Causes and treatment of hypogonadism in men
Hypogonadism in men: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment

Hypogonadism - a a disease that is characterized by a total lack of male hormones in the body, which leads to the fact that a representative of the stronger sex loses its sexual characteristics. Develop this serious pathology can independently or on the background of testicular diseases. What hypogonadism in malesWe consider in more detail.
pathology Description
Hypogonadism code in ICD 10 - E23. Consider what hypogonadism in men.
The disease develops in the presence of inadequate functioning gonads, resulting in greatly reduced production of male hormones.
Prolonged exposure in this state causes a significant change in the appearance of a man for the worse. Also male hypogonadism a negative impact on quality of life and its duration.
classification of diseases
This pathology is associated with the production of hormones in the brain. Depending on the extent of damage the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, distinguish these types of this disease:
- Hypergonadotrophic hypogonadism in males. The essence of this kind is the minimum testosterone production by the testes or the complete absence of this process. At this stage, you can select Primary congenital hypogonadism - a syndrome or Klinefelter anorchia. Also in this group applies secondary hypogonadism. This form of disease develops as a result of injury, toxic damage of the testes, advanced forms of diseases associated with the functioning of the testes.
- hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. For this type of disease is characterized by a reduced rate of pituitary hormones that promote the production of testosterone, or its complete absence. This type of pathology may be either congenital or acquired in nature.
- Normotropny hypogonadism. This form of disease is characterized by an extremely low testosterone. But while there is the normal rate of gonadotropins. This group can be attributed age hypogonadism, The disease on the background of obesity or hyperprolactinemia.
more isolated subclinical hypogonadism - a pathology that develops as long as it does not appear the first signs.
The causes of the disease
The prerequisites for the emergence of this disease are many. It depends on its type. Let us examine them in more detail.
congenital hypogonadism
This pathology is caused by certain congenital diseases, namely:
- Klinefelter syndrome. It characterized by a pathological condition, wherein the testosterone index largely reduced.
- Anorchia. Insufficient development of the testes or lack thereof.
- Shershevskii syndrome, Turner. This congenital pathology that is characterized by abnormalities of physical development, short stature and sexual infantilism.
congenital hypogonadism most often associated with a genetic predisposition.
Acquired primary hypogonadism
The disease begins to progress because of the impact of such adverse factors:
- brain injury in an intermediate portion;
- insufficient concentration of gonadotropins;
- testicular descent latency in the scrotum;
- congenital tumors of the central nervous system;
- breach of the functioning of the adrenal and thyroid glands.
primary hypogonadism It has acquired the character, since developing against the background of other diseases.
Secondary hypogonadism is congenital
The causes of this pathology forms may be:
- Kallman syndrome. It is characterized by delayed sexual development.
- The disadvantage in the organism luteinizing hormone, which is responsible for the quality and quantity of sperm.
- Inherited diseases that are accompanied by indicators in the body of male sex hormones.
Acquired secondary hypogonadism
The causes of this disease are external irritants. These include:
- the appearance of tumors in the pituitary and hypothalamic area;
- surgery to remove tumors in the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus;
- radiation therapy or chemotherapy hypothalamic area;
- bleeding in the brain;
- appearance hyperprolactinemia;
- hypophyseal syndrome.
A source: https://mzdorov.com/andrologia/gormony/gipogonadizm-u-muzhchin.html
Hypogonadism in men: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment

Hypogonadism in men - congenital or acquired disorders, which is expressed in short supply sex hormone testosterone.
The disease is often accompanied by underdevelopment of secondary sexual characteristics and genital violation metabolic processes (obesity or dystrophy), cardiac problems to the functioning and bone system.
However, in each case, male hypogonadism can occur in their own way - symptoms depend on the degree of testosterone deficiency and disease duration. That is why the treatment of hypogonadism in men assigned to only the doctor after a thorough inspection.
Sex hormones - this is what makes a man a man.
Features of occurrence
Accepted provide primary and secondary hypogonadism, which may be either congenital or acquired. Reasons for each different form of the disease.
The primary form
Primary hypogonadism occurs in disorders of functioning of the testes, their inability to produce testosterone.
This hormone in the body of the patient is much less than the luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones (LH and FSH).
This form of the disease called normogonadotropic (ie, LH and FSH levels remain in the normal range). Congenital primary hypogonadism appears on the background of the following offenses:
- ectopia - vice when in intrauterine fetal testis displacement occurs in the scrotum, it remains in the peritoneal cavity or at the level of the inguinal canal. As a rule, undescended testicle remains underdeveloped and has a disproportionate size;
- aplasia - unilateral or bilateral absence of the testes in the fetus;
- Klinefelter's syndrome - a genetic disorder expressed in the presence of excess X chromosome;
- Sertoli cell syndrome - as a result of hereditary factors occurs effect on germinal elements testicles and seminal epithelium atrophy;
- Turner syndrome - a chromosomal disease, expressed by a number of anomalies of the physical and sexual development.
