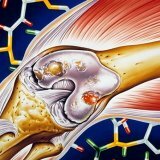
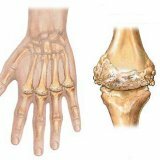
Types of arthritis and methods of treating the disease

Arthritis is a collective name for diseases characterized by inflammatory joint damage.People of all ages are exposed to arthritis.It is estimated that approximately 2% of the world's population suffers from arthritis.
Table of contents:Causes of arthritis development
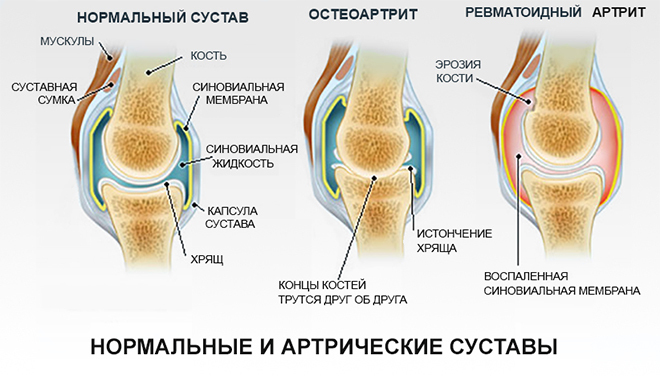
The inflammatory process often begins with the synovium, cartilages, articular capsule, epiphyses of bones are gradually involved.
There are a number of factors that trigger the development of arthritis:
- Infectious diseases;
- Injuries to the joints;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Metabolic changes in the joint;
- Endocrine disorders;
- Features of the profession - a long stay in one working posture;
- Overweight;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Disturbance of nutrition - lack of vitamins and minerals;
- Subcooling.
Types of arthritis
When one joint is affected, it is customary to talk about monoarthritis, two or more - oligoarthritis, many joints - polyarthritis.For each type of arthritis is characterized by the defeat of certain joints.
Depending on the cause, the following types of arthritis are distinguished:
- Arthritis of unknown etiology( rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, Felty syndrome, Reiter's syndrome, reactive arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis);
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Infectious arthritis of established etiology( chlamydial, yersiniosis, gonorrhea, syphilitic, brucellosis, dysentery, typhoid, borreliosis( with Lyme disease)
- Dystrophic arthritis( gout, endocrine arthritis)
- Traumatic arthritis;
- Arthritis associated withOther diseases( purpura, systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, psoriatic arthritis)
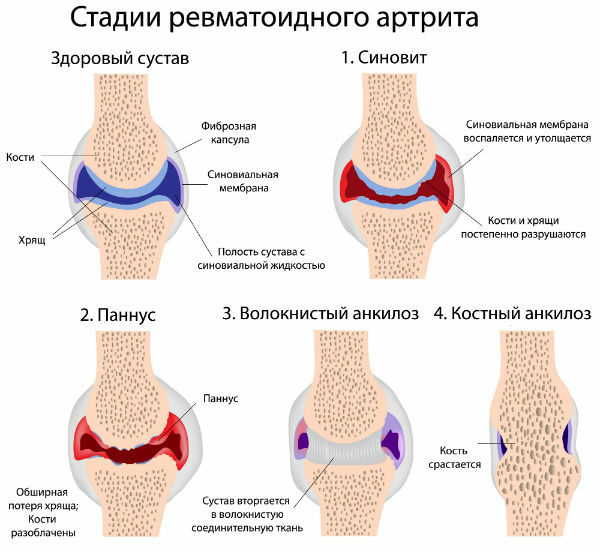
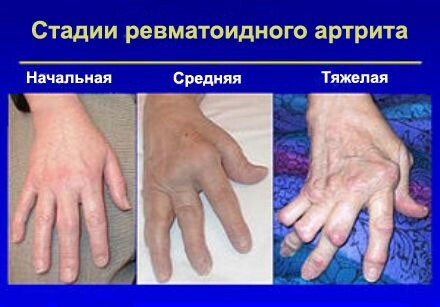
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is aA systemic disease called rheumatism caused by beta-hemolytic streptococcus usually occurs about two weeks after a sore throat and often rheumatism is affected at a young age
Joint damage in rheumatism is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Pain in the knee, ankle, Sometimes in the wrist, ulnar joints;
- Redness of the skin above the joint;
- Puffiness of the joint.

