Diverticular disease of the colon: symptoms and treatment

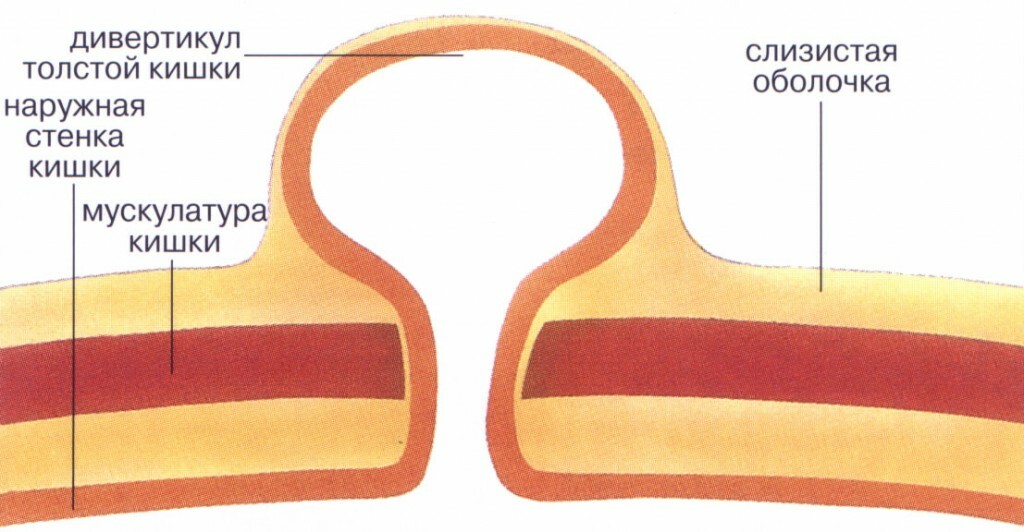
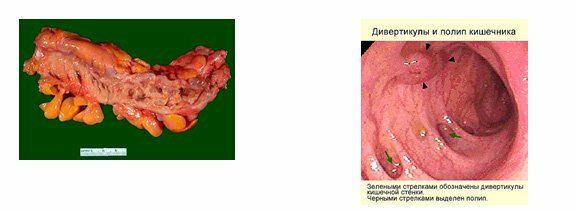
Diverticular disease of the colon is an acquired pathology, which is characterized by the formation in the intestinal wall of diverticula - small protrusions of the saccular form.The size of these formations, as a rule, does not exceed 1-2 cm.
Diverticula are usually formed in those parts of the intestinal wall where blood vessels emerge into the circular muscle.In these "weak" zones, the mucosa is ejected through the submucosal and muscular layer due to increased pressure in the luminal gut and divergence of the muscle fibers.
Table of Contents: Classification of diverticulosis of the colon Reasons for diverticular disease of the colon Symptoms of diverticular disease of the colon Possible complications Diagnosis of diverticular disease Treatment of diverticular disease of the colonClassification of diverticular disease of the colon
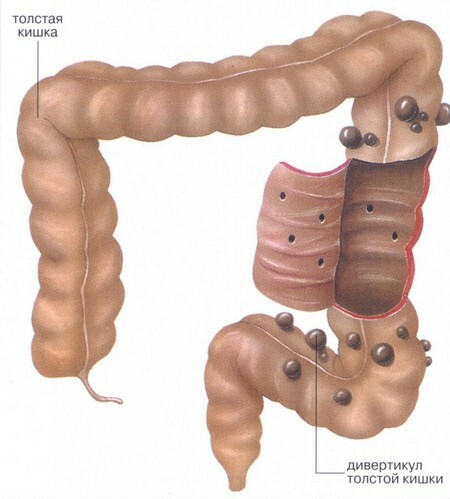 Large intestine can be affected in separate areas orTotally.The most common protrusion is formed in the sigmoid colon.
Large intestine can be affected in separate areas orTotally.The most common protrusion is formed in the sigmoid colon.
The medical term "diverticulosis" implies the very presence of blindly terminating protrusions;Clinical symptoms may be absent."Diverticular disease" is an expanded concept that unifies diverticulosis and its possible complications, which develops only in 20% of cases.
Note: diverticular disease of the colon is most often diagnosed in elderly people living in countries with a high standard of living.
In people younger than 30, diverticula are not found very often, but by the age of 50, pathology with an asymptomatic course is already detected in 30% of the population.
