All About Prolonged Pneumonia
 Prolonged pneumonia is a disease that is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the lungs. This process begins sharply and is resolved slowly, for more than four weeks. Prolonged pneumonia differs from chronic pneumonia in that the first, of course, ends in recovery. Only in thirty percent of the disease takes a protracted character.
Prolonged pneumonia is a disease that is accompanied by an inflammatory process in the lungs. This process begins sharply and is resolved slowly, for more than four weeks. Prolonged pneumonia differs from chronic pneumonia in that the first, of course, ends in recovery. Only in thirty percent of the disease takes a protracted character.
The causes of prolonged pneumonia
The main cause of prolonged pneumonia is a decrease in the immunity of the human body, that is, there is a change in specific and nonspecific protective factors, namely, decrease in B- and T-lymphocyte activity, suppression of phagocytosis and complement, a decrease in interferon synthesis, Macrophages. As a result, the body's defense against infections weakens, and this contributes to a sluggish and protracted resolution of the inflammatory process in the lungs.
There are the following reasons leading to prolonged pneumonia:
- Wrong antibiotic therapy, that is, the antibacterial drug is picked up incorrectly, the treatment started late enough, the antibiotic was canceled too early, and so on.
- Damage to the drainage function of the bronchi, which prevents timely recovery from acute pneumonia.
- Foreign bodies in the bronchi.
- Complications of acute pneumonia, such as lung abscess, atelectasis, pleural empyema.
- Immunodepression and weakening of the human body, which is caused by various diseases of the internal organs or by any medications, for example, steroids, which were used for anti-inflammatory therapy, HIV infection, and so on.
- In children, the cause of the disease can be prematurity, in adults - the elderly.
- Etiological factor.
- Permanent intoxication of the body, for example, alcoholic, industrial, nicotine and others.
Classification of protracted pneumonia
This disease can develop with focal pneumonia and segmental acute inflammation.
With prolonged pneumonia, the focus of inflammation can be located in one segment - it is a monosegmentary pneumonia, it can cover several segments in one lobe of the lung - polysergmental pneumonia or occupies the entire share - lobar pneumonia.
Polysegmentary pneumonia is one-sided, that is, individual segments of one lung or bilateral are affected, where two lungs are immediately affected.
Symptoms of prolonged pneumonia
Pneumonia monosegmental compared with polysegmentary lingering pneumonia has a very smooth course. The second is characterized by severe manifestations, relapses, and a long-term regression of the inflammatory focus.
When the foci of inflammation merge, the patient's condition worsens two or three weeks after the primary manifestations of the disease. Again, cough, weakness, sweating, fever, and lethargy increase.
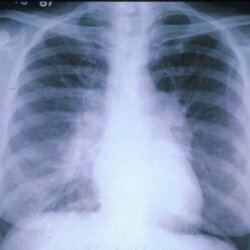
With prolonged pneumonia, you can notice pronounced radiological changes in the lungs.
In the place where the segment is affected, wet rales are heard, and the percussion sound is reduced.
Complications of prolonged pneumonia.
Complications that occur with prolonged pneumonia, significantly affect the course of the disease and its outcome.
Complications can be pulmonary and extrapulmonary.
There are extrapulmonary complications of pneumonia such as pulmonary edema, DIC syndrome, anemia, bacterial shock, nonspecific myocarditis and endocarditis, meningitis, psychosis, toxic hepatitis.
Pulmonary complications include: acute respiratory failure, deforming bronchitis, exudative pleurisy, obstructive syndrome, abscess of the lungs and gangrene, pneumosclerosis.
If prolonged pneumonia is constantly repeated and has the same localization, with the disease has a severe course or pneumonia develops as a result of ingress of foreign bodies into the respiratory tract, especially in the child, it leads to chronic pneumonia.
Diagnosis of lingering pneumonia
For the diagnosis of pneumonia, the basis is clinico-radiographic and laboratory data. If the patient is suspected of protracted pneumonia, he undergoes the following examinations: general urine and blood test, blood immunogram, lung radiograph, biochemical blood test, sputum examination, bronchography, bronchoscopy to exclude foreign bodies of bronchi.
There are diagnostic criteria that indicate prolonged pneumonia - this is:
- a prolonged course of pneumonia, namely more than four weeks;
- is a phenomenon of segmental local endobronchitis, which is determined by bronchoscopy;
- focal and peribronchial infiltration of lobar or segmental localization, which is determined radiologically and for more than four weeks does not regress. And also strengthening of the vascular and pulmonary pattern in the affected area;
- laboratory tests that show the ongoing inflammatory process;
- an indicator of immunological disorders;
Laboratory, clinical, radiological recovery occurs within an individual period of up to one year.
Treatment of prolonged pneumonia
Treatment of pneumonia of a protracted nature has its own characteristics. Whether it is expedient to continue antibacterial therapy with prolonged pneumonia is determined after the analysis of the technique and previous results. Continue antibacterial therapy is necessary if the expressed infiltrative changes in the lung tissue, signs of intoxication and changes in peripheral blood are preserved. Antibiotics are selected, taking into account the data of bacteriological analysis of sputum. Usually, antibiotics are prescribed with a wide range of actions, for example, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides and so on.
With prolonged pneumonia, much attention is paid to the restoration of drainage and patency of the bronchi. Therefore, designate positional drainage, expectorant, chest massage, bronchodilators. There are cases when bronchoalveolar lavage is performed to sanitize bronchial tubes.
LFK, respiratory gymnastics, reflexotherapy, physiotherapy treatment are often used to treat prolonged pneumonia.
With this disease, attention is drawn to the study of the immunity system, as well as to the evaluation of factors of nonspecific protection. If necessary, perform drug immunocorrection.
With frequent relapses of prolonged pneumonia with the same location, it may be the basis to consult a thoracic surgeon, and surgical treatment may be necessary.
Prophylaxis of prolonged pneumonia
Pneumonia of a protracted nature can have an unfavorable outcome, for example, the development of various forms of complications: pulmonary or extrapulmonary. Usually complete recovery with prolonged pneumonia occurs within 2-6 months - the pneumonic foci resolves and the ventilation functions of the lungs recover.
Prevention of this disease consists in conducting an adequate and complete course of treatment of acute pneumonia, careful sanitation of the oral cavity and nasopharynx, refusal from alcohol and smoking, strengthening immunity.