Acquired primary hypogonadism occurs due to mechanical damage to tumors and testicular boys or men. Normogonadotropic hypogonadism (hypogonadism age) sometimes seen in people for a long time abusing drugs and alcohol.
secondary form
It is this area of the brain responsible for the production of sex hormones.
Secondary hypogonadism occurs when malfunction of the hypothalamus or pituitary gland responsible for the production of LH and FSH. This disease is called "hypogonadotropic hypogonadism".
As a result of development in the male is a decrease in testosterone levels in combination with increased LH and FSH hormones.
If there is an increase in the level of hormones produced by the pituitary gland, then this form of the disease called "hypergonadotrophic hypogonadism."
Congenital secondary hypogonadism develops, if present:
- congenital hypoplasia hypothalamus generating insufficient gonadotropic hormones;
- Kallmena syndrome - congenital disorders on the X chromosome affecting the deficiency of gonadotropins and sex steroids in combination with underdeveloped smell;
- dwarfism - pituitary dwarfism is caused by underdevelopment of the thyroid gland, the testes and the adrenal glands. Height of the patient does not reach above 130 cm;
- craniopharyngioma - pituitary developmental disorders due to the pressure inherent to it a brain tumor;
- Maddock syndrome - congenital disorder caused by underdevelopment of the pituitary, where broken and gonadotropic adrenocorticotropic function;
- Prader-Willy syndrome - a rare genetic disease in which some of the genes on the paternal chromosome absent or does not operate normally.
Acquired hypogonadotropic hypogonadism may occur due to birth trauma suffered by scarlet fever, typhoid, viral infections, tuberculosis, syphilis, brain injury, brain tumor, thrombosis, embolism.
These problems can be the basis for the development of hypothalamic syndrome, or syndrome hyperprolactinemic adiposogenital dystrophy, in which there is loss of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, which manifests itself in violation of the normal production of sex hormones, obesity.
Obesity appears on the female type, the lack of hair on the body.
What are the symptoms
Hypogonadism in men may manifest themselves differently in different forms.
Congenital hypogonadism, which began to form in the first trimester of fetal development, may manifest impaired sexual differentiation - male genitals are underdeveloped (formed mikrofallos occurs undescended testicles), manifested some signs of female genital authorities. Often formed syndrome: a disproportionately elongated hands and feet, weak, narrow shoulders and chest, short neck.
In some cases, congenital male hypogonadism does not have an effect until puberty. If the deviation is acquired in childhood, it may also have symptoms persist until puberty.
The disease is accompanied by symptoms such as underdevelopment of the muscular system, high-pitched voice, reduction in size of the scrotum and penis, the absence of hair in the pubic and underarm area.
Age hypogonadism expressed decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, nervous disorders, reduced concentration, poor memory, tendency to depression and aggression.
It manifested rapid hair loss.
Other symptoms are: hair loss, irritability, sweating, dry skin, anemia, Breast augmentation men, reduced potency, obesity, especially in the abdominal area, increase the risk of fractures bones. In most cases, congenital diseases and acquired in the case of running form hypogonadism accompanied infertility.
medical intervention
Typically, the treatment program has two main objectives - the normalization of hormonal levels and recovery of sexual function.
To do this, doctors prescribe hormones (hypogonadism they treated age, children are assigned hormones in exceptional cases).
If the testicles are completely lost its functionality, the man will have for a lifetime to take preparations containing artificial testosterone deputy. When the secondary form are written stimulating gonadotropins.
Displaying treatment of hormonal drugs.
If the disease is caused by natural variations in the development of sexual organs, then a doctor's prescription can be carried out operation (for example, when bringing down testicular cryptorchidism, transplantation of testicular hypoplasia at phalloplasty member and etc.).
As a result of the timely and proper treatment of the disease decreases androgen deficiency, normal levels of hormones in the body male sexual function resumes stabilizing the development of secondary sexual characteristics, decreases the severity of symptoms.