With rheumatoid arthritis, the pain is "volatile", that is, it switches from joint to joint with another rheumatic attack.After the end of the attack, the function of the joints is restored.
Note : with regard to rheumatism they say: "He licks joints and bites the heart."Therefore, it is important to start treatment of the disease in time to prevent the development of rheumatic heart disease.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
Recommended to read:The disease is infectious-allergic in nature and characterized by high disability.
The disease can begin acutely or gradually.Provoke arthritis capable of transferred acute tonsillitis, acute respiratory disease, stress, intense physical stress.
http: //spina.net.ua/tinyMCE/plugins/filemanager/filez/ ra1.jpg
Rheumatoid arthritis manifests itself as such:
- Lesion of the second and third metacarpal phalangeal, proximal interphalangeal metazophalangeal, knee, wrist, elbow, ankle joints;
- Distal interphalangeal joints, as well as the first metacarpophalangeal joint are not characteristic;
- Arthralgia;
- Puffiness of the joint;
- Symmetry of joint damage;
- Local increase in temperature;
- Restriction of movements;
- Flexion and flexion-leading contractures;
- Smoothness of the contour of joints;
- Morning stiffness;
- The appearance of subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules.
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect the organs of vision, respiratory, cardiovascular, nervous systems, kidneys.
Children have juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.The disease can have articular form( ankylosing polyarthritis) and joint-visceral form( Still's syndrome).
The articular form occurs at an early age, in 54% of cases up to the age of five.The rheumatoid process develops subacute in any joint, progressing imperceptibly with or without the involvement of new joints.Mostly affected mainly knee joints and finger joints of the hand.The backbone can be affected with further ankylosing.
The joint-visceral form( Still's syndrome) occurs in the second to third year of a child's life.For the disease, joints( knee, wrist, wrist), poly-lymphadenopathy, enlarged spleen, anemia, fever, skin rashes are common.
In rare cases, rheumatoid arthritis can be manifested by Felty's syndrome.The syndrome is characterized by joint damage, increased spleen size, anemia, weight loss, lymphadenopathy, pellagrogenic pigmentation of open skin areas.
Symptoms of Reiter's Syndrome
The cause of the disease remains unclarified.Presumably, the bacteria play a role in the development of the syndrome, in particular, chlamydia and gonococci.
Syndrome is characterized by a combination of three symptoms:
- Conjunctivitis;
- Urethritis;
- Arthritis.
The disease begins with signs of urethritis and cystitis: frequent urination, the presence of mucous discharge from the urethra.
Catarrhal conjunctivitis may persist for several months.
Joint damage occurs a few weeks after the onset of the disease.Most often affected knee, less often ankle, foot joints.Sacroiliitis may be observed.
Symptoms of post-traumatic arthritis
Is a consequence of a joint injury, accompanied by hemarthrosis, pain, swelling of the joint.Sometimes arthritis can form much later than trauma.
With frequent repetitive microtraumas due to, for example, working posture, there arises a special traumatic arthritis, which manifests itself in the form of stiffness of movements, as well as aching pains in the joints, muscles appearing at the end of the working shift.When performing movements in the joints, you can hear a crunch.Sometimes there develop tendovaginitis, bursitis.
Symptoms of arthritis
Recommended to read:Gout is a disease that is caused by an increase in the level of uric acid in the blood. In the structure of the disease, the following components are distinguished:
- Acute relapsing inflammation of the joints;
- Gouty nodules;
- Chronic, increasing arthropathic changes in joints;
- Disorders of the genitourinary system.
