Cryptogenic epilepsy
 cryptogenic epilepsy - this psycho-neurological disease that is accompanied by a series of seizures, the most common type of epilepsy, but the etiopathogenesis remains unknown to this day.
cryptogenic epilepsy - this psycho-neurological disease that is accompanied by a series of seizures, the most common type of epilepsy, but the etiopathogenesis remains unknown to this day.
word "cryptogenic" is translated as "secret" or "unmarked", "hidden", so all episindroma that the genesis of the complex diagnostics cryptogenic epilepsy and remain ignorant of or obscure, and referred to as - cryptogenic. The imperfection of the complex diagnostics of cryptogenic epilepsy does not allow to determine the cause even in our days.
For the first time the mention of cryptogenic epilepsy was described even in the days of Ancient Greece, then this disease was associated with the punishment of the gods for committed sins, because no other explanation could be found.
According to the world statistical data, nowadays, only 40% of episodic diseases are detected in the epicentricles, while the remaining 60% of epizootics are attributed to cryptogenic forms.
The task of medical development at the present stage is to create and study the nature of the occurrence of failures in electroactive impulses produced by the cerebral cortex within the nerve glia. A particularly complex building is the diagnosis of cryptogenic epilepsy in children, because the disease is in its infancy and becoming.
It is cryptogenic epilepsy in children that can transform into an already known form and transform with age, or even fade away. In childhood, such a diagnosis can be called intermediate, it is important to monitor the development of the process in such a child, resorting to electroencephalographic monitoring.
etiology of the changes occurring in the brain at disease cryptogenic epilepsy is unknown, but in addition to all diseases have no specific age limits and definitely folded symptom.
Cryptogenic epilepsy is multifocal and cryptogenic temporal epilepsy.
Cryptogenic epilepsy: what is it?
Cryptogenic epilepsy is a chronic, psychoneurological disease with an unknown genesis. The disease, which is manifested predisposition to sudden onset epipristupov - convulsions( motor failures with temporary impairment of tangible, mental processes and autonomic mechanisms), short-term outages of human consciousness( absence seizures manifestations, particularly common in younger age period) and often transforming the personality. When
cryptogenic epilepsy cortex arise excessive spontaneous impulses leading to nervous overexcitation transmission to form convulsive gipersinhronnogo chamber under the influence of neuronal discharge. This focus provokes an epileptic attack, this is the consequence of organic pathological processes or functional changes in specific areas of the cerebral cortex.
reasons for the formation of a convulsive focus: ischemic modifications circulation, perinatal abnormality, intrauterine hypoxic events, hereditary idiopathic epileptic predisposition, traumatic head injuries, somatic diseases, virus-related disease, neoplasm tumor character, neyroinfektsy, anomalies in the development of brain cells, disturbances of the realExchange, stroke, toxic-chemical damage, other symptomatic damaging fKtorov.
Epipristupy can be generalized throughout the body or focal( limited to the scope of manifestations).Focal epileptics are divided in the location of a pathologically active focus of epilepsy in the brain on cryptogenic temporal epilepsy, frontal, parietal and occipital.
The cryptogenic form of focal epicuspids develops very often and affects most of the adult age group, and symptomatic epipripages appear in children. There is a propensity in the childhood of the transition of the cryptogenic variant of epipriposition into the classic symptomatic form, if during periodic surveys all the same it is possible to establish the specific causes of epicasis.
In order to provide evidence of the symptomatic nature of cryptogenic epilepsy, the diagnosis of cryptogenic epilepsy is used - a complete examination of the patient. Locally meaningful epi-offs can be determined by carrying out and decoding a tomogram obtained with magnetic resonance imaging.
The cryptogenic frontal form of epicasis is a subspecies closely related to the subcortex. With this type of epiprip start suddenly without aura-precursor. Often short epiprustupy last series, sometimes even turning into generalized and epistatus. Attacks happen also not only during the waking period of the sick person, but also during sleep. Characterized by automated uncontrolled movements - complex gestures-automatisms.
Separate cryptogenic epilepsy according to the form of the disease, these include: a common generalized form or Lennox-Gastaut syndrome( generalized cryptogenic epilepsy, inherent in the age range of 3 to 8 years, often a continuation and a consequence of the already existing Vest syndrome), directly the West syndromeMore often inherent in the children's population, especially in the age range studied 4-6 months), subspecies with characteristic myoclonic-astatic epipripeds( characteristic for babies in the period 1-3 years, basicallyIt manifested as generalized and myoclonic epipristupy with myoclonic-aesthetic epipripadki).
The diagnosis of "cryptogenic epilepsy" is rather a preliminary or intermediate stage to finding and establishing the final cause of the disease for effective treatment. The development of diagnostic neuroimaging allows us to assume that in the near future, with the help of modern diagnostic techniques, etiopopogenesis will be fully disclosed, since at this stage the specific weight of cryptogenic epilepsy is steadily increasing.
