Hemorrhagic diathesis in children: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
 Bruising on the child's body usually results from bumps and falls.If the bruises are formed for no apparent reason, it is necessary to consult a doctor, as this is how hemorrhagic diathesis can manifest itself - diseases accompanied by increased bleeding.
Bruising on the child's body usually results from bumps and falls.If the bruises are formed for no apparent reason, it is necessary to consult a doctor, as this is how hemorrhagic diathesis can manifest itself - diseases accompanied by increased bleeding.
Hemorrhagic diathesis is a collective name for a large number of congenital and acquired ailments, in which there is a tendency for repeated bleeding ( external, internal, soft tissue).In patients suffering from hemorrhagic diathesis, bruises on the body appear spontaneously for no reason or because of light injuries and touches( the size and amount of bruises do not correspond to lesions at all).
Contents: Varieties hemorrhagic diathesis manifestations of hemorrhagic diathesis in children When to see a doctor diagnosis of hemorrhagic diathesis Principles of treatment of hemorrhagic diathesis in childrenVarieties hemorrhagic diathesis
All hemorrhagic diathesis is divided into three major groups:
- RelatedWith pathology of platelets.
- Caused by blood clotting disorder
- Due to damage to the vessel walls.
The first group includes:
-
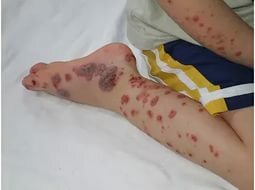
Thrombocytopenia , which is accompanied by a critical drop in the number of platelets in the blood.Such conditions develop in malignant diseases of the bone marrow, immunopathological processes.A vivid example of thrombocytopenia is Verlhof's disease( thrombocytopenic purpura).
- Thrombocytopathies are diseases characterized by abnormal platelet function.Are hereditary and acquired.Acquired thrombocytopathy occurs due to cancer of the hematopoietic or lymphatic system, DIC syndrome, toxic effects of certain drugs, vitamin deficiency( B12, C), blood transfusion and other factors.
The second group is the coagulopathies of ( with them coagulation or clotting of blood is impaired).Coagulopathies are also congenital( various variants of hemophilia, Willebrand's disease) and acquired, which in childhood can arise as a result of infectious diseases, liver diseases, intestinal heavy pathologies, myeloproliferative diseases, amyloidosis.An example of acquired coagulopathy, which develops due to vitamin K deficiency, is a late hemorrhagic disease of the newborn.
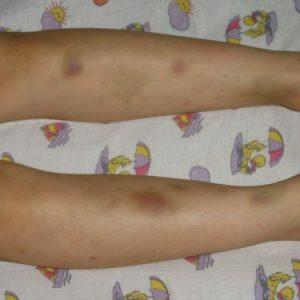 The third group of hemorrhagic diathesis - vasopathy , in which the walls of the vessels become very brittle.An example of congenital vasopathy is Rundu-Osler's disease( characterized by the formation of multiple bleeding hemangiomas and telangiectasias).Vasopathies can also be acquired - for example, Shenlaine-Henoch disease( or hemorrhagic vasculitis).In children, it can develop in response to a serious infectious process, the administration of certain medicines.
The third group of hemorrhagic diathesis - vasopathy , in which the walls of the vessels become very brittle.An example of congenital vasopathy is Rundu-Osler's disease( characterized by the formation of multiple bleeding hemangiomas and telangiectasias).Vasopathies can also be acquired - for example, Shenlaine-Henoch disease( or hemorrhagic vasculitis).In children, it can develop in response to a serious infectious process, the administration of certain medicines.
Manifestations of hemorrhagic diathesis in children
The main manifestation of any hemorrhagic diathesis is increased bleeding.Depending on the causes of the emergence, five variants are distinguished:
-
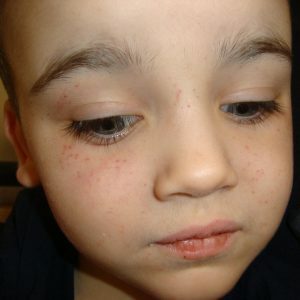 The hematoma .With this type of bleeding, any stroke or fall leads to the outflow of blood in large quantities into soft tissues, joints, internal cavities, and a violation of the integrity of the skin or mucous provokes the development of severe bleeding.This type of bleeding is typical for hemophilia and acquired coagulopathy( the blood does not turn off for a long time, therefore, bleeding occurs).
The hematoma .With this type of bleeding, any stroke or fall leads to the outflow of blood in large quantities into soft tissues, joints, internal cavities, and a violation of the integrity of the skin or mucous provokes the development of severe bleeding.This type of bleeding is typical for hemophilia and acquired coagulopathy( the blood does not turn off for a long time, therefore, bleeding occurs). - Capillary ( it is also called microcirculatory).The main manifestations are small blood spots( petechiae and ecchymosis) on the skin and mucous membranes.There may be nasal bleeding, bleeding gums.This type of bleeding occurs mainly with thrombocytopenia and thrombocytopathy.
