Fournier disease: a clinic and treatment
 All diseases are equally unpleasant.They spoil the quality of life, and in difficult cases can pozaritsya and life.But as for the intimate sphere, these diseases are doubly troublesome.In addition to physiological suffering, they also cause psychological suffering.Such pathologies include Fournier disease, because of which the scrotum suffers - an organ whose safety for a man is critical.
All diseases are equally unpleasant.They spoil the quality of life, and in difficult cases can pozaritsya and life.But as for the intimate sphere, these diseases are doubly troublesome.In addition to physiological suffering, they also cause psychological suffering.Such pathologies include Fournier disease, because of which the scrotum suffers - an organ whose safety for a man is critical.
Definition of the disease and its features
 Fournier disease - scrotal disease,Which begins as a purulent process, then continues as gangrenous-necrotic. The process covers all layers of the body, not sparing the skin, testicles, their appendages and spermatic cord.
Fournier disease - scrotal disease,Which begins as a purulent process, then continues as gangrenous-necrotic. The process covers all layers of the body, not sparing the skin, testicles, their appendages and spermatic cord.
The disease has a few more names, "settled down" among clinicians.The name "Gangrenous rye of the scrotum" is not entirely correct, because the disease does not affect the skin completely, as happens in the classic erysipelas of the skin, and often begins "from the depths", and the skin covers are retracted again.The names "Phlegmon scrotum" and "Phlegmon Fournier" also do not reflect the reality, because the disease is not limited to one suppuration: the process develops very quickly, and it is impossible to stop it at the stage of purulent formation, so that you can officially isolate the phlegmonous form of this pathology. In the clinic, doctors write in the case histories diagnoses of "Phlegmon Fournier" and "Gangrene Fournier" - in fact, these are two stages of the same disease.
Among the least common in the domestic clinics of synonymous diagnoses - "Acute tissue necrosis" and "Subfascial phlegmon of the genital organs", they are more often used by our foreign colleagues, which should be taken into account when looking for educational literature.Again, the diagnosis with the mention of the only phlegmon is incorrect, but like no other, it accurately reflects the anatomical feature of the disease - the process spreads under the fascia - a thin connective tissue "film", which means "generalization" of the process when the scrotum is "not enough"And it goes to a wider level, capturing the tissues of adjacent parts of the body.
From the history of the disease
 Fournier disease is a pathology from the category of those that are rare, therefore each time cause a resonance in the medical community. Since the first description in 1764 and up to 1992( hereinafter exact data are somewhat contradictory and require revision), that is, little more than two centuries, described only about 600 cases of this disease.Pathology develops very quickly and affects mainly young healthy men, still causing clinicians a lot of questions.
Fournier disease is a pathology from the category of those that are rare, therefore each time cause a resonance in the medical community. Since the first description in 1764 and up to 1992( hereinafter exact data are somewhat contradictory and require revision), that is, little more than two centuries, described only about 600 cases of this disease.Pathology develops very quickly and affects mainly young healthy men, still causing clinicians a lot of questions.
For the first time the disease was recorded in the distant 1764 year. German physician Bauren described the unprecedented, lightning-fastening necrosis of the scrotum of a 14-year-old boy, which was provoked by a minor trauma and developed violently, although the teenager was absolutely healthy before that, grew up and developed in a safe environment.And about a hundred years later, Russian surgeons described the first successful results of treatment of Fournier's disease, when he managed not only to save the patient, but also to return him to a full life.Although gangrene at the same time "ate" the entire scrotum, exposing the "live" testicles and seminal cords.
In 1883, the French physician J. F Fournier described the next case of the disease, most systematized the already available information on the pathology, and the disease was named after him.
Etiology of the disease
Until now, the exact causes of the disease have not been established. Etiological factors are highlighted, but are in question - because under the same conditions, some men fall ill, the disease goes on violently, and others it does not affect even with repeated multiple and pronounced influence of provoking factors.Part of the confusion and inaccuracy in determining the causes of the illness is explained by the fact that patients, trying not to sound a delicate problem until the last, turned to doctors at different stages of the disease.
