Why do men there Hypothyroidism: common causes
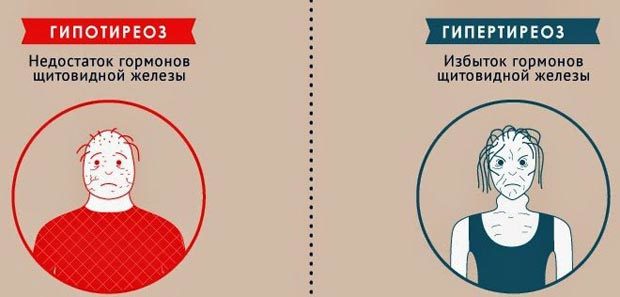
Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism - a common pathology of the thyroid gland, where it comes hypofunction. Thyroid hormones cease to be synthesized in sufficient quantities, disrupting the work of all organs and systems.
The essence of the problem
The thyroid gland is controlled by the pituitary gland, which in hypofunction produces increased TSH - thyroid-stimulating hormone, it stimulates. When hypofunction there is a high level of TSH and decrease of T3 and T4 hormones.
In the analysis it is important to define the free T4. Most often, the level of TSH in hypothyroidism greater than 2.0 mU / l. "Male" hypothyroidism occurs in 8-10 times less often than women.
Symptomatology is about the same, but there are and their sexual differences.
The latent form of hypothyroidism is detected in 10 - 20% of the population, and in men while at 0.2% male reproductive age and 2.5% - the elderly (over 60 years). Without treatment hypofunction is a big risk for men's health. This will not only affect the reproductive function, but also on the cardiovascular system.
The causes of thyroid hypofunction
The main causes of hypothyroidism include:
- Thyroid removal in whole or in part, at which its function is surely broken;
- RIT treatment;
- AIT;
- malfunction of the pituitary or hypothalamus.
- sick and hypothyroidism can lack iodine, selenium and zinc;
- allergic to gluten (celiac disease) and casein (A1).
- frequent stress with increased levels of cortisol;
- eating disorders - a little fat and a lot of sweet;
- taking certain drugs - drugs lithium, dopamine, interferon, etc .;
- autoimmune processes in the body - diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and so forth.
- bad ecology - radiation, increasing the fluorine and chlorine;
types of hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism on causal factors is 4 types: primary, secondary, tertiary and tissue.
Primary or thyrogenous - 95% and developing with:
- iodine deficiency, inadequate treatment of iodine salts;
- abnormalities of the thyroid gland;
- congenital disorders synthesis of T4 and T3;
- thyroidectomy or resection;
- thyroid cancer;
- for TB;
- syphilis;
- chronic thyroiditis;
- inadequate treatment tireostatikami;
- RIT.
Secondary or variant pituitary lesion develops in the adenohypophysis, wherein the TTG is synthesized.
The reasons for the defeat of the pituitary:
- pituitary adenoma;
- brain tumor;
- brain abscesses,
- TB;
- congenital hypoplasia of the pituitary;
- radiation;
- head trauma;
- brain surgery with pituitary damage;
- impaired blood flow in the portal system of the hypothalamus - pituitary;
- autoimmune chronic inflammation of the pituitary gland;
- Skien syndrome;
- prolonged use of corticosteroids.
Tertiary or hypothalamic type - due to lower production thyrotropin-releasing hormone.
Causes of secondary and tertiary hypothyroidism are similar.
Tissue or peripheral hypothyroidism occurs due to dead cell receptors target tissues to the effects of thyroid hormone for all other normal links - thyroid, pituitary - hypothalamus.
The causes and mechanism of development of this disease are not clear. It is believed that the violation is at the gene level. The disease is often hereditary, when there are anomalies in certain organs - internal and musculoskeletal system.
According to the severity of symptoms also highlighted several forms:
- Subclinical (hidden) hypothyroidism appears normal levels of T3 and T4.
- Manifest forms - increased TSH, and the T3 and T4 decreased.
- Hypothyroidism, myxedema complicated by - this is the most severe degree, occurs in the absence of treatment of hypothyroidism. This may develop myxedema coma with a fatal outcome.
symptomatic manifestations
When the latent form of hypothyroidism symptoms in men does not occur for a long time. Available weakness, fatigue, desire to constantly lie down, reduced memory and attention, no inner vitality - all this is written down on fatigue.
Hypothyroidism is detected only at the time assays. Most men have heard about the signs of decline in testosterone, but they do not realize that these symptoms are very similar to hypothyroidism. And, in turn, hypothyroidism can cause a decrease in testosterone.
Another manifestation of hypothyroidism in men is an increase in the number of testicular cells. In these patients, the testes grow larger, but the number and quality of sperm is reduced. By the number of sperm cells reduced their mobility is also low. Developing impotence.