Causative factors of the risk of developing the disease cryptogenic epilepsy are as follows:
- narcotic and alcohol-containing substances, their abuse( it is especially important to focus society, parents or guardians on this issue in young adolescence);
- traumatizing craniocerebral lesions;
- parasitic and viral infections, especially those suffered in the history of neuroinfections;
- pathological conditions of organ systems, malfunctions in their functioning, especially in the urinary system, kidneys and liver;
- flares and a sharp change of bright light rays, which can provoke the overexcitation of neural connections in the brain;
- extremely loud sounds;
- critical changes in the temperature index( for example, when flying from hot countries to cold and vice versa, visiting the sauna);
- forced oxygen production;
- the main cause of metabolic disorders in cryptogenic epilepsy: pancreatic pathology, hepatic dysfunction and gastric disorders;
- ischemia and stroke;
- infectious diseases of the brain( meningococcemia, encephalitis, meningoencephalitis, brain abscess);
- cephalic tumors;
- epibootens of newborns in critical hyperthermia;
- a young age of up to twelve years and an elderly age is over sixty years old;
- genetic inheritance predispositions;
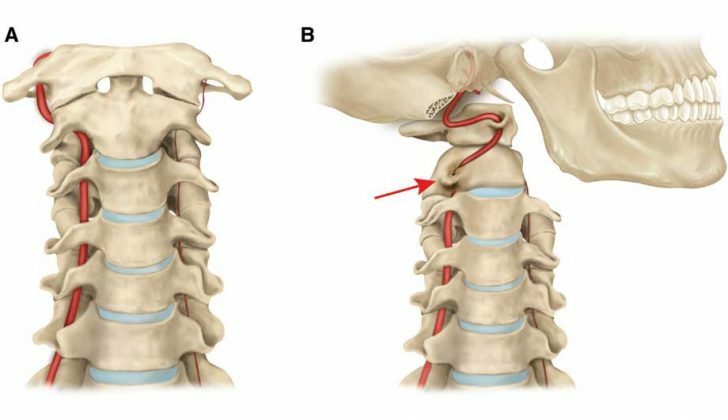
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- antiphospholipid syndrome;
- imbalance between brain processes of excitation and inhibition.
Cryptogenic epilepsy: symptoms of
Symptom complex occurs in three successively changing stages:
1. Suddenly arising convulsive epi;
2. Mental disruptions, which have an unstable character;
3. Destruction of personal characteristics of an individual and his intellectual abilities.
Signs of the cryptogenic epiprime:
- Motor. Sometimes there are unpleasant feelings and provoke motor activity: running, shouting individual phrases, phrases.
- Sensitive, autonomic and mental disorders. Quite often there is an unmotivated fear with hallucinations, visual flashes.
- Neurological symptoms: a drop in muscle tone, lack of speech( delay and underdevelopment in children, degradation in adults), drowsiness or confusion.
- During the epiprust, there comes a complete apathy, often loss of consciousness, affective disorders with neurological disruptions.
- Prolonged attack begins after such precursors as tachycardia, debilitating insomnia aura Harbinger, hallucinatory visions.
Sequence of the symptomatic complex of epicas:
- a person loses consciousness and falls sharply to the ground, the body is very relaxed;
- a cry or a patient cries out inarticulate sounds, all from a contraction of the laryngeal muscles, a spasm of the glottis;
- clonic convulsions with rhythmic bends of hands and feet, tilting back of the head, tension of the trunk;
- increased pressure, tachycardia;
- the head nods in time to contract the muscles;
- epitheap sensory sensation: a touch of wind, stroking the skin;
- with the progression of epiprip start the rotation of the eyeballs and nystagmus;
- hoarse breathing, possibly with seizures - apnea;
- skin with a marble tint;
- muscular tremors;
- tongue twisting, foam and blood from the mouth;
- epipristup ends with a smooth decrease in pressure, normalization and stabilization of respiratory functions and pulse characteristics occur. Full relaxation of the body, deep sleep, after the patient has a migraine headache, excessive fatigue and "weakness", a violation of visual character.
cryptogenic focal epilepsy
Cryptogenic subtype focal epilepsy is an epilepsy embodiment percolation disease with limited scope occurrence elektrooaktivnogo pathological nidus. The transition of the focal epiprip to the generalized paroxysmal is possible.