Given the etiological factors adopted by most physicians to date, Fournier's disease is classified as:
-
 is post traumatic - caused by mechanical damage to the scrotum of varying severity( from minor bruises to the presence of wound surfaces);
is post traumatic - caused by mechanical damage to the scrotum of varying severity( from minor bruises to the presence of wound surfaces); - postoperative - occurred after surgery on the bladder or urinary tract;Fournier's disease arose after operations performed not only about injuries, but also, for example, plastic surgery, this is confirmed by the fact that the pathology was caused by a surgical intervention rather than a primary trauma;
- is idiopathic, or spontaneous, arising on the background of absolute physiological and anatomical well-being, without provoking factors and previous diseases;
- developing after or against a background of some organic diseases, primarily associated with a metabolic disorder.
Factors contributing to the onset of this disease or worsening of the course of an existing disease:
- obesity;
- cirrhosis of the liver of various genesis;
- vascular disease located in the pelvic region;
-
 malignant neoplasms;
malignant neoplasms; - alcoholism( including in the early stages);
- addiction to drugs( including in the early stages);
- chronic disorders of the endocrine system;
- treatment with glucocorticoids;
- condition after chemotherapy course;
- miscellaneous food insufficiency( lack of necessary food for the body in the diet);
- trauma to the perineal tissues;
- rectal bleeding;
- previously suffered fissures of the rectal mucosa;
- urinary fistula;
- intoxication of various genesis;
- septicopyemia - the presence of secondary purulent foci in the tissues( in this case, the scrotum), formed due to skidding from the primary purulent focus.
A "triple" of pathological conditions, against which Fournier's disease was most frequently observed in patients:
- diabetes mellitus;
- cardiovascular insufficiency;
- kidney failure.
Diseases that are more likely to be complicated by Fournier's disease:
- erysipelas of the scrotum - is rare, mainly in the generalization of( widespread) erysipelas that have affected the skin of the lower limbs;
- purulent inflammation of the tissues of the testicles and their appendages( purulent orcoepididymitis);
- urinary incontinence;
- surgical treatment of prostate diseases( in particular, its removal - adenomectomy);
- paraproctitis( inflammation of the tissues around the rectum).
The role of infection in the etiology of the disease
There are two opinions about the role of infection in the development of Fournier disease:
- according to the first opinion, the infectious agent is the cause of suppuration in the scrotum;
- fundamentally different opinion - Fournier disease occurs without the influence of microbial pathogens - they join later, when pathological changes in the tissues of the scrotum have come, and aggravate the course of the disease, but in no way serve as its primary cause.
In an altered scrotum tissue, a patient with Fournier disease was diagnosed with both anaerobic( living without oxygen) and an aerobic infection( requiring oxygen for its development). In most cases, with Fournier disease, the following were found:
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- hemolytic staphylococcus;
- E. coli;
- fecal enterococcus.
Fusobacteria and spirochaetes were less frequently isolated. In some cases, associations( stable complexes) of representatives of both aerobic and anaerobic infections are found.Such "commonwealths" are especially dangerous: aerobes consume oxygen in the scrotum tissues, contributing to this very prosperity of oxygen-donating anaerobes - such synergy leads to especially rapid suppuration and necrosis of the scrotum tissues.
There are also opinions on the introduction of an infectious agent in tissue with Fournier disease:
- it provokes an endogenous infection - one that lived in the tissues of the scrotum( and not only) in a semi-dormant state, without manifesting itself, butAt some point became more active.The hypothesis of endogenous infection in this disease is not meaningless, since it makes it easier to understand why the scrotal suppuration with subsequent gangrenous process arose "on an equal footing", for no apparent reason, and developed rapidly;
- it causes an exogenous infection - one that penetrates from the external environment.