According to the accepted clinical classification, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- asymptomatic diverticulosis;
- diverticulosis with clinical symptoms;
- complicated diverticulosis.
Possible complications of diverticulosis:
- diverticulitis;
- bleeding;
- parietal infiltrate;
- formation of a fistulous course;
- perforation.
Causes and mechanism of development of diverticular disease of large intestine
Specialists believe that a definite value in the development of the disease has a hereditary predisposition, which determines the weakness of the intestinal walls, and certain unfavorable environmental factors.
An important reason for diverticular disease of the colon is malnutrition, in which a small amount of plant fiber is consumed, and animal proteins, fats and bakery products from fine flour predominate in the diet.Consumption of such products often leads to a violation of intestinal motility and chronic constipation, which is the cause of increased pressure in the lumen.
Among the causes of pathological changes with diverticular disease of the colon are also:
- infectious diseases of the intestine( in particular - dysentery);
- irrational long-term use of laxatives;
- local ischemic disorders( including due to atherosclerotic vascular disease);
- increased gassing in the intestine;
- obesity.
Important: in individuals who adhere to a vegetarian diet, diverticula are very rarely detected.
As the aging process gradually decreases the elasticity of the intestinal wall.Periodic increase in pressure in the lumen of the gut( on the background of excessive gas formation and constipation) causes the appearance of protrusions on weak areas.
Symptoms of diverticular disease of the colon
Diverticulosis usually proceeds asymptomatically and is detected accidentally.
In some cases, the following clinical manifestations occur:
- Kolikoobraznye pain in the abdominal area( usually - on the left side);
- constipation( possibly alternating constipation and diarrhea);
- rumbling and a feeling of raspiraniya in the abdomen.
Symptoms of diverticular disease of the colon are non-specific;Similar manifestations are observed, in particular, in irritable bowel syndrome.
Note: after defecation, the intensity of spasmodic pain is usually reduced.In some patients there is a constant, dull, aching pain between spasms.
Against the background of frequent constipation inside the diverticulum waste of life accumulates, which provokes an inflammatory process.
Symptoms of acute diverticulitis( inflammation of the bulging of the intestinal wall) are:
- increase in total body temperature( within the subfebrile digits);
- tachycardia;
- intense pain in the left ileal fossa;
- marked flatulence;
- presence in feces of blood and mucus( not always).
In the general analysis of blood, a leukocytosis characteristic for the inflammatory process is revealed.
Possible complications
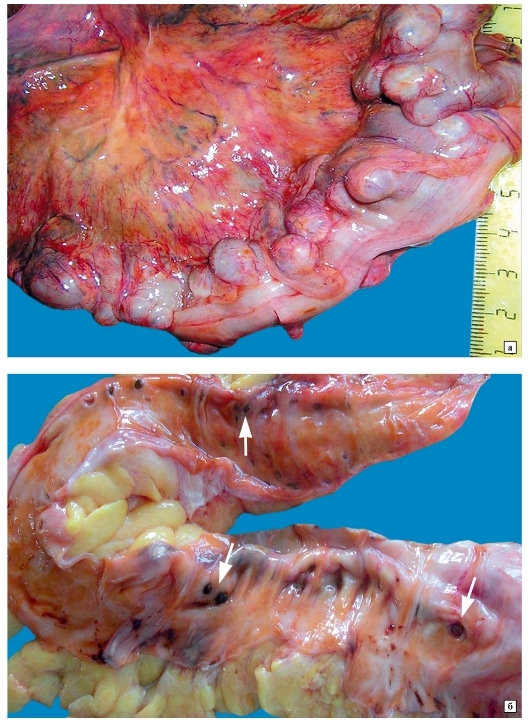
Diverticulitis in some cases causes serious( including life-threatening) complications.
A dangerous complication of diverticular disease of the colon is profuse bleeding when the integrity of the vessel wall is violated in the area of the neck of the bulge.Blood clots and scarlet blood appear in the stool( a symptom called "raspberry jelly").The patient complains of general weakness, a marked decrease in blood pressure, abdominal pain and stool disorders.The skin of the patient pale against the background of blood loss.
As the lumen of the intestine can narrow considerably in the area of protrusion, the development of intestinal obstruction can not be ruled out.The patient complains of pain in the abdomen and the impossibility of emptying the intestine.
Inflammation of the diverticulum in a number of cases causes the formation of abscesses( ulcers).They can resolve themselves, but more often such complications of diverticular disease of the colon require surgical intervention.