How the paroxysm of the focal character manifests itself depends on the finding of an epiotic in the cerebral cortex. If the epoelectroactivity is in pyramidal neurons( whose function is to control motor activity), then the epiproduct will manifest itself as a suddenly occurring motor activity. When surrounds the device sensory organs epipripadki are hallucinatory character type( tactile touch, visual images, auditory noises and sounds, smelling and flavor deceptive illusion).At the location in the occipital lobe, the patient sees illusory non-existent things, people;In the convective zone of the temporal cortex of the brain - auditory hallucinations;In the sagittal zone and the hook of the ammon horn - illusions associated with taste and smells;In the parietal area - sensory epitopes in the skin by the type of parasthesia. For
focal forms of epilepsy of cryptogenic type of mental disorder characterized by the following:
- Psychiatric abnormal shifts - the type of thought process viscosity, polarity, mood disorders, thoroughness, the propensity to impulsive actions and dysphoria.
- Nonpsychotic configurations( melancholy, emotion, hypochondriacal phenomena).
- Signs of intellectual degradation.
symptom, as described above, depends on the affected areas of the brain, but the diagnostic measures carried out are the same for all the subspecies once: anamnesis of life and disease( carefully inquire about the nature of the attack, it is desirable from the witnesses - a sketch of the case paroxysm from the lips of third parties).Necessarily examination by a neurologist, with the isolation of the patient in the presence of a focal neurological symptom complex;The doctor-oculist with definition of infringements of visual disks. Conducting instrumental techniques: MRI, EEG, CT, PET.
The treatment plan is tailored for each individual individually. Antiepileptic and sedative - these are the drugs of choice( Carbamazepine, Trileptal and Depakin).They prefer monotherapy with a single medicine and gradation with a small dosage initially, and gradually increasing it throughout the month, further assessing the effect of the therapy. This type of epilepsy can be treated relatively well.
cryptogenic generalized epilepsy
Cryptogenic kind of generalized epilepsy and Lennox-Gastaut syndrome - it is inherent in children or epientsefalopatiya disease of childhood, with a characteristic polymorphism epipripadkov and quite uncharacteristic distinctive EEG changes, also noted persistent resistance to therapeutically useful drugs. The frequency of occurrence of 3-7% among all the episodes of the children's age cohort is characterized by the prevalence of the number of cases among boys.
Infantile convulsions in this syndrome are modified into tonic episprints without a period of latency and slowly pass into the syndrome complex. After the disappearance of spasms, the development of the child improves;EEG smoothly normalizes, but after a short while there are epicas and abnormal absences, the encephalogram reads the widespread slow peak-waves.
A triad is typical: paroxysms of falls, tonic-characterized epicas and abnormal absences. Consciousness persists( often), after falling there are no convulsions, the child immediately comes to consciousness and rises.
Atypical absences are multifaceted, the violation of the brain elements with them is incomplete, the mobile function and the apparatus of speech reproduction, hypomymia, salivation, atony of the neck muscles, "limp" of the whole body can be preserved.
On EEG - recorded during the study, irregular and slow wave peak activity. At neuroimaging the oiled picture.
Carbamazepine and Lamycal are used in the treatment. The prognosis is complex, only 9-20% of epileptic patients come at least the slightest improvement, the rest - the prevalence of epicasis and strong intellectual degradation.
Cryptogenic epilepsy: treatment with
Timely diagnosis of cryptogenic epilepsy helps to prescribe an adequate curative program and prevent the development of serious side effects from the use of antiepileptic medications. Treatment can take place in two versions: on an outpatient basis or in a hospital hospital.
Therapy of cryptogenic epilepsy is carried out according to protocols and standards of treatment for patients with epilepsy. Treatment is recommended only after the diagnosis is determined and the therapeutic measures themselves begin at the end of the second epileptic episode in the patient.
Stage before treatment:
- Diphdiagnosis of epilepsy.
- Coping of the epistatus.
- First aid and treatment regimen selection.
The purpose of the therapeutic procedures is the following subparagraphs:
- anesthesia of epicasures, leveling when taking anticonvulsant or analgesic drugs, food correction( food containing calcium and magnesium or taking vitamin complexes);
- prevention of new epicas, resorting to surgery or conservative method - oral medication;
- reduce the frequency of emerging epicasis and maximally shorten their duration;
- ideally achieve a complete withdrawal of drug use;
- minimization of side effects from the drugs used.
For the treatment of cryptogenic epilepsy, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Anticonvulsants( reduce the frequency and duration of epicas), this is Carbamazepine, Levetiracetam, Ethosuximide.
- Neurotropes( depress or stimulate the process of origin as a nervous impulse of the brain).
- Psychotropes( change a person's psychostatus and functioning in the nervous sphere of a person).
- Psychoactive nootropics.
Non-pharmacological methods: surgical interventions - neurosurgery, Wojta method, special diet.
Until today, a single method of complete cure has not been established, but anti-epileptic measures of therapy help in 60-80% of epizootics.