Exogenous infection can enter the tissues of the scrotum:
- through damage to the skin of the scrotum and penis;
- from the urogenital tract or the pararectal area( tissues located around the rectum) with their infectious lesions.
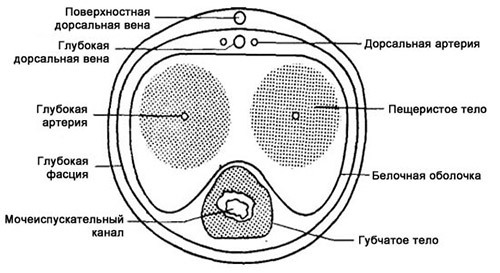
Anatomical features of the scrotum that contribute to the onset of Fournier disease
The scrotum is a gentle creation. Its anatomical and physiological characteristics that contribute to the onset of Fournier disease are:
- epidermis, which nature has provided with protective abilities, is thinner than other areas of the skin, weaker and not as confidently regenerate as the epidermis of the skin in other areas;
- epithelial layer is more friable, if we consider it under a microscope, then there is a certain "fluffiness" - it facilitates the microorganisms insertion into deeper tissues of the scrotum;
- in the thickness of the skin there are more sweat and sebaceous glands than in any other areas of the human body - and they like to accumulate and live microorganisms;Also the accumulation of infection contributes to the presence in this place of hair follicles, where potential microbial pathogens can also "live".This concentration of "housing" for infection makes the scrotum more vulnerable to infection;
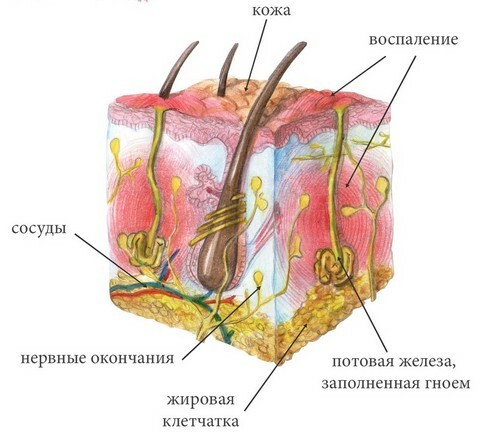
- subcutaneous fatty tissue of the scrotum is weakly developed, its fatty tissue is also loose, which contributes to the faster penetration of pathogens into deeper tissues.
Pathogenesis( development) of Fournier disease
 Primarily in the scrotum tissues an inflammatory process that triggers the thrombogenesis process develops.Small venous and lymphatic vessels, with which the scrotal tissue is densely pierced, are filled with small thrombi rather quickly - and since the vascular network in this area is well developed, the focus of the thrombus is quite extensive. After a very short time, when the number of blood clots accumulates, and the blood flow is no longer able to wash them, thrombosis( blockage) of the venous and lymphatic vessels of the scrotum develops.Clinically, this is manifested by her edema.
Primarily in the scrotum tissues an inflammatory process that triggers the thrombogenesis process develops.Small venous and lymphatic vessels, with which the scrotal tissue is densely pierced, are filled with small thrombi rather quickly - and since the vascular network in this area is well developed, the focus of the thrombus is quite extensive. After a very short time, when the number of blood clots accumulates, and the blood flow is no longer able to wash them, thrombosis( blockage) of the venous and lymphatic vessels of the scrotum develops.Clinically, this is manifested by her edema.
Swollen tissues pressurize arterial trunks. The arterial mesh of the scrotum is poorly developed, because of the "overlap" of the arteries and the sharp deterioration of the microcirculation, very shortly there is a shortage of oxygen and nutrients in the tissues of the scrotum. Swollen tissues also press on venous vessels, the blood flow in them slows down, this triggers a so-called vicious circle. Ischemia develops( oxygen starvation), cessation of blood flow to tissues( infarction) and, as a consequence, tissue necrosis. Infectious agent does not sleep - in the tissues of the scrotum microabscesses are formed, which, merging, for a relatively short period of time turn the scrotum into one large purulent focus. At terminal stages, festering and necrotic tissues are difficult to distinguish visually - in the words of the classic, "horses, people" have become mixed.
