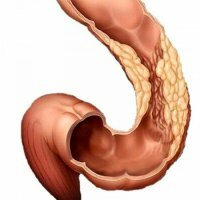
Loss of hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are a chronic, progressively progressive disease characterized by thrombosis, inflammation and varicose enlargement of the hemorrhoidal veins with the formation of nodes in the rectal area.One of the most common complications in this pathology is the prolapse of the hemorrhoidal nodes, i.e. their outflow from the anal canal.
Note: , according to the medical statistics, affects up to 20% of the adult population from hemorrhoids.Pathological changes in the veins of the rectum are diagnosed in almost 80% of women giving birth;Repeated childbirth repeatedly increases the likelihood of relapse.
Table of contents: Causes of prolapsed sites Clinical manifestations Diagnosis Treatment and preventionCauses of prolapse
Factors leading to progression of hemorrhoids and complications:
- Pregnancy and childbirth( especially repeated or related to trauma);
- physical inactivity( insufficient physical activity);
- excessive physical activity( in particular - lifting weights);
- sedentary work;
- improper power supply;
- alcohol abuse( domestic drinking and alcoholism);
- overweight and obesity;
- chronic constipation;
- regularly occurs diarrhea;
- old age.
Important: persons with hereditary( genetic) predisposition belong to the risk group.
Immediate causes of proliferation and prolapse of nodes are stagnation of blood, dystrophic changes in connective and muscular tissue, weakness( and stretching) of the venous walls.
As the growth grows, the internal nodes begin to move lower to the anus.The walls of the cavernous sinuses become thinner;In most cases they become inflamed and begin to bleed.Since the dystrophic changes extend not only to the mucous membrane, but also to the supporting apparatus, the relative weakness of the locking ring develops, i.e., the circular muscles of the anus sphincters.They lose the ability to keep the cavernous formations, and the plexuses of varicose veins protrude outward from the lumen of the intestine.
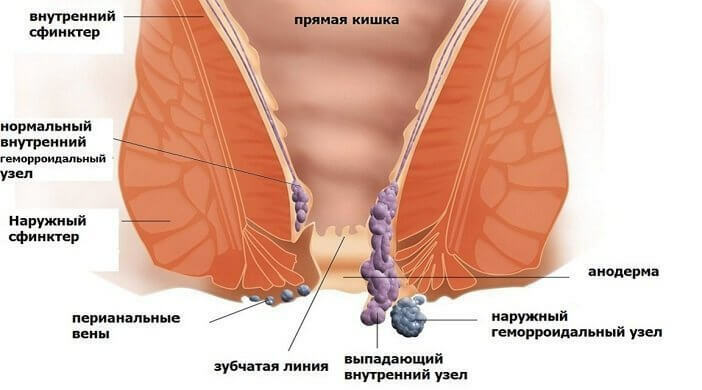
Blood is accumulated inside the cavities separated by walls from connective tissue and smooth muscle cells.Often, they identify single or multiple thrombi.
Clinical manifestations
Internal( latent) nodes are usually painless.They are covered with a mucous membrane, similar to that that lining the walls of the rectum.
Important: in the early stages of hemorrhoids is virtually asymptomatic.Patients turn to the proctologist already with considerable discomfort.In most cases, specialists have to deal with the advanced stages of the disease, accompanied by knee prolapse and bleeding.
Against the background of progression of hemorrhoids, pathologically altered venous plexuses( cavernous formations) protrude outwards with significant physical activity or during bowel evacuation.
The leading symptom of prolapse is the presence of palpable and noticeable seals in the anus and a constant foreign body sensation in the anus.
The average loss of cavernous sinuses occurs 5 years after the appearance of the first clinical signs of hemorrhoids.Clinically, the disease is divided into 5 stages;The beginning of the drop of nodes gives grounds for talking about the transition of the first stage to the second.

In the early stages, the nodes fall out only against a background of considerable physical exertion, straining, severe coughing or sneezing.Since the sphincters still function normally, and the dystrophic changes in the connective( fibrous) and muscle tissue are moderately expressed, the cavernous sinuses are able to independently retract back into the intestinal lumen.
As the patient progresses, the patient must consciously strain the pelvic floor muscles and sphincters, so that the nodes return to the rectum.Over time, it is necessary to carefully adjust their fingers, which characterizes the transition of the second stage of chronic hemorrhoids into the third.Prolapse in this phase of development of pathology is possible not only with the load, but even with a sharp change in the position of the body.