With local necrotic changes and perforations of the diverticulum, the contents of the intestine and pus from the abscess fall into the abdominal cavity.This causes a peritonitis - a purulent inflammation of the peritoneum.Complication is accompanied by acute diffuse pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, a significant increase in temperature.It often leads to the development of septic shock.
 Another possible complication of diverticulitis may be perforation of the wall of a nearby organ with the formation of a fistulous course.The most often diagnosed are colovesical pathological passages, in which the diverticulum is associated with the bladder.For this complication, the infection of the urinary system, as well as the release of gas in the urine.Fistula can open into areas of the small intestine, and in women - into the vagina.In rare cases, fistulas are formed on the skin of the abdomen.
Another possible complication of diverticulitis may be perforation of the wall of a nearby organ with the formation of a fistulous course.The most often diagnosed are colovesical pathological passages, in which the diverticulum is associated with the bladder.For this complication, the infection of the urinary system, as well as the release of gas in the urine.Fistula can open into areas of the small intestine, and in women - into the vagina.In rare cases, fistulas are formed on the skin of the abdomen.
The perforation of protrusion into the mesentery of the sigmoid colon leads to the development of retroperitoneal phlegmon.
Diagnosis of diverticular disease of colon
The gastroenterologist diagnoses on the basis of patient complaints, examination data, laboratory tests and instrumental examination.
The patient needs to take a blood test( general) and feces( for the presence of blood).
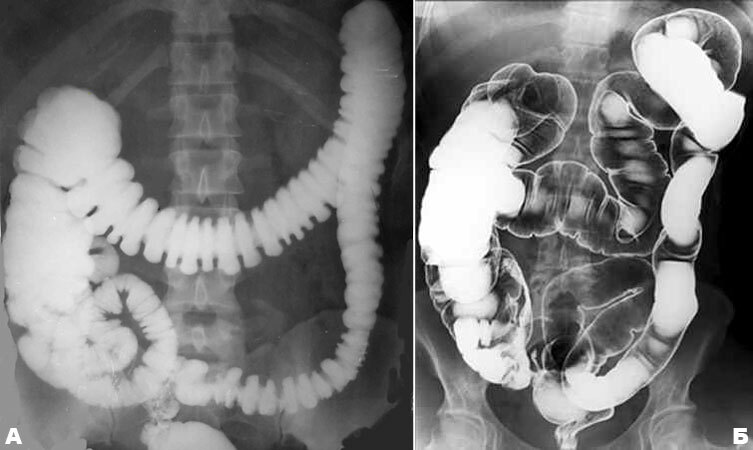
Irrigoscopy is mandatory - X-ray examination with pre-filling of the intestine with a contrast agent( barium suspension is injected with enema).
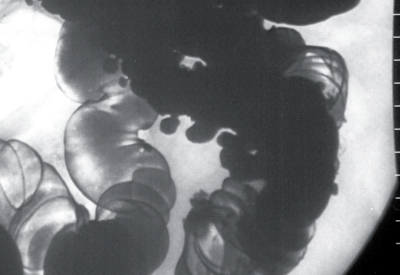 Important: Irrigoscopy can be performed no earlier than 4-6 weeks after the end of an attack of acute inflammation of the diverticulum.
Important: Irrigoscopy can be performed no earlier than 4-6 weeks after the end of an attack of acute inflammation of the diverticulum.
At present, with the suspicion of acute diverticulitis, computed tomography with contrast enhancement is widely used to confirm the diagnosis.An alternative to CT is sonography, but it can detect only large purulent foci and abnormal thickening of the intestinal wall.