Clinical manifestations of the disease
Fournier disease has clearly defined clinical symptoms and does not require additional methods for diagnosis.
In rare cases, the so-called prodrome stage, that is, the stage before the development of indicative symptoms, is prolonged to 2-7 days - during this period the swelling of the scrotum gradually increases, and pain slowly builds up.In the overwhelming majority of cases, the disease begins suddenly, "on an equal footing," the clinic grows rapidly. From the scrotum side, the classic signs of the inflammatory process are clearly defined:
- redness of the skin;
- swelling of the tissues;
- local temperature increase;
- pain when feeling, then without it;
- pain during ejaculation and in the future its violation.
If anaerobic infection prevails, when the scrotum is felt, crepitation is observed - a characteristic crunch due to the burst of air bubbles accumulated in the tissues.
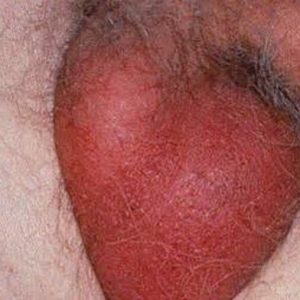
Very quickly the swelling of the scrotum grows, it increases in size and becomes strained, because of the pain before it can not be touched.Puffiness rapidly increases on the penis and nearby tissues - perineum, pubis.Because of the spread of pronounced edema on the penis, its soft tissues can squeeze the urethra until the cessation of full patency and the occurrence of an acute retention of urination. Just a few hours after the onset of clinical manifestations of the disease, the skin of the scrotum becomes dark red, like boiled beet, then violet, the color of the eggplant.
After a short stress in the scrotum tissues, softening sites are identified, which means that the infiltration step goes to the suppression stage of . Foci of pus appear, which rapidly increase in size, "sweep away" the soft tissues between them and merge into one huge abscess.Sometimes before fusion, the superficial foci of suppuration break through, the pus is released outward, while the strain of the scrotum decreases slightly.
Literally a few hours after the beginning of the process begins the process of necrosis of tissues. It is significant that necrosis of subcutaneous fat develops more rapidly than necrosis of the skin.Therefore, what is visible to the eye, may not correspond to the severity of the disease - under the unchanged or slightly modified skin, the necrosis of tissues in the depth can develop rapidly.
In some cases, the entire scrotum may be dead. The dead tissue is separated until the testicles, their appendages and the vas deferens are bare. In some cases, the destruction of soft tissues affects the penis - the ulceration of its head may occur.
Along with the development of suppuration and necrosis, inguinal lymphangitis( inflammation of the inguinal lymphatic vessels) and lymphadenitis( inflammation of the inguinal lymph nodes) are attached. Lymph nodes large, painful, palpable in the form of compact rolling balls.If such globules are soldered to surrounding tissues, this may be a sign of oncogenesis - but other characteristic symptoms will not lead to a mistake in the diagnosis of Fournier disease.
Due to the presence of pus and dead tissue in the body, there are signs of severe intoxication:
- hyperthermia( body temperature increase) to 39-40 degrees Celsius;
- chills;
- headaches;
- nausea and vomiting that are not related to eating.
The increase in signs of intoxication( especially temperature) indicates the onset of sepsis, when the infection, not limited to the scrotum and nearby tissues, penetrates the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body.