Thyroid - a power generator of the body; so hypothyroidism disrupted the whole organism. Many of the symptoms of hypothyroidism in men like women, but has its own legal characteristics. For example, while women are gaining weight, man, it lost due to muscle atrophy and strength.
Hypothyroidism in men and women can total about 300 signs and symptoms, which affects almost all organs and systems. But each person has their own combination of them. Hypothyroidism in men: the signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism are in direct proportion to the increase of severity of the condition.
Without timely or improper treatment of hypothyroidism progresses always. With the progression of disease signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism in men are pronounced and they are all connected with the slowing of metabolism:
- CNS side effects - headaches, poor concentration and memory; unexplainable mood swings and nervousness.
- From the CCC - bradycardia, hypotension, heart pain.
- GIT - due to lower the tone of smooth muscles of the digestive violated.
- Decreased appetite.
- Develops slowing motility and gall bladder operation.
- Appear constipation.
- Periodically, the patient complains of nausea and vomiting.
- Changes in appearance: the face is pasty, puffy due to edema.
- Nasal breathing is difficult, there is a wheezing while breathing.
- The lips also become swollen.
- The vocal cords become swollen and the voice becomes hoarse.
- Reduced hearing.
- The manifestations of the skin: it becomes a pale yellowish, waxy tinge, dry, facial expressions disappears - myxedema face; nails break, they appear lateral stripes; loss and brittle hair eyebrow eyelashes head.
- Reduced body temperature to 35-36,2 °; constantly feel cold hands and feet;
- Joints - swollen. In the body of muscle weakness and myalgia; movement and fettered gait.
- Retardation of thought and speech.
Decreased libido; disturbed potency, erections and ejaculation. At the beginning of the pathology sperm count is normal, but the mobility is reduced. Reduced sperm count and motility observed in the later stages.
Most often, medical attention men pay when clearly manifested dyspnea, there are severe pain in the heart and constipation. You may notice a clear decrease in muscle mass. It is for this reason, they are often unable to perform normal operation. Rare disease in men is replaced by the severity of its course.
For a long time, men are hoping that all the symptoms appeared shortly take place, and that's because it does not go to the doctor.
The men in the development of hypothyroidism, changes occur in the bones, it happens due to the fact that in the male body is a violation of calcium-phosphorus metabolism.
Level manifestations varying symptoms depends only on the severity of the disease.
diagnostic merorpriyatiya
If there is hypothyroidism, there is a decrease of T3 and T4, while the TSH usually normal or elevated.
The diagnosis of "hypothyroidism" a man should be put on the basis of several symptoms, tests for hormone levels (TSH, T3, general, free T3, T4 free, TPO - necessarily must pass all) and ultrasound research.
In addition to blood tests, instrumental methods are used:
- Ultrasonography (ultrasound) determines the size and density of the thyroid gland.
- Upon detection units carried aspiration biopsy - TAB - to eliminate the cancer process.
To confirm the diagnosis of symptoms include:
- low acidity;
- the absence of albumin necessary to maintain normal oncotic pressure of the blood;
- increased levels of bad cholesterol and TSH;
- reduction of triiodothyronine and tetraiodothyronine;
- decrease ATP synthesis;
- occurrence of bradycardia;
- reducing body temperature;
- hypertrophy of the heart.
treatment Guidelines
Treatment of the disease - this is HRT. The formulations may be natural or synthetic. The most commonly performed levothyroxine preparations. The most effective of them - Eutiroks - a synthetic form of the hormone T4. The dose is calculated according to the formula available to the endocrinologists.
The dose depends on the weight, age and severity of pathology. Some men levothyroxine sodium helps to completely remove the symptoms of hypothyroidism, while others require the addition of a second thyroid hormone, T3 - Liotironin.
Symptoms and treatment are related because of their sheer numbers, so the other medications usually symptomatic. Autoimmune lesion or after complete removal of the thyroid gland receiving thyroxine is appointed for life. During HRT periodically donates blood on hormones to control the correctness of treatment and the need for adjustments.
Treatment of myxedema coma: to be held only in the intensive care unit. IVL is necessary, intravenous administration of high doses of corticosteroids; thyroid hormones, stabilize metabolism and blood sugar levels.
Lethal outcome myxedema coma occurs in 40%, prognosis depends on the age of the men and the presence of cardiovascular pathologies.
Measures to prevent hypothyroidism:
- Do not drink water from the tap; there's always a lot of fluorine and chlorine, which slows the absorption of iodine - a basis for the production of thyroid hormones.
- Refusal of gluten and casein A1 - is a wheat and dairy products because the proteins gluten and casein a1. These proteins may cause a syndrome of "leaky intestines", which results in thyroiditis. It is better to eat dairy products containing casein A2.
