Behcet's syndrome
 Behcet's syndrome was described back in 1937.The disease even then denoted a combination of ulcerative stomatitis, ulcerative lesions of the genital organs, and also uveitis. When the term and the disease itself became public, it turned out that the syndrome can include more than just three indicators. Arthritis, skin vasculitis( type of erythema nodosum), thrombophlebitis, arthritis in the nervous system, aneurysm in large arteries, intestinal lesions, etc. can also be attributed to manifestations of the syndrome.
Behcet's syndrome was described back in 1937.The disease even then denoted a combination of ulcerative stomatitis, ulcerative lesions of the genital organs, and also uveitis. When the term and the disease itself became public, it turned out that the syndrome can include more than just three indicators. Arthritis, skin vasculitis( type of erythema nodosum), thrombophlebitis, arthritis in the nervous system, aneurysm in large arteries, intestinal lesions, etc. can also be attributed to manifestations of the syndrome.
The most common disease occurs in the Mediterranean, the Middle East and Japan. Although the syndrome also exists everywhere, indigenous ethnic groups also suffer from it. For example, in Japan very often Behcet's syndrome is the main cause of blindness. It is important to know that the syndrome can affect the body at any age. But the most peak is considered to be the age of the third decade of life. As a rule, men are most often exposed to infection.
What causes the disease?
What is the cause of the syndrome is not known. But it is clear that the main signs of the disease include vasculitis. Vasculitis affects the arteries, as well as veins, as a rule - these are medium and small sizes. With the syndrome, swelling can often be seen, so the lumen of the vessels often narrows. Sometimes there may be ruptures and vessels and walls.
Often the pathogenesis of the disease is associated with disorders in the body's immune system.
Symptoms of
There are no real signs that directly indicate the disease, because in each case this is a purely individual course. In most cases, those diagnoses that are specific to the disease may not appear immediately, but for some time. They can go on for months or even years, until the disease manifests itself in full force. And when this time comes, the primary signs may already have a reverse development. Proceeding from the foregoing, it is worthwhile to determine that only a few of the whole range of symptoms can manifest in the patient during the entire period of the lesion. It is these factors that complicate the work of doctors, since the syndrome is difficult to recognize in practice.
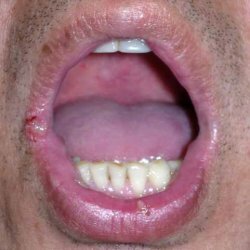
The most characteristic clinical diseases are such diseases as aphthous, or else it is called ulcerative, stomatitis. A shallow lesion of the mucosa may occur on the mucosa in the oral cavity. The majority of patients are determined precisely on this basis. Ulcers have a diameter of 2 to 10 mm. They can be located in the mouth and separately, and as some clusters. Localized ulcers can be over the entire oral cavity: on the cheeks, gums, lips, tongue, sometimes even in the pharyngeal region or on the nasal mucosa. Based on the ulcer a little yellowish color.
There is another indication - an ulcer of the genital organ or organs. Such ulcers can occur in large numbers, and in small numbers. Outwardly they completely resemble the same ulcers that are in the mouth cavity. Such manifestations are quite frequent, so they are detected in 80% of patients. In the female body, the disease can be localized in the labia, on the vulva, the mucous membrane of the vagina. In men, the disease manifests itself on the genitals: the scrotum, the penis. Both male and female can be affected by skin crotch. As a rule, the ulcers on the vagina can be completely painless, so they are rarely detected. Often they are in the body for a long time and are detected with gynecological examination or with complaints of discharge from the vagina. In most cases, the sexual organs suffer less often, the oral organs suffer more. The timing of healing and the expiration of the disease do not differ either in the case of men or women.
But lesions on the area of the bladder may be less common. There are also symptoms of cystitis.
Eye damage may occur. These are the rarest, and perhaps the most serious, manifestations of the disease. The lesion is called uveitis and it occurs in about 2 or 3 patients. The syndrome is bilateral and it can rarely be found at the earliest stages of the disease. Meanwhile, as the first signs of the syndrome, such as lesions of mucous membranes and ulcers on the genitals and the onset of uveitis, may last about 6 years. In order to determine the syndrome or not, you need to undergo an examination with an oculist. The doctor determines the parameters by examining the anterior chamber of the eye.
Another eye pathology may be konjuktiv or ulcer of the cornea, neuritis of the optic nerve, chorioretinitis, retinal vasculitis, thrombosis of the arteries and so on. Loss of vision can be partial, and complete, but in addition, glaucoma or cataracts may manifest.
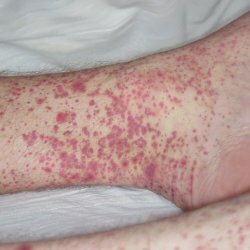
In the case of Behcet's syndrome, joints are also affected. Approximately 50% of cases have arthritis. Often there is a combination of diseases, for example, knotty arrhythmia and arthritis. Most zealously affected joints under the guise of common diseases and with time they acquire the opposite development.
The course of the disease
The disease can be variable. Depending on the period of the course of the disease, which may be very different, some clinical symptoms may start to manifest. The syndrome can then sharply become inflamed, then also abruptly cease its activity. But almost every exacerbation there are increases in body temperature, stomatitis and some skin changes. Remissions in the syndrome can occur from several weeks to several years. These types of leakage depend on the severity of the disease and the patient's capacity to work.
Some patients can easily and carelessly perceive the passage of the syndrome, since it does not affect their life significantly. But there are cases when the disease proceeds with pain, so signs can appear in full force: no remissions, complete polysystemic lesions, etc. The syndrome can lead to death, the causes of which are vascular lesions and meningoencephalitis. Also, fatal thrombosis can result in a variety of localizations and embolism due to thrombophlebitis. Similar and other signs can greatly worsen the passage of the disease. The syndrome associated with uveitis does not affect mortality. But this is also a heavy forecast, as he already talks about loss of vision.
Diagnosis of Behcet's Syndrome
In order to diagnose Behcher's syndrome, it is sufficient to identify a combination of the three main components: lesions of the eyes, genital organs and stomatitis, which are accompanied by ulcers. The diagnosis of Behcet's syndrome is also made with the following clinical signs: recurrent aphthous stomatitis;Aphthous ulcers of the genital organs;Uveitis;Synovitis;Cutaneous vasculitis;Meningoencephalitis. A mandatory symptom is the presence of aphthous stomatitis.
Treatment of
There are currently no general therapies in therapy. Drugs for solving problems with the syndrome can be used( assigned) individually, because they are checked for the fact of the patient's sensitivity to the main constituent components. For the majority of symptoms, immunosuppressants are used in treatment.