The more pronounced the symptom, the higher the risk of damage or infringement of the varicose plexus .Signs of bleeding for a long time remain unnoticed, and are detected only in the laboratory study of the stool.Then the patient begins to notice scarlet blood on toilet paper or even on the surface of the fecal matter.In blood tests, there are signs of anemia, which is associated with chronic blood loss.
The patient is concerned with such symptoms as anal itching, and intense pain in the anorectal area.During the period of remission, the intensity of the pain syndrome decreases.
In the fourth stage of hemorrhoids, anal muscles and ligaments are almost untenable.Their destruction occurs with the replacement of the connective tissue .Fallen and inflamed cavernous formations can not be fixed even manually, as this causes bleeding and severe pain.The walls of the nodes are constantly injured when walking, defecating and even carefully conducted hygienic manipulations.Their tissues become denser and more coarse.Often, cracks appear on the walls, into which the microflora enters;Thus developing infectious complications, accompanied by increased pain, pronounced inflammation and signs of general intoxication of the body( in particular - malaise and increased total body temperature).
Important: is one of the most common problems with advanced hemorrhoids - thrombosis of hemorrhoids.
Diagnosis
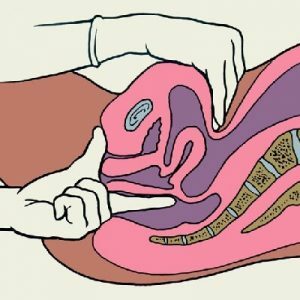 The presence of nodes, their sizes and localization proctologist determines when finger research.The doctor evaluates the condition of the anorectal zone, revealing cracks, maceration and signs of bleeding. An important criterion is the compliance of the dropped nodes and the possibility of their manual correction.
The presence of nodes, their sizes and localization proctologist determines when finger research.The doctor evaluates the condition of the anorectal zone, revealing cracks, maceration and signs of bleeding. An important criterion is the compliance of the dropped nodes and the possibility of their manual correction.
During the examination, the strength of the anal reflex is checked, that is, the sphincter's consistency.For this purpose, the skin around the anus is slightly affected by fingers or a probe.
To verify the diagnosis, it is often necessary to resort to endoscopic methods of diagnosis - anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy.
Anoscopy provides an opportunity to assess the state of the caudal gut during 8-12 cm. The patient is offered to slightly strain;Thus the shift of pathological formations to the bottom becomes well appreciable.
Study by means of a sigmoidoscope allows to examine about 25 cm of the rectum.
An endo-rectal ultrasonography of the distal intestine is performed less often.With its help, not only the pathological changes in the hemorrhoidal veins are determined, but differential diagnosis of hemorrhoids with hypertrophy of the anal papillae, hemangiomas, polyps, cysts and other benign and malignant tumors of the intestinal wall, as well as with the prolapse of the rectum.
Prolaps of nodes is the basis for carrying out an irrigoscopy - X-ray study with a preliminary retrograde introduction into the intestine of a contrast agent - barium sulfate.
In parallel, the patient is referred for laboratory tests( general blood test, feces for occult blood, etc.).
Colonoscopy is required if other( related) diseases of the colon are suspected.
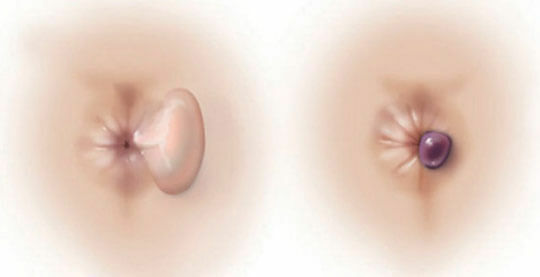
It is not difficult for the experienced proctologist to determine the loss of pathologically altered plexuses at 3-4 stages.In the course of external examination, single or multiple formations of a rounded shape with rather distinct boundaries are noticeable.The degree of their mobility and dimensions are variable.The color of the nodes is usually crimson or cyanotic, and through their walls there are clearly visible enlarged vessels( mesh).The surface of the fallen cavernous bodies can be macerated, which is associated with a constant inflammatory exudation.It often shows damage and individual foci of inflammation.