- Bisphenol A (BPA) - negative for thyroid, contained in a plastic container.
- Check the level of iodine in the blood. If it is low, add in food seaweed, seafood. It is also recommended to be tested for TPO, if these antibodies are elevated, iodine should not drink.
- Shoe liver and body - phytotherapy milk thistle, turmeric, chlorella and coriander (cilantro).
- More selenium - its sources: nuts, salmon, sunflower seeds, beef, mushrooms and onions.
- Adaptogen - helps to reduce cortisol (adrenal stress hormone) and improve thyroid function (ginseng, Rhodiola rosea, basil, poppy and others.). Between the thyroid and adrenal connection is so close that hypothyroidism is rarely seen without disruptions to the adrenal glands. Thyroid is also very sensitive and reacts to stress.
- Avoid fillings with amalgam - they are heavy and can also adversely affect the thyroid.
- Reducing carbohydrate intake, eat more protein. Healthy fats - coconut oil and milk, avocado, organic beef, wild salmon, flaxseed and chia seeds; nuts, nut oils, legumes. Of soy protein and rapeseed oil should be abandoned. Grease - predecessor of the hormones. Lack of cholesterol negative for thyroid.
- Prophylactic administration of vitamins and minerals. Deficiency of vitamin D, A, B; Fe, Se, Zn, Cu, omega-3 fatty acids, may aggravate the symptoms of hypothyroidism in men.
- Goitrogens - goitrogenic substances - from their diet should be excluded, because they interfere with the normal operation of the thyroid gland. Among them are: all kinds of cabbage; turnips and radishes, peanuts, peaches, strawberries, spinach, millet, soybeans. These foods are better to eat little or cooking.
- Supplementation with glutathione - a powerful antioxidant that boosts the immune system and fights with the AIT. It can inhibit the autoimmune attack, protect and heal the thyroid tissue.
- Check the intestine - is to be healthy and active microflora; 20% of the thyroid gland functions depend on it. Therefore needs periodic intake of probiotics.
See also:What does a lump on the penis?
You should also protect themselves from exposure - cover neck during an X-ray. Do not use pans with non-stick coating.
A source: http://endokrinologiya.com/diseases/gipotireoz-u-muzhchin-simptomy
The first signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism in men, treatment methods of pathology and stabilize hormonal levels

Thyroid hormones are synthesized, which perform a very important function in the body. They are responsible for the metabolic processes, the formation of immune control mechanism of many systems. The thyroid gland in men has some differences from the female. Any changes that occur in the body are found more easily in the male body.
Due to various reasons may be disrupted activity of the thyroid gland and appear stable hormone deficiency, hypothyroidism develops. Men's syndrome is diagnosed most often after 40 years. If time does not detect and begin treatment of hypothyroidism, it can cause serious complications.
hormonal regulation
Thyroid produces the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine (T3, T4). To their synthesis was normal, the body must have enough iodine. T3 and T4 are the regulators of metabolism, heart beat, blood pressure, reproductive functions.
The regulation of the thyroid gland and controls the production of hormones it performs the pituitary gland. Organ synthesize thyroid hormone, which depends on the concentration of T3 and T4 levels. hypophysis hypothalamus regulates function by thyrotropin-releasing hormone. By reducing thyroid hormone stimulates the pituitary gland activity, increased TSH levels.
Normal male TTG can be varied within 0.4-4.0 mU / l. Preferably, the hormone was not above the level of 2.0-2.5. Increasing these values may indicate a predisposition to hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism code ICD 10 - E03.
The causes of the disease and species
Most often, hypothyroidism occurs against a background of inflammation in autoimmune thyroid gland.
Other causes of the syndrome may include:
- Congenital changes in the gland;
- treatment with iodine toxic goiter;
- iodine deficiency in the body;
- thyroid tumors.
Based on the causes of hypothyroidism in men are divided into several types:
- primary (thyrogenous);
- secondary (pituitary);
- tertiary;
- tissue.
In 95% of cases the disease occurs primary hypothyroidism. It arises due to the impact of negative factors:
- chronic iodine deficiency;
- prolonged use of iodine-containing formulations;
- congenital underdevelopment of the thyroid gland;
- an inherited disorder synthesis T3 and T4;
- organ resection;
- malignancies;
- thyroiditis;
- radiation exposure;
- effects of dopamine, lithium perchlorate on the body.
Secondary hypothyroidism is a thyroid gland is associated with disruption of the pituitary gland, failure occurs when the production of TSH. This happens for a reason:
- congenital underdevelopment of the pituitary gland;
- head trauma with damage to the prostate;
- brain tumor;
- pituitary adenoma;
- lymphocytic hypophysitis;
- the impact of radiation therapy;
- long-term use of glucocorticoids;
- pituitary tissue necrosis as a result of severe blood loss.