Men of thirty or fifty years are more likely to suffer from gout.The ailment begins suddenly with the appearance of a night of pain in the ith foot of the foot, from which a person wakes up.The finger swells, becomes reddish-cyanotic, movements in the joint are almost impossible.There is an increase in temperature.In the morning the temperature drops and the pain subsides.The next night the attack repeats, it can last one to two weeks.
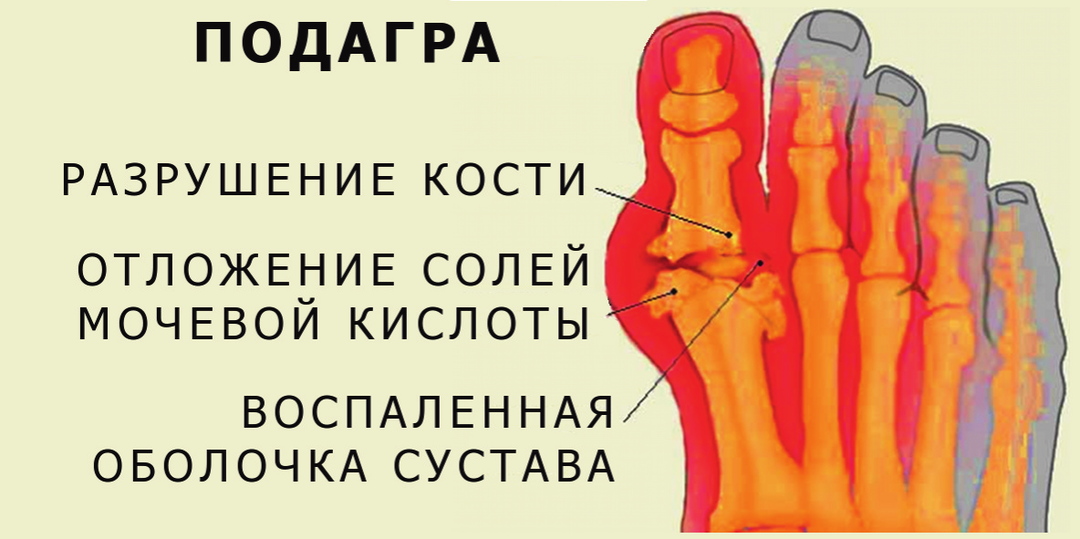
The pathological process gradually fades away, but several months later it re-emerges with the defeat of other joints( ankle, knee, finger joints, elbow, wrist).
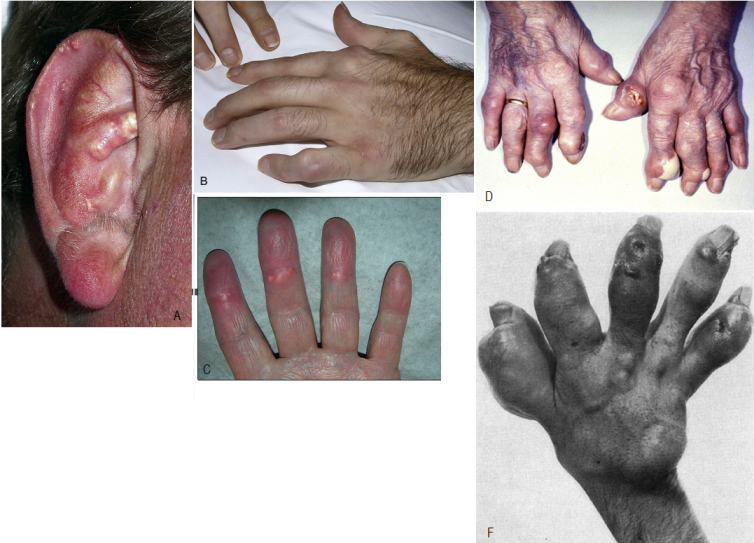
For gout, the deposition of uric acid crystals in the form of cutaneous tofus( nodes) around the joints is characteristic.A pathognomonic sign is the appearance of tophi in the cartilages of ear curls.
