Silicosis: causes, treatment, prevention
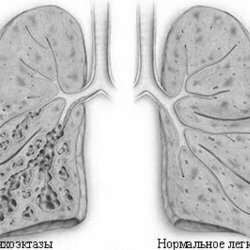
 Silicosis -( silicium - silicon from lat.) Is a type of pneumoconiosis, the most common and quite difficult to flow. Characterized by silicosis diffuse proliferation of fibrous connective tissue and the formation of nodules in the lungs. As a result, connective tissue disrupts the ability of the lungs to produce oxygen exchange.
Silicosis -( silicium - silicon from lat.) Is a type of pneumoconiosis, the most common and quite difficult to flow. Characterized by silicosis diffuse proliferation of fibrous connective tissue and the formation of nodules in the lungs. As a result, connective tissue disrupts the ability of the lungs to produce oxygen exchange.
Silicosis also increases the risk of other lung diseases, such as tuberculosis, bronchitis and emphysema.
This is a professional disease, most often it occurs in people working in specialties, whose activities are related to metallurgy, mining, machine building and porcelain industry.
The cause of the development of the disease is the prolonged inhalation of dust containing silicon dioxide. Silica dust can be found in many industrial plants, even in ordinary sand contains about 60% silicon. But here the most important point is the size of the silicon particles. The particles of sand are too large to enter the lungs by inhalation, but if the silicon particles are finely dispersed, 2-3 nm in size, they easily enter the bronchioles and alveoli when inhaled, cause their damage and the development of fibrous tissue.
An important role in the development of silicosis is played by the duration of contact with silicon dust and the quantitative contamination of the inhaled air. If air dusting is moderate, then silicosis develops after about 10-15 years of work in production. But if the concentration of dust is significant, then literally in 1-2 years, an acute form of silicosis can develop. Sometimes the disease develops a few years after contact with silicon in the workplace. This is the so-called late silicosis.
This disease was discovered in 1705 by the Italian physician Bernardino Ramadzini, who noticed the presence of sand in the lungs of stone workers.
Symptoms of the disease
Silicosis can not disturb the patient in any way for a long period of time.
The first symptoms of the disease will manifest as:
- Dry, rare cough.
- Pain in the thoracic region.
- Appearance of dyspnea( especially after physical exertion)
- Periodic sputum production.
When the pathological process begins to progress, the symptoms of the disease become brighter and become more pronounced.
Painful sensations and dyspnea become worse. Dyspnea begins to manifest even in a state of rest. The cough is getting worse, the sputum is still being separated. Associated diseases can join, for example, bronchial asthma or chronic bronchitis.
In advanced forms of the disease, cough becomes a constant patient companion, the sputum is abundantly separated, the intensity of pain in the chest increases, the feeling of squeezing joins, cyanosis and hemoptysis may occur.
Pathogenesis of
The development of silicosis is associated with physical, chemical and immune processes that are triggered by the action of dust particles of silicon on the tissues of the human body.
There are several theories explaining the pathogenesis of silicosis
- Toxico-chemical theory, in another way it is called "solubility theory".According to this theory, crystalline silicon dioxide, dissolving in the tissue liquid, forms a colloidal solution consisting of silicic acid. This acid has a damaging effect, and the development of fibrosis is started.
- Physico-chemical theory. According to her, the destructive effect of silicon particles is due to the peculiarities of the structure of the crystal lattice, as a result of which interaction occurs, an active chemical reaction between tissues and silicon particles, silicic acid is formed, which, as already known, triggers the development of fibrosis and takes part in the construction of collagen fibers.
- Immunological theory, according to which, under the influence of silicon dioxide on cells and tissues, autoantigens and, respectively, autoantibodies are formed. The resulting immune complexes have an effect on the growth of connective tissue.
The pathogenesis itself in the modern view includes several important stages:
- Inhalation of a fine particle of silicon, its penetration into the final sections of the respiratory airways( alveoli, bronchioles).
- The stage of absorption by alveolar macrophages of silicon particles( the process of phagocytosis).
- There is a death of macrophages with the release of the contents, including silicon particles.
- Recurrent phagocytosis and repeated death of macrophages.
- Education in places of damage to fibrous connective tissue.
- Development of fibrosis.
- Substitution by connective tissue of healthy lung tissue.
- Disturbance of oxygenation processes and development of pathological process.
Features of the clinical course, complications.
Depending on the clinical and radiological features, three forms of silicosis flow are distinguished:
- The interstitial form is the most favorable, characterized by a relatively benign course.
- Nodular form - the most common course of silicosis, occurs most often.
- Tumor form - can develop due to interstitial fibrotic process, but more often appears as the third stage of the nodular form.
Silicosis can cause a large number of complications, the most common of these is the adherence of concomitant lung diseases: emphysema, tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, chronic bronchitis, bronchial asthma.
Also can develop, such conditions as: respiratory failure, pulmonary hypertension, pneumothorax.
Some patients may experience a decrease in the functional activity of the liver( in detoxification of toxins or in the formation of prothrombin).In the late stages of the disease, there are manifestations of neurological disorders, it can be headache, depression of vegetative reactions, dizziness.
Treatment, prognosis, prophylaxis
In the first place, a diseased silicosis, you need to stop contacting silicon dust. Patients are shown breathing exercises and oxygen inhalations.
If the course of the disease is complicated by the adherence of tuberculosis, then the patient is assigned at least three antituberculous chemotherapy drugs.
Nutrition of the patient should be high-grade, with a high content of protein products. Regular visits to resorts are appropriate. Cough and bronchodilators help cope with coughing and shortness of breath. In case of infection, antibiotics and sulfonamides are used.
Forecasts for the disease depend on its stage and nature. Of great importance are the individual characteristics of the patient's body. Chronic silicosis always has a more favorable prognosis. Acute silicosis often leads to serious complications, even if contact with silica is completely stopped.
Prevention of silicosis disease includes:
- Mandatory, regular medical examinations of persons in contact with silica.
- Reduces dustiness in work areas.
- Use of personal protective equipment( respirators).