Tertiary hypothyroidism occurs due to hypothalamic dysfunction. The tissue form of the disease caused by the organism resistance to thyroid hormone, or violation of their transportation.
The first signs and symptoms
When reduced activity thyroid, primarily occurs metabolic abnormalities:
- reduced process of splitting proteins;
- develops hypoglycemia due to increased resistance to carbohydrates;
- increases cholesterol in the blood;
- there is a delay of sodium and fluid in the tissues.
On a note! In hypothyroidism increases the permeability of lymphatic vessels, lymph flow is slowed down. This leads to the exit through the walls of the protein albumin into the surrounding cavity. Increased oncotic pressure. Tissue begin to attract water, which leads to edema.
Depending on how these processes can be expressed, identified a number of degrees of hypothyroidism:
- easy (Subclinical hypothyroidism) - external symptoms are absent or are very weak. Blood test shows improvement TTG, T3 and T4 are normal.
- manifest - there are outward signs of hypothyroidism, increased levels of TSH, thyroid hormones decrease.
- Weight - symptoms are severe with prolonged hypothyroidism, the patient may experience a coma.
Characteristic signs of hypothyroidism in men:
- puffiness of the face;
- dry, pale skin;
- hair loss;
- a feeling of weakness;
- low body temperature, feeling of coldness;
- lack of exercise;
- deterioration of brain activity;
- emotional instability;
- hypotension;
- decreased heart rate;
- poor appetite.
Hypothyroidism affects on the reproductive system, which is manifested opredelnie symptoms:
- decreased libido;
- ejaculation disorder;
- erectile dysfunction.
Diagnostics
If you suspect a hormonal disturbances in the body is necessary to address to the endocrinologist. The main method of diagnosis of hypothyroidism - a blood test for hormones.
Determined concentrations of thyroxine and triiodothyronine, TSH level. In primary hypothyroidism, TSH level will be raised, and the T3 and T4 level is lowered.
If the TSH concentration is significantly reduced, it is evidence of a secondary or tertiary hypothyroidism.
To confirm the diagnosis and determine the reasons for the decline of thyroid function appoint additional research:
- blood autoantibodies to thyroid cells;
- biochemistry of blood (an important indicator of the level of cholesterol and lipids);
- Thyroid ultrasound;
- scintigraphy;
- needle biopsy (for suspected malignant process in the iron).
How to treat hypothyroidism in men
The main direction in the treatment of hypothyroidism - the use of hormones, T3 and T4 replacement deficit. The dosage and duration of medication endocrinologist determines based on the obtained analysis results.
Due to hormone replacement therapy there were positive effects:
- normal energy metabolism;
- restored carbohydrate and lipid metabolism;
- stabilize the cardiovascular system;
- improving the state of the central nervous system and the musculoskeletal system.
Autoimmune thyroid lesions requiring life-long reception of a thyroxine. With a certain periodicity man should control the hormones, to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. If necessary, the dosage adjusted.
It is important to observe a special diet in hypothyroidism. At deficiency of iodine in the diet is recommended to increase products, the content of this element (seaweed, persimmon). You can take dietary supplements with iodine after consulting your doctor.
In the case of coma patient is placed in the intensive care unit. There he made mechanical ventilation, intravenous glucocorticoids and thyroid hormones in large doses. In 40% of cases, coma with hypothyroidism in men are fatal.
helpful hints
For the prevention of hypothyroidism in men is recommended:
- Do not drink unfiltered tap water. Fluorine and chlorine are present in it, cropped iodine absorption.
- Drinking water from glassware or stainless steel tanks. Do not use plastic bottles with bisphenol A (BPA) for the liquid.
- Eat foods rich in selenium (salmon, sunflower seeds, beef, onions).
- Do not put seals with amalgam.
- Reduce the consumption of carbohydrates, proteins increased in the diet. Sugar, flour, caffeine substitute healthy fats contained in avocados, flax seeds, coconut oil. Thanks to the proteins of thyroid hormones are transported rapidly to the tissues. It is advisable to increase the intake of protein foods, like nuts, legumes.
- To stimulate the immune system can take supplements with glutathione.
- Maximally protect themselves from all sorts of exposures. During the X-ray to request to issue a protective agent for the thyroid gland.
Hypothyroidism in men may be an indication of serious violations in the body. If you suspect a hormonal disruptions is necessary to address to the endocrinologist, to hand over the necessary tests. To obtain a positive result in the treatment of hypothyroidism should strictly follow the doctor's recommendations, to constantly monitor the state of the thyroid gland. Otherwise, it may cause irreversible complications significantly impair the individual's quality of life.