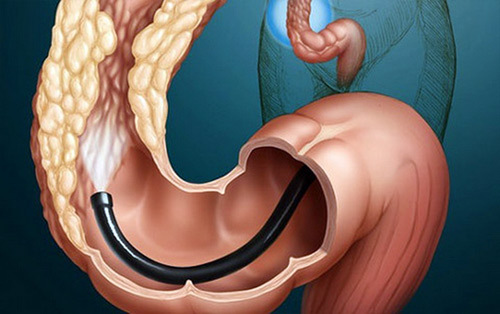
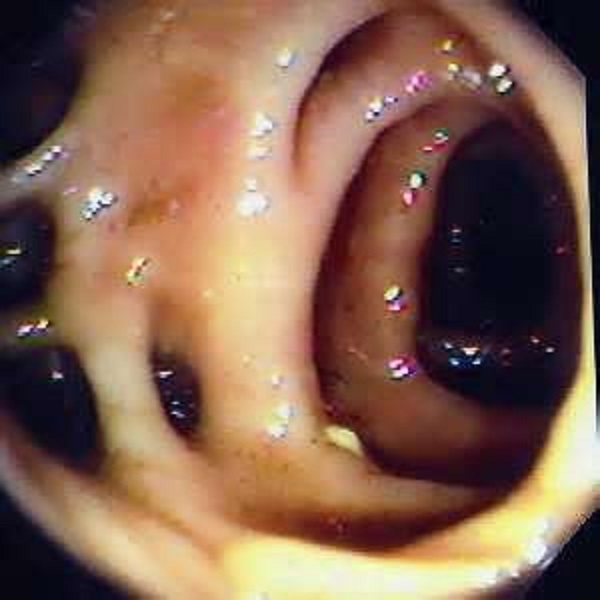
Colonoscopy is used to examine the intestinal wall for the diagnosis of diverticular disease of the colon, in which a flexible endoscope with optics and backlight is inserted into the patient.The technique allows to investigate a significant area( up to 1 m) of the lower parts of the digestive tract.Before the beginning of the diagnostic procedure, the patient is treated with a cleansing enema and given sedatives.Colonoscopy is resorted to if the double-contrast irrigation was not very informative, or if the patient entered a hospital with rectal bleeding.
It is not always possible to examine the gut with an endoscope due to tension or spasm of the intestinal wall against the background of a large diverticular disease.
If there are reasons to assume the presence of a fistula opening into the bladder, an additional cystoscopy is performed.
The source of bleeding allows to detect angiography and such an innovative technique as scanning with labeled erythrocyte-labeled technetium.
Diseases with which differential diagnosis is performed:
- malignant neoplasms;
- acute appendicitis;
- renal colic;
- peritonitis of unclear etiology;
- Crohn's disease;
- ischemic colitis;
- adnexitis.
Treatment of diverticular disease of the colon
Uncomplicated form of diverticular disease of the colon is subject to conservative treatment in outpatient settings( at home).The primary task is to normalize the stool to prevent the formation of new diverticula and prevent inflammation already present.The patient is shown a therapeutic diet with a predominance in the diet of plant foods rich in fiber.In order to increase the volume of the stool, it is advisable to designate the husks of the spaghetti.
It is recommended to take spasmolytics( Drotaverin, No-Shpa, Mebeverin, etc.) and analgesics to relieve the pain syndrome.
If the pain does not disappear within a few days or if the pain intensifies and becomes diffuse, this is an indication for urgent hospitalization.To send to hospitals also follows patients with such symptoms of acute inflammation as fever and heart palpitations.
Non-absorbable and large diverticular abscesses are an indication for percutaneous drainage of a purulent focus.Intervention is carried out under the control of a tomograph or ultrasound machine.
Important: The medical tactics for bleeding depends on its intensity.
 In case of ineffectiveness of conservative methods of treatment of diverticular disease of the colon, as well as with intestinal obstruction or perforation of its wall, urgent surgical intervention is required.Surgical treatment of complicated diverticular disease of the colon usually involves resection of the segment affected by the pathological process.In fistulas, in addition to removing the part of the intestine, a primary anastomosis is required.In some cases, it is necessary to create above the affected area of the colostomy - holes for communication of the intestinal cavity with the external environment.Approximately in 80% of cases it can then be closed, restoring the normal patency of the lower parts of the digestive tract.
In case of ineffectiveness of conservative methods of treatment of diverticular disease of the colon, as well as with intestinal obstruction or perforation of its wall, urgent surgical intervention is required.Surgical treatment of complicated diverticular disease of the colon usually involves resection of the segment affected by the pathological process.In fistulas, in addition to removing the part of the intestine, a primary anastomosis is required.In some cases, it is necessary to create above the affected area of the colostomy - holes for communication of the intestinal cavity with the external environment.Approximately in 80% of cases it can then be closed, restoring the normal patency of the lower parts of the digestive tract.
From the onset of a bypass anastomosis without resection of the affected segment, surgeons have now been abandoned because of the high risk of complications and the large number of deaths with this method of treating diverticular disease of the colon.
If a patient is hospitalized with a percutaneous peritonitis that develops during diverticulum perforation, a set of resuscitation measures, including intravenous fluids and shock doses of antibiotics, is performed prior to surgery.With this complication of diverticular disease of the colon, mortality, unfortunately, is very high.
Plisov Vladimir, medical reviewer