Before the next attack of gout, precursors may appear in the form of general weakness, renal colic.Attacks are provoked by the ingestion of fatty, protein foods, alcohol.
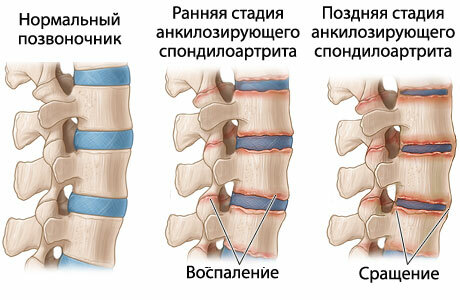
Symptoms of ankylosing spondylitis
This is a chronic progressive disease with affection of the joints of the spine.The disease occurs in the age group of 20-30 years, more often among men.
First of all the disease affects the sacro-vertebral articulation, then the intervertebral, costal-vertebral joints.The disease manifests aching pains in the sacrum, which are more pronounced in the night and morning.In the morning, stiffness is noted in the back and it is difficult for a person to get out of bed.Gradually the pains appear already in the region of the entire back.The torso of the trunk is difficult and painful.Even coughing and sneezing can cause severe pain.
The patient is impaired mobility of the spine, until complete immobilization.The patient's posture acquires the "supplicant's posture", when the back hunches, the arms and legs are bent, and the head is lowered.
In addition, there may be damage to the organs of the cardiovascular system, as well as kidneys.
Symptoms of infectious arthritis
 Develop against a background of different infectious diseases.Thus, urogenital chlamydia can occur with joint damage.One to four weeks after the appearance of the first signs of urethritis, asymmetric polyarthritis occurs, accompanied by pain, local fever, swelling of the joints.Often knee, ankle joints, less often the toes are affected.And the joints of the wrist are rarely affected.Also characteristic is the development of tendonitis, in particular, the Achilles tendon.
Develop against a background of different infectious diseases.Thus, urogenital chlamydia can occur with joint damage.One to four weeks after the appearance of the first signs of urethritis, asymmetric polyarthritis occurs, accompanied by pain, local fever, swelling of the joints.Often knee, ankle joints, less often the toes are affected.And the joints of the wrist are rarely affected.Also characteristic is the development of tendonitis, in particular, the Achilles tendon.
In yersiniosis, symptoms of gastroenteritis first appear, followed by signs of damage to the liver, spleen, lungs, musculoskeletal system.The knee and ankle joints are affected mainly, the elbows and interphalangeal joints of the hand are somewhat less frequent.Joints swell, become painful, and the skin above them - red.
In brucellosis, arthritis occurs predominantly at fever level.The defeat of the joints is manifested by arthralgia, swelling of the joint, local redness of the skin.This clinical picture is typical for the acute form of the disease.These manifestations soon disappear.
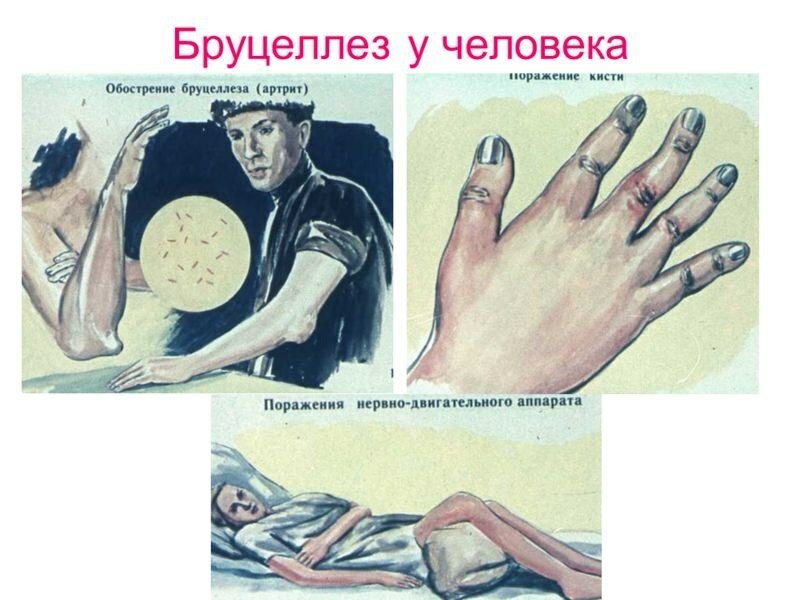
When chronic brucellosis arthritis affects one or more joints( knee, ankle, less often ulnar, even less often intervertebral discs, sacroiliac joint).These arthritis occur after the fever and are accompanied by destruction and deformation of the joint.In brucellosis, peri-and paraarthritis are observed, manifested clinically as bursitis, tendovaginitis.