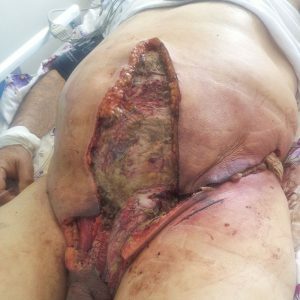
In parallel, necrosis extends to tissues far beyond the scrotum and perineum. In severe cases, necrosis of tissues can pass to the hips, coccyx, sacrum, anterior abdominal wall( even to the level of the navel and above). Ulceration - deep, their surface is covered with pus mixed with dirty detritus( the remains of dead tissue, with which the immune system struggles on a local level, trying to purge them of the body). In severe cases, gangrene "eats out" soft tissues to such an extent that aponeurosis( dense connective tissue covering) of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall may become bare.If the process "crawls" on the hips - the femoral fascia may become bare.
After 5-8 days from the onset of the disease, the process becomes stable. The so-called demarcation line is formed, which is a kind of separator between the dead and surviving tissues of . The rehabilitation period can last several weeks - during this time on the place of dead tissues a connective tissue forming scars forms that deform the external genital organs and those areas on the tissues of which necrosis has spread.
Diagnostics
In the overwhelming majority of cases, the diagnosis of Fournier's disease without difficulty is made solely on the basis of clinical symptoms:
- patient complaints;
- examination of external genitalia;Cautious feeling of the scrotum
- .
Diagnosis is based on three main diagnostic "whales":
- scrotum is suppressed and then necrotic;
- tissue destruction occurs lightning fast;
- signs of intoxication - pronounced and come very quickly.
The characteristic clinical picture allows to do without using additional( laboratory and instrumental) research methods. A general blood test is done to see if the body's reaction to local changes in the scrotum is expressed - there are non-specific signs characteristic of the inflammatory process:
- increase in the number of leukocytes with a typical shift of the formula to the left;
- increase in ESR( ESR).
A laboratory study can also be used to ascertain which pathogen caused suppuration and to prescribe targeted antibacterial treatment. For this use:
- crops and study of grown crops;
- microbiological examination of tissues under a microscope.
Additional diagnostic methods are available for slow development of the disease, which is rare:
- Radiography - with the onset of Fournier disease, provoked by anaerobes, will help to identify gas in soft tissues;
- testis ultrasound - will facilitate differential diagnosis with other diseases of the testicles;
- blood clotting study - will help to evaluate the so-called sepsis-induced coagulopathy( coagulation disorder due to the onset of sepsis, which will clinically manifest later than changes in blood).
Differential diagnosis
The characteristic symptoms will not confuse Fournier's disease with other diseases. But sometimes, especially with slow spreading, the pathology should be distinguished from such conditions as:
- purulent stage of acute orchiepididymitis;
- inguinal and scrotal hernia at the stage of infringement;
- consequences of traumatization of the scrotum and its contents;
- mild chancre - syphilitic lesion of external genital organs;
- gangrenous balanitis - necrosis of the glans penis( in particular, it is observed in severe diabetes mellitus).
The lightning spread of the process is one of the main clinical nuances that confirms the diagnosis of Fournier disease.
Treatment
Due to the rapidly developing changes that can endanger life, a patient with Fournier disease should be identified in the intensive care unit - in extreme cases, in the intensive care unit in the surgery department( purulent surgery in large clinics).
Treatment - combined:
- surgical intervention;
- conservative therapy.
