Methods of treatment of a brain tumor
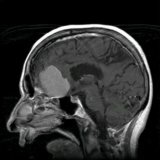
Primary tumors.
Primary are tumors that are formed directly in the brain tissues, and do not migrate from other tissues and organs.
The peculiarity of benign tumors is that they can not spread further than the area of the brain in which they originated, thus they do not spread to other organs and tissues and do not violate their functions. Benign tumors are characterized by slow growth, and their clinical manifestation depends on the site of localization. Characteristic symptoms are: severe headaches, seizures of epilepsy, impaired vision and hearing. Cases of asymptomatic disease are described, and the detection of such neoplasms is an accidental event in the procedure of MRI or examination of the fundus. For well-equipped neurosurgical clinics, the diagnosis and treatment of benign tumors is not very difficult. At the heart of the treatment is the surgical removal of the neoplasm, except when the tumor is located in a hard-to-reach place or next to the vital structures of the brain. In this case, there is a risk of damage to these areas at the time of surgery, which will lead to severe psychoneurological consequences. In addition, radiation therapy or repeated resection is used in the case of a tumor resuming its growth after its removal.
Malignant tumors are a group of cancer cells that have the ability to spread into healthy, unconverted brain tissue. They disrupt the function of normal brain cells, reincarnating them into cancerous cells. The ability of brain cancer cells to metastasize to other organs and tissues is extremely rare, however, it is possible. Malignant tumors are characterized by rapid growth and penetration into vital areas of the brain, which is why they are detected when surgical intervention is ruled out.
Secondary tumors.
Secondary tumors of the brain are those tumors that are caused by the penetration of cancer cells from other organs and tissues into the brain.
Symptoms.
The clinical manifestation of such tumors depends on the site of localization, size and type. Especially obvious manifestations arise when the tumor damages nerves and brain tissue. In addition, the appearance of a secondary tumor can lead to disruption in the distribution of intracranial fluid and cerebral blood flow, which will inevitably lead to high intracranial pressure. The most frequent symptoms include nausea, vomiting, severe headaches, sudden mood swings, seizures, lack of attention and memory impairment, as well as changes in normal coordination of movements, numbness of limbs, convulsions, hearing, speech and vision impairment. The presence of such symptoms should be the reason for undergoing a thorough examination for a secondary brain tumor, although they are not unique to the disease by themselves.
Classification.
The following are the main types of brain tumors:
Gliomas are a neoplasm consisting of glial cells of the brain. There are several stages of glioma. In this case, if the first stage is represented by slowly growing benign tumors, then at the fourth stage glioma develops rapidly, degenerating into a malignant tumor. A variety of gliomas are ependymoma, oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, mixed glioma, etc.
It should be noted such gliomas as medulloblastomas. These are primary neuroectodermal tumors related to malignant formations. The disease is particularly affected by children.
Lymphoma of the central nervous system is a cancer of the lymphatic system. Rarely affects only the brain, quickly spreads throughout the entire body's lymphatic system.
Tumors of the pituitary( pineal body): germinoma, pineoblastoma, pineocytoma, teratoma. Types of human brain tumors are meningiomas, which are predominantly related to benign neoplasms;Schwannoma or neurinoma of the auditory nerve( also benign tumors);Hemangioblastoma,( benign degeneration of the blood vessels of the brain), pituitary adenoma.
Treatment of a brain tumor.
Methods of treatment of a brain tumor include: surgery, radiation and radiotherapy, chemotherapy. Surgical intervention is most effective when the tumor can be excised without damaging the healthy tissues surrounding the tumor. In such cases as glioma of the 1st stage, there is often no need for surgical intervention. Such a tumor can be cured by several sessions of chemotherapy.