our blade, thyroid cancer was not recognized in only four cases. Therefore, at the present time all over the world TAB is performed for all patients who have a node larger than 1-1.5 cm in the thyroid gland.
Thyroid cancer treatment
The only method of treatment for thyroid cancer is a surgical operation. The volume of surgical intervention depends on the form and stage of the tumor process and can fluctuate from the removal of one lobe( with small highly differentiated cancers) to complete removal of the thyroid gland together with the regional lymph nodes of the neck and with the widespread tumor process - other nearby structures.
Unfortunately, in these cases the parathyroid glands involved in the tumor process can be damaged, which will lead to hypoparathyroidism and require further special treatment. Trauma to the laryngeal nerves can lead to a complete or partial loss of voice or a change in its timbre, but this has to be tolerated, since the surgeon must fulfill his main task - to ensure the radicalism of the performed surgical intervention to save the patient's life.
After surgery, the patient is prescribed thyrotropic hormone replacement therapy, which will not only replace the lost function of the gland, but also reduce the production of TSH as much as possible, which, according to available data, promotes the growth of tumor cells. Therefore, doses of hormones should provide a level of TSH at the lower values of the normal level.
If all of the gland is removed and the cancer has been differentiated, thyroglobulin levels should be regularly determined and, if it is increased, hormones should be abolished, and after four weeks a whole body is radioisotope scanned to find the remaining tumor cells that will capture radioactive iodine. If such cells are detected, then the patient is assigned radioactive iodine before the complete cure.
Be Healthy!