See also:Stage prostate cancer and forecasts
A source: http://vse-o-gormonah.com/zabolevaniya/gipotireoz/u-myzhchin.html
How is the diagnosis and treatment of male hypothyroidism

Hypothyroidism is diagnosed in men are much less likely than women to suffer affliction mostly elderly people.
Pathogenesis
Primary hypothyroidism develops in congenital hormonal disorders, pronounced deficiency of iodine, selenium, autoimmune thyroiditis, after receiving thyreostatics, radioactive iodine or complete removal of the thyroid gland (iatrogenic hypothyroidism).
Symptoms occur when secondary hypothyroidism dysfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary regulation. The cause of pathology can be hypopituitarism, thyrotropin violation synthesis and transport, decreased generation TSH, brain tumor, traumatic brain injury.
The reasons for tertiary hypothyroidism:
- autoimmune reactions, development of antibodies to thyroid hormones T3, T4, TSH;
- deiodination of the hormones in the blood serum T3 and T4 bound to transport proteins and are inactive.
In primary hypothyroidism males decreases the amount of thyroid tissue, therefore decreasing production of thyroxine and triiodothyronine organ follicles. Autoimmune processes provoke the production of specific antibodies which shchitovidku perceived as a foreign body and damage its cells. This reduces the amount of glandular tissue develops hypothyroidism.
symptoms
Failure of the thyroid gland in men can occur for a long time virtually asymptomatic and discovered incidentally during a medical examination.
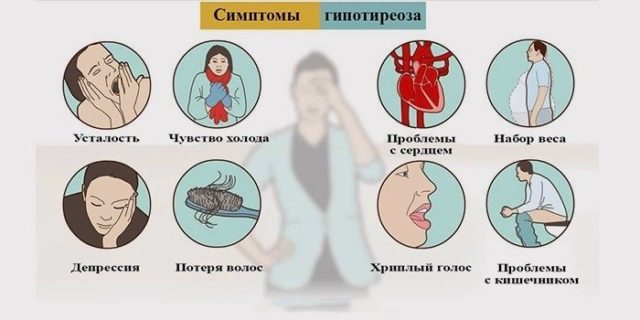
Manifestations initial stage hypothyroidism expressed clearly, for patients receiving their usual fatigue, feeling weak, lack of energy, they have a reduced concentration of attention, there is a lethargy.
Subsequently, the clinical picture is changed, and signs of the disease appear more pronounced.
The symptoms of overt hypothyroidism thyroid:
- From the nervous system: myalgia, headache, paresthesia, sleep disturbance (daytime sleepiness, insomnia night), deteriorating mental abilities, developed polyneuropathy, men irritable, prone to depression.
- Cardio-vascular system: low blood pressure, bradycardia, tachycardia, inflammation of the serous membranes of the heart, peritoneum, joints.
- Reproductive system: hypothyroidism in men decreased libido, erection is deteriorating, there is premature ejaculation, reduction in the number and motility, in severe forms of the disease develops impotence, infertility.
- Metabolic abnormalities: hypothermia, overweight, cold intolerance, chilliness hands, feet.
- Changes in appearance of hypothyroidism thyroid: puffy face, swelling of the eyelids, the increase in the lips and tongue, swelling of the lower extremities, hoarseness, difficulty in nasal breathing, hearing impairment, yellowness, dryness of the skin. Much hair falls on his head, eyebrows, body, nail plates become thinner, on the surface of the transverse bands are formed. In patients with severely swollen abdomen, umbilical hernia may occur.
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract in hypothyroidism thyroid: biliary dyskinesia, colon, chronic constipation, flatulence, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, increased liver size.
- Musculoskeletal system: inflammation, swelling of the joints, malignant muscle weakness, muscle hypertrophy, stiffness in the movements.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism every man can manifest in different ways. The intensity of the clinical picture depends on the duration of the course of disease and the patient's age. In most cases the malfunction of one of the systems, making it difficult to correct diagnosis.
classification of hypothyroidism
Decreased thyroid function in men may be congenital or acquired in nature, the latter form occurs in 90% of cases.
Depending on the degree of disruption of the internal organs and systems are classified hypothyroidism:
- Subclinical (compensated) type is characterized by the lack of pronounced symptoms, increased levels of TSH, while T3 and T4 remain in the normal range.
- Symptomatic (decompensated) hypothyroidism thyroid has multiple features, increased thyrotropin, thyroxine and triiodothyronine, and significantly lowered.
- Complicated or myxedema coma - a condition caused by incorrect treatment or lack of it, while picking up the characteristic symptoms, slows down all the vital processes, the lethal Exodus.