Treatment and prevention
The symptomatology of prolapse is usually suppressed by conservative methods, but after the inflammation subsides, operative treatment of the underlying disease is expedient.
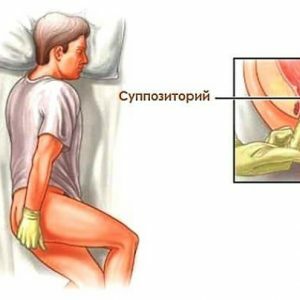 Conservative therapy in the early stages of the development of chronic hemorrhoids involves the use of local drugs in the form of gels, ointments, creams and rectal suppositories.The goal of the treatment is to stop the pain syndrome and other symptoms of inflammation.Suppositories, which include thrombin or adrenaline, can successfully fight with bleeding.
Conservative therapy in the early stages of the development of chronic hemorrhoids involves the use of local drugs in the form of gels, ointments, creams and rectal suppositories.The goal of the treatment is to stop the pain syndrome and other symptoms of inflammation.Suppositories, which include thrombin or adrenaline, can successfully fight with bleeding.
For the prevention and treatment of such complications as the prolapse of the nodes, oral ingestion with repeated courses of 3 months is indicated.
Important: to facilitate the condition during an exacerbation is helped by warm sessile baths with a weak solution of potassium permanganate( pale pink potassium permanganate).The optimal duration of each procedure is 10-15 minutes.
Drug treatment is not always possible to completely cure the underlying disease, i.e. hemorrhoids .Often it is prescribed in the period of preparation for surgery or in those cases when the operation for one reason or another is impossible.
 In the early stages of prolapse of varicose plexuses, sclerotherapy is practiced.During the procedure, a special sclerosing drug is locally administered, which causes desolation, collapse, adhesion and subsequent degeneration of the affected veins.Alternative methods are laser photocoagulation and infrared coagulation of plexuses.Manipulations are carried out on an outpatient basis, that is, there is no need for hospitalization of the patient in the profile department of the hospital.The patient remains fully functional for the duration of treatment.
In the early stages of prolapse of varicose plexuses, sclerotherapy is practiced.During the procedure, a special sclerosing drug is locally administered, which causes desolation, collapse, adhesion and subsequent degeneration of the affected veins.Alternative methods are laser photocoagulation and infrared coagulation of plexuses.Manipulations are carried out on an outpatient basis, that is, there is no need for hospitalization of the patient in the profile department of the hospital.The patient remains fully functional for the duration of treatment.
In the second and third stage, ligation is widely used( suture or latex rings).The ring applied to the base of the node tightens it, stopping the local blood flow.After a few days, the plexus that is deprived of nutrition disappears with the latex device, and the wound heals in 7-10 days.
Note: among other methods of eliminating drop-down nodes include bipolar electrocoagulation and cryotherapy( freezing formation with liquid nitrogen).Now these methods of treatment are used very rarely.
When hemorrhoids are started, surgical intervention is performed - hemorrhoidectomy with transanal access( according to Milligan-Morgan or Longo's method).
The best result allows to achieve a combination of different methods, i.e. complex treatment.
With early diagnosis and timely initiated adequate therapy, the prognosis for complete cure is quite favorable.From the prolapse of hemorrhoids can completely get rid of, and the probability of relapse after complex treatment is low.In the later stages, the forecast is less optimistic.There is a high risk of bleeding, infectious complications and thrombosis of the veins of the anorectal region.
If the initial stage of hemorrhoids is diagnosed, then it is strongly recommended that the patient be radically changed in order to prevent the enlargement and prolapse of the nodes.He needs to move more and perform sets of gymnastic exercises, at the same time, avoiding significant physical exertion.
It is important to make certain adjustments to the diet.It is necessary to avoid fast food and "snacks on the run."It is recommended to consume foods rich in fiber and to abandon food that can provoke constipation or diarrhea.
 Please note: is a high-fiber food product necessary for the normalization of intestinal motility - fruits, vegetables and bread with bran.
Please note: is a high-fiber food product necessary for the normalization of intestinal motility - fruits, vegetables and bread with bran.
Particular attention should be given to the hygiene of the anorectal area.After each act of defecation, this area should be washed with warm water and soap to avoid infectious and inflammatory complications.
Important: preparations that stimulate intestinal peristalsis( laxatives) should be taken only as directed by the doctor in charge.
Recommended to read:Plisov Vladimir, medical reviewer