Note: Arthritis can develop in children after having had scarlet fever or measles.Inflammatory process is able to localize in any joint of extremities.As a rule, arthritis is serous, but there are also purulent.
Treatment of arthritis
The goals of arthritis treatment are the inhibition of the inflammatory process and the restoration of metabolism within the joint, and the preservation of its function.
In the fight against arthritis, the following approaches are used:
- Medicated;
- Non-pharmacological;
- Surgical.
Medical therapy
To eliminate inflammation and pain, the drugs from the NSAID group( indomethacin, diclofenac, ibuprofen) are used.These drugs can be taken either inside( intramuscularly, orally), and externally( ointments, gels).
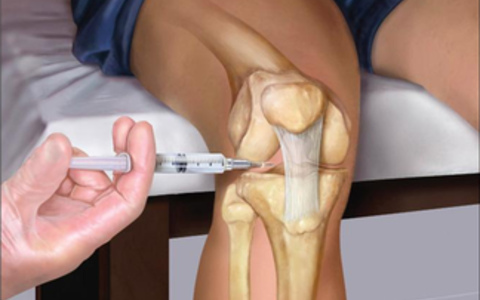 In the absence of effect on the background of NSAIDs, corticosteroid preparations( hydrocortisone, triamcinolone) and cytostatics( cyclophosphamide, thiophosphamide), which are injected into the joint, may be prescribed.
In the absence of effect on the background of NSAIDs, corticosteroid preparations( hydrocortisone, triamcinolone) and cytostatics( cyclophosphamide, thiophosphamide), which are injected into the joint, may be prescribed.
These medications can also be administered orally if there is no result from treatment with NSAIDs and local administration of corticosteroids.
For the control of rheumatoid arthritis, basic drugs are used: gold preparations, cytostatics, antimalarials, sulfonamides, D-penicillamines.
If arthritis is caused by a specific infection, antibiotics are prescribed taking into account the causative agent of the infection.
Non-drug therapy
 This includes LPT, physiotherapeutic treatment( magnetotherapy, ultrasound, mud and hydrotherapy, phonophoresis), massage, selection of orthopedic shoes, use of insteps, knee pads for walking.Reduce the load on the joint can reduce weight.
This includes LPT, physiotherapeutic treatment( magnetotherapy, ultrasound, mud and hydrotherapy, phonophoresis), massage, selection of orthopedic shoes, use of insteps, knee pads for walking.Reduce the load on the joint can reduce weight.
Therapeutic exercises should be moderate, not to cause pain.As an alternative, patients with arthritis can be shown to swim.
Surgical treatment of arthritis
With progression of arthritis that is not amenable to conservative therapy, a synovectomy is indicated.With rheumatoid arthritis, the operation is rational to carry out if the disease progresses, after the third exacerbation.
Some orthopedists prefer to operate in the inactive phase of the process, while others operate regardless of the phase of the disease, subject to proper preoperative drug preparation.
When the joint is badly damaged and all the available methods have been tried, they resort to arthroplasty of the joint.
Grigorova Valeria, medical reviewer