Classification of hypothyroidism thyroid based on etiology:
- primary;
- secondary;
- tertiary;
- tissue.
Depending on the type of disease is assigned further treatment. Men with a hidden (subclinical) hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland may be a long time did not go to the doctor and not have pronounced symptoms. Usually visit the doctor with complaints of systemic violations. the true cause of sickness set in the survey.
diagnosis of hypothyroidism
Examining a patient and assigns a laboratory, instrumental studies endocrinologist. Patients pass analysis on the level of thyroid hormones. There is reduction of levels of T3 and T4, TSH can be raised or remain in the normal range.
And also conducts research ELISA for antibodies to the tissues of the thyroid gland: a ATPO AT, AT to TTG. According to the biochemical composition of the blood was a high concentration of cholesterol. Hypothyroidism is a characteristic marker of the development of various forms of anemia.
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland allows us to estimate the size and body condition. In the presence of nodules shown holding needle aspiration cytology with further biopata cancer cells.
Differential diagnosis includes congenital thyroid abnormalities, Down syndrome, Hirschsprung's disease, Chondrodystrophy.
hypothyroidism treatment
Hormone replacement therapy is natural or synthetic analogs of thyroxine. Dosage is adjusted individually for each patient, begin taking pills from small doses with gradual increases.
Improving the condition of patients with compensated form of hypothyroidism the thyroid gland occurs in the first week, and the main symptoms disappear within a month. In older men, the susceptibility to therapy is worse, so the result is achieved more.
The main effects of hormone replacement therapy in hypothyroidism:
- regulation of energy metabolism;
- normalization of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism;
- Stabilization of the cardiovascular system;
- impact on the musculoskeletal and nervous system.
Autoimmune lesion or after complete removal of the thyroid gland receiving thyroxine is appointed for life. During treatment required periodically be tested for thyroid hormone levels to assess the effectiveness of substitution therapy and correction of dosing regimen.
In marked iodine deficiency is assigned to a special diet that includes foods high in iodine. In addition, patients taking pharmaceutical supplements (Jodomarin). Symptomatic therapy is to relieve symptoms associated hypothyroidism.
Treatment of myxedema coma is performed in an intensive care setting, do artificial respiration, intravenously administered high doses of glucocorticoid and thyroid hormones stabilize metabolic processes, the level of blood sugar. Lethal outcome myxedema coma occurs in 40%, the prognosis depends on the age of the men and the presence of cardiovascular complications.
A source: https://gormonys.ru/zabolevaniya/gipotireoz/simptomy-u-muzhchin.html
hypothyroidism
hypothyroidism - the most common form of functional disorders of the thyroid gland, which develops as a result of long resistant hormone deficiency of the thyroid gland or reducing their biological actions at the cellular level. Hypothyroidism can not be detected for a long time.
This is due to a gradual, noticeable beginning of the process, a satisfactory state of health of patients in the light and moderate disease symptoms erased assessed as fatigue, depression, pregnancy.
The incidence of hypothyroidism is about 1% among women of reproductive age - 2%, increasing to 10% in the elderly.
The lack of thyroid hormones causes systemic changes in the body. Thyroid hormones regulate energy metabolism in the cells of organs and their deficit is manifested in reducing tissue oxygen consumption, reducing power consumption and processing power substrates.
In hypothyroidism disturbed synthesis of various volatile cellular enzymes necessary for normal cell activity. In the case of running hypothyroidism occurs mucinous (slimy) edema - myxedema, most pronounced in the connective tissue.
Myxedema develops as a result of excessive accumulation of glycosaminoglycans in tissues, which, having increased hydrophilicity, retain water.
Classification and causes of hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism can be acquired and congenital (diagnosed after birth and can be of any genesis). The most common is acquired hypothyroidism (99% of cases). The main causes of acquired hypothyroidism are:
- chronic autoimmune thyroiditis (direct damage to the parenchyma of the thyroid gland by the body's own immune system). Leads to hypothyroidism later years and decades after its inception.
- iatrogenic hypothyroidism (for partial or complete removal of the thyroid gland, or after treatment with radioactive iodine).
The above-mentioned reasons cause often irreversible persistent hypothyroidism.
- treatment of diffuse toxic goiter (reception thyreostatics);
- an acute shortage of iodine in food, water. Mild to moderate iodine deficiency in adults does not lead to hypothyroidism. In pregnant women, newborns and mild to moderate iodine deficiency causes a transient disturbances of thyroid hormone synthesis. In the case of transient hypothyroidism thyroid dysfunction may disappear during the natural course of a disease or after the disappearance of the calling factor.