- Mixed .In this condition, there are signs of two previous forms of bleeding, that is, hematomas and small blood spots.There is a state where there are violations from both the platelet system and plasma coagulation factors.For example, a similar pattern is very characteristic of von Willebrand disease.
- Angiomatous .By the name it is clear that this form of bleeding develops because of the pathology of the walls of the vessels.The main manifestations are persistent bleeding from the nose, the organs of the digestive tract( usually from the same vessels).
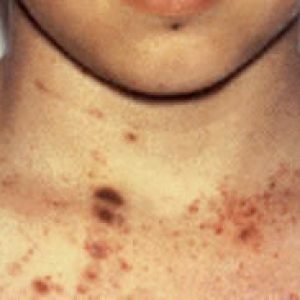
- Vaseline-purple .The main problem and the cause of this variant of bleeding lies in the immune, toxic or allergic lesions of small vessels.Hemorrhages appear most often symmetrically in the area of large joints, although intense internal bleeding is also possible.There is such a type of bleeding in Shenlen-Henoch disease.
All other symptoms of hemorrhagic diathesis in most cases are a consequence of hemorrhagic syndrome.Children can get joints( due to the formation of bruises in them), stomach( with bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract), signs of anemia( pallor, weakness, dizziness).If the vessels of the kidneys are affected, the color of urine may change.Neurological disorders may also be present - this is a sign of hemorrhages in the brain.In general, the condition of a child suffering from hemorrhagic diathesis deteriorates significantly every day.
When to call a doctor
Parents should periodically inspect the children for bruises.On the shins, the children can normally have several bruises, since the lower limbs are a very vulnerable place, especially for toddlers who have started to walk actively.In addition, bruises of a certain localization can be found in children involved in sports( for example, football, wrestling).If there are no other complaints besides a few bruises, you do not need to panic. But to sound the alarm and to call the child's doctor is necessary in the following cases:
- If the hematomas are formed for no apparent reason and in unusual places( the arms and legs are usually the usual places), for example, on the back, on theBreast, belly, face.
- If, after minor damage to soft tissue, prolonged bleeding occurs.
- If blood or blood appears in the feces or urine.
- If the baby's skin becomes pale.
- If the child has excessive fatigue.
Diagnosis of hemorrhagic diathesis
A child with suspected hemorrhagic diathesis must undergo a comprehensive examination, which should include:
- Consultation of a children's hematologist.
- General analysis of blood and urine, blood biochemistry.
- Study of the hemostasis system.This includes a lot of tests.There is no need to take them all at once.The doctor will first give directions to the most necessary( usually bleeding time, platelet count, platelet aggregation evaluation, fibrinogen concentration, APTT and PT) to find out which link is the problem.Further, depending on the results, more complex analyzes will be assigned to determine the exact cause of hemorrhagic diathesis.
- Other studies and consultations of narrow specialists on indications.
Principles of treatment of hemorrhagic diathesis in children
Tactics of treatment are determined by the cause and type of hemorrhagic diathesis, as well as the severity of the hemorrhagic syndrome ( serious bleeding).So, with the development of life-threatening conditions( massive internal and external bleeding, hemorrhages in the brain), the child is hospitalized in the intensive care unit and carries out all necessary measures to stop bleeding and restore blood loss.In other cases, the treatment is carried out in a hematological hospital or outpatient.
With thrombocytopenia ( Werlhof disease), the main treatment is glucocorticoid therapy, if there is evidence, the spleen is removed.With thrombocytopathy , various haemostatic drugs( eg, aminocaproic acid) are used.
To prevent the development of bleeding patients coagulopathy is injected with missing clotting factors.With such diseases as hemophilia, this has to be done all life.With hemorrhagic vasculitis , antiaggregants and anticoagulants are shown to improve microcirculation, as well as corticosteroids for the relief of inflammatory changes in the vessel walls.With Rundu-Osler , patients receive haemostatic therapy, in some cases, surgery( for suturing bleeding vessels) or cryotherapy is performed.
And, of course, with the acquired hemorrhagic diathesis, treatment of the underlying disease( malignant processes in the organs of blood, digestive tract diseases, liver, allergic reactions, etc.) is shown.After arresting the underlying disease, as a rule, the manifestations of hemorrhagic diathesis disappear.In addition, the mandatory component of therapy for hemorrhagic ailments is the symptomatic treatment of anemia, hemarthrosis( joint hemorrhage) and other pathological conditions accompanying these diseases.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical reviewer, epidemiologist-doctor