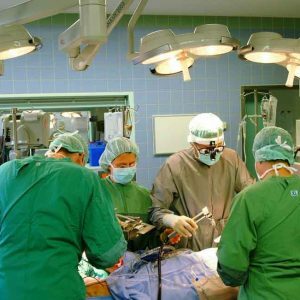
Surgery is performed immediately. During the operation, the following actions are performed:
-
 performs a wide dissection of the skin( up to the capture of unchanged skin, remembering the hidden destructive process under it);
performs a wide dissection of the skin( up to the capture of unchanged skin, remembering the hidden destructive process under it); - excrete necrotic tissue with the capture of healthy tissues, in which the process can already be started on a histological level;
- fabrics maximally cleaned from pus, inspect for its presence, even the smallest "pockets";While the sparing principle is contraindicated - tissue jumpers are destroyed, instrumentation and fingers inspect the slightest "loophole" in order to maximally clean the cavities of pus and detritus ;
- sanitize the scrotum cavity in several steps( washed with antibacterial solutions), and with extensive dissemination of suppuration and necrosis - and all cavities formed during the opening of the purulent necrotic foci by the surgeon;
- drains all the cavities entangled in the process - they are immersed in them with one end of the tube, after the other end of which a few more days purulent-necrotic contents will be released outward;
- , when suspected of anaerobic infection, make so-called lamp-skin incisions to give oxygen access to the tissues in which the infection dying if present.
Surgical intervention is also important in the post-convalescence period - in the case of deforming scars, plastic tissues( in particular, the scrotum) are made.
With Fournier's disease, conservative therapy is not just a medication.The treatment complex includes:
-
 antibacterial therapy taking into account the sensitivity of microorganisms detected in the patient's tissues;
antibacterial therapy taking into account the sensitivity of microorganisms detected in the patient's tissues; - infusion therapy for dehydration;
- detoxification is not only infusion therapy, but also so-called extracorporeal methods( ultraviolet effect on the blood( UFO), plasmapheresis, with the technical capabilities of the clinic - hemosorption);
- immunostimulating drugs;
- injection vitamins( especially group B, which promote tissue regeneration);
- in advanced and severe cases - anti-gangrenous serum;
- if suspected of anaerobic infection - hyperbaric oxygenation( stay in special pressure chambers to saturate tissues with oxygen).
Forecasts and outcome of Fournier disease
With timely treatment and immediately started treatment, the prognosis is favorable.In this case, the duration of the Fournier disease is on the average 8-12 days. With the rapid spread of the process after curing, extensive scarring of the tissues occurs, which in most cases leads to a cosmetic defect, but can also lead to disability( for example, impaired urination due to deformation of the penis).
Lethal outcomes are quite frequent. Statistical data on Fournier disease, provided by different authors, differ significantly - the occurrence of a lethal outcome is fixed in such limits: from 1.5-11% to 35-80% of cases.In most cases, such an outcome occurs because of the untimely detection of Fournier disease. The main causes of late diagnosis:
- marked obesity, when the patient can not look at his genitals and does not see increasing changes in the scrotum, while the pain threshold can be quite high, and subjectively the disease starts to worry not at its early stages;
- delicacy of the problem, because of what patients are long pulling with a visit to the doctor, and even completely refuse to go to the clinic, trying to be treated by folk remedies;
- arrogance, the hope that "it will pass by itself".
Important! Therefore, despite the fact that Fournier disease is regarded all over the world as a rare disease, with the slightest changes from the scrotum and penis, you should consult a doctor in order to "outrun" the rapidly developing fetus.
Preventative measures
 To avoid the risk of developing Fournier disease, factors that contribute to its occurrence should be avoided. Men should remember that the scrotum needs to be treated very carefully, even if it seems that nothing foretells the woes of - for example, be careful during sex, not to mention the possibility of more serious traumatism in the home and at work.
To avoid the risk of developing Fournier disease, factors that contribute to its occurrence should be avoided. Men should remember that the scrotum needs to be treated very carefully, even if it seems that nothing foretells the woes of - for example, be careful during sex, not to mention the possibility of more serious traumatism in the home and at work.
Daily careful personal hygiene of the vulva will prevent the development of infection, which is the immediate cause of suppuration with Fournier disease. It is recommended to create such sanitary and hygienic conditions that after each visit of the toilet there was the possibility to wash the external genitals, crotch and the area around the anus with water with soap( gel). It is significant that Muslims and Indians, who use toilet paper after a toilet visit, and ablution, Fournier disease was extremely rare.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, consulting physician