Congenital hypothyroidism is caused by congenital structural abnormalities of the thyroid gland or hypothalamus - pituitary system, the synthesis of thyroid defect hormones and various exogenous influences in utero (use of drugs, the presence of maternal antibodies in autoimmune thyroid pathology). Maternal thyroid hormones, penetrating through the placenta, offset control fetal development, who has a thyroid abnormality. After the birth of blood levels of maternal hormones newborn falls. Deficiency of thyroid hormone causes irreversible underdevelopment of the central nervous system of the child (eg, cerebral cortex) that mental retardation is manifested in various degrees, up to cretinism, disturbance and other skeletal development authorities.
See also:Kriptospermiya and low concentration of spermatozoa
Depending on the level of disturbances occurring isolated hypothyroidism:
- primary - occurs due to pathology of the thyroid gland and is characterized by increased levels of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone);
- Secondary - associated with damage to the pituitary gland, T4 and TSH levels are low;
- Tertiary - develops in violation of the hypothalamus.
Primary hypothyroidism is caused by inflammation, aplasia or hypoplasia of the thyroid gland, hereditary defects of the biosynthesis of thyroid hormones, subtotal or total thyroidectomy, insufficient intake in body iodine. In some cases, the cause of primary hypothyroidism is unclear - in this case, is considered to be idiopathic hypothyroidism.
Rarely observed secondary and tertiary hypothyroidism can be caused by various damage hypothalamic-pituitary system, lowering control of thyroid activity (tumor, surgery, irradiation, trauma, hemorrhage). Self-released peripheral (tissue, transport) hypothyroidism caused by tissue resistance to thyroid hormone, or a violation of their transport.
Clinical features of symptoms of hypothyroidism are:
- absence of specific features unique to hypothyroidism;
- symptoms similar to symptoms of other chronic physical and mental illnesses;
- the absence of correlation between the level of deficiency of thyroid hormones and the clinical severity symptoms: manifestations may be absent in clinical phase or be already strongly expressed in a subclinical phase hypothyroidism.
Clinical manifestations of hypothyroidism depends on its cause, the patient's age, as well as the rate of increase of the deficit of thyroid hormones.
Symptomatology of hypothyroidism is generally characterized polisistemny, although individual patients prevail complaints and concerns on the part of some - or a single organ system that often prevents to put right diagnosis. Moderate hypothyroidism may show no signs.
When persistent and prolonged hypothyroidism, the patient is a distinctive appearance - swollen, bloated a person with a yellowish tinge, edema of the eyelids, limbs, associated with fluid retention in the connective tissue. Concerned about a burning sensation, tingling, muscle pain, stiffness and weakness in the hands.
There have dry skin, brittle and dull hair, thinning and increased their loss. Patients with hypothyroidism are in a state of apathy, lethargy. For severe form of the disease is characterized by slowing of speech (like "tongue-tied").
Voice changes occur (to Low, hoarse) and hearing loss due to edema of the larynx, tongue, and the middle ear.
Patients noted a slight increase in weight, hypothermia, constant chilliness, indicating that the decrease in the level of metabolic processes. Disorders of the nervous system manifest deterioration of memory and attention, decreased intelligence, cognitive activity, interest in life.
There are complaints of weakness, fatigue, sleep disturbance (daytime sleepiness, difficulty falling asleep at night, insomnia). General condition manifested depressed mood, sadness, depression. Neuropsychiatric disorders in children older than 3 years of age and in adults are reversible and completely bypass the appointment of replacement therapy.
Congenital hypothyroidism, lack of replacement therapy leads to irreversible consequences for the nervous system and body as a whole.
Marked changes in the cardiovascular system: bradycardia, diastolic hypertension and mild degree pericardial effusion (pericarditis).
There are frequent, then persistent headache, increased blood cholesterol, anemia develops.
On the part of the digestive system a decrease in production of enzymes, poor appetite, constipation, nausea, flatulence, may develop biliary dyskinesia, hepatomegaly.
The women on the background of hypothyroidism develop disorders of the reproductive system, which is associated with the failure of the menstrual cycle (amenorrhea, dysfunctional uterine bleeding), mastitis development.
A pronounced deficiency of thyroid hormones threaten infertility, less overt hypothyroidism in some women does not preclude the pregnancy, but it threatens the high risk of miscarriage or birth of a child with neurological violations.
In both men and women, there is a decrease of sexual desire.
Clinical manifestations of congenital hypothyroidism are often unable to help in its early diagnosis. Early symptoms include bloating, umbilical hernia, muscle hypotonia, large tongue, posterior fontanelle and increase thyroid, low voice.
If timely treatment is not started, then at 3-4 months of age develop difficulty in swallowing, reduced appetite, a little weight gain, bloating, constipation, pale and dry skin, hypothermia, muscle weakness.
At the age of 5-6 months manifested delayed psychomotor and physical development of the child, there is a disproportion of growth: delayed closure of fontanelles, broad bridge, increasing the distance between the paired organs - hypertelorism (between the inner edges of the sockets, pectoral nipples).
Complication of congenital hypothyroidism is a violation of the central nervous system and the development of a child's mental retardation (mental retardation), and sometimes it is extreme - cretinism.
The child lags behind in growth, sexual development, prone to frequent infections with prolonged chronic course. Independent chair it is difficult or impossible.
Hypothyroidism during pregnancy is manifested in a variety of fetal anomalies (heart defects, pathology of the internal organs), with functional impairment of the child's birth the thyroid gland.
The most serious but rare complication of hypothyroidism - hypothyroid (myxedema) coma. Generally it occurs in elderly patients with long-flowing, untreated hypothyroidism, comorbidity having low social status or no maintenance.
Development of hypothyroid coma contribute to infectious disease, trauma, hypothermia, the administration of drugs which depress the central nervous system activity.
Hypothyroid coma manifestations are: progressive CNS inhibition, confusion, low body temperature performance, appearance dyspnea, decreased heart rate and blood pressure, urinary retention, swelling of the face, hands and body, E. obstruction.
Accumulation of fluid in the pericardial and pleural cavities dramatically disrupt heart activity and breathing. A significant increase in blood cholesterol level provokes early development of coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, cerebral arteriosclerosis, ischemic stroke.
Men and women with hypothyroidism may suffer from infertility, they disturbed sexual function. In hypothyroidism there are serious disturbances of immunity, which appear frequently arise infections, the progression of autoimmune processes in the body, the development of cancer diseases.
diagnosis of hypothyroidism
For the diagnosis of hypothyroidism endocrinologist established fact reduce thyroid function on the basis of examination of the patient, his complaints, and laboratory results:
Diagnosis of congenital hypothyroidism is based on neonatal screening (definition of level TTG at 4-5 days of life of the newborn).
hypothyroidism treatment
Thanks to the achievements of the pharmaceutical industry, allowing artificially synthesize thyroid hormone, modern endocrinology is an effective method for the treatment of hypothyroidism. The therapy is conducted by replacing the missing thyroid hormone in the body of a synthetic analogue - levothyroxine (L-thyroxine).
Symptomatic (clinical) hypothyroidism requires hormone therapy regardless of patient age and comorbidity.
Individually assigned embodiment the start of treatment, the initial dose and the speed of its increase.
When latent (subclinical) hypothyroidism absolute indication for substitution Therapy is his diagnosis of a pregnant woman, or planning to become pregnant in the near future time.
In most cases normalization of the general condition of the patient hypothyroidism begins in the first week of initiation of drug. Complete disappearance of clinical symptoms usually occurs within a few months.
In the elderly and debilitated patients response to the drug develops more slowly.
Patients with cardiovascular disease, it takes particular care to select a dose of the drug (excessive intake of L-thyroxine increases the risk of angina, atrial fibrillation).
In the case of hypothyroidism, resulting from the removal of the thyroid gland or radiotherapy, shows a typical synthetic hormones throughout life. Lifelong treatment of hypothyroidism is also necessary against the background of autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's disease). During treatment the patient to visit a doctor regularly is necessary for the correct dose of the drug, to control the level of TSH in the blood.
If hypothyroidism occurs against a background of other diseases, normalization of thyroid function often occurs in the course of curing the underlying pathology. The symptoms of hypothyroidism caused by intake of some drugs, are removed after withdrawal of these drugs.
If the cause of hypothyroidism - a lack of iodine consumption with food, the patient is prescribed iodine-containing drugs, consumption of iodized salt, seafood.
Treatment of hypothyroid coma spend in intensive care units, and intensive care unit with the purpose of intravenous injections of large doses thyroid hormones and corticosteroids, correction of hypoglycemia, electrolyte and hemodynamic violations.
Prediction and prevention of hypothyroidism
The prognosis of congenital hypothyroidism is dependent on the timeliness started replacement therapy.
With early detection and timely treatment of hypothyroidism launched substitutionary in infants (1 - 2 weeks of life) the development of the central nervous system almost does not suffer and correct.
When later compensated congenital hypothyroidism develops pathology of the central nervous system of the child (mental retardation), disrupted the formation of the skeleton and other organs.
Quality of life in patients with hypothyroidism, compensating host treated, usually not reduced (there are no restrictions except the necessity of daily administration of L-thyroxine). Mortality in the development of hypothyroid (myxedema) coma is about 80%.
Preventing the development of hypothyroidism is good nutrition with adequate intake of iodine and aimed at its early detection and timely replacement therapy initiated.
A source: http://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/diseases/zabolevanija_endocrinology/hypothyroidism