A source: http://MensGen.ru/hormones/gipogonadizm-u-muzhchin.html
Hypogonadism in males: the treatment of primary, secondary, age
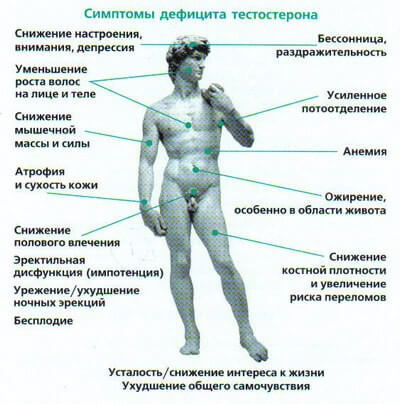
Hypogonadism in men is a state, as a result of deficiency of male hormones occurs testicular failure with reduced functional usefulness of the gonads.
hypogonadism syndrome designated as the term "androgen deficiency" in its development occurs a number of characteristic symptoms are indicative of failure of sex hormones in men body.
Such changes can occur due to a pathological condition of the testicles, as well as by the impact of other causes.
What are the main reasons
This pathological condition in an organism develops as a result of hormonal imbalance decrease the production of sex hormones, as well as the reason may be in violation of the processes biosynthesis. According to the ICD that is used for converting the diagnosis of verbal form in numeric code is designated hypogonadism E29.1.
See also:The use of apple cider vinegar with Athlete's Foot
The main causes of the disease are as follows:
- anomalies having congenital nature lead to an altered structure or in testicular seminiferous tubule;
- toxic effects on the fetus in pregnant women, consisting in the use of alcohol, narcotic drugs or nicotine;
- treatment with radiation or chemotherapy;
- therapy with hormonal drugs and drugs of antibacterial conducted for a long period;
- carry-forward of infectious diseases as mumps, vezikulita, orchitis;
- varicose testicular damage;
- adverse environmental conditions.
Types of hypogonadism disease
On the basis of the underlying causes, will be the beginning of pathological changes in the body of men, the lack of work gonads is primary, secondary and age. Primary testicular or shape is different from the rest of the influence of unfavorable factors that cause a violation of testicular function.
Secondary hypogonadism in men is caused by a violation of the pituitary due to the hypothalamus, which is responsible for hormone production, also affect testicular function. Age hypogonadism in men is a sign of changes in their reproductive system in connection with the achievement of a certain age, the reasons for which the timing and onset of medicine are not well understood yet.
Depending on the period of life when the symptoms first appeared, the disease is classified as follows:
- embryonic form - develops during location of the fetus in the womb;
- prepubertal form - occurs before the onset of puberty (usually before the age of 14);
- postpubertatnom form - is formed after the formation of the final secondary sexual characteristics.
Comparing the value produced by the androgen, the disease has the following varieties:
- Gipogonadotropnyygipogonadizm in men characterized by a decrease in the production of gonadotropins, which inevitably lead to a decrease in testosterone levels.
- Hypergonadotrophic type of hypogonadism causes a change in the testicular tissue of the testes.
- Normogonadotropnyygipogonadizm in men leads to a decrease in the functioning of the testes without disrupting normal production of pituitary hormones.
There is also another form - an idiopathic, the causes of which are unknown until the end of development.
The primary type of hypogonadism
The primary form of hypogonadism in males can be congenital or acquired as a result of postponed diseases. The most common pathological changes in men occur in utero. In this case, a newborn boy was born with a penis having a small size and underdeveloped scrotum.
As soon as the boy will grow, the pathological process is progressing well, already a teenager with diagnosis indicated the presence of extra kilos, the initial symptoms of gynecomastia and inadequate for his age, hair growth on the body.
Acquired a kind of disease the most common among men, manifests itself as a result of inflammatory processes affecting the testes in the following cases:
- disease chickenpox;
- mumps;
- epididymitis;
- vesiculitis;
- orchitis.
Secondary hypogonadism view
There may also be congenital in nature, and can be acquired as a result of inflammation, propagating in the brain membrane. Lead to such changes capable of meningitis, encephalitis, or arachnoiditis, which can occur at any age.
In the case of a congenital form of a hormone deficiency can cause disorders at the genetic level in the following pathologies:
- Prader-Willi syndrome;
- Maddock syndrome;
- Pasqualini syndrome.
All of them are explained in violation of gonadotropin secretion produced by the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus in the form of luteinizing hormone (LH) and FSH.
By reducing the concentration testosterone deficiency occurs, leading to disturbances in the genital area of men and underdevelopment of genitals.
symptoms
Primary and secondary hypogonadism forms exhibit different symptoms, depending on the age of the patient in many ways.
Prepubertal correspond to symptoms such as:
- truncated torso with elongated upper limbs;
- disproportionate addition in too high a growth or dwarfism;
- hypoplasia of the muscles;
- signs of gynecomastia with breast enlargement;
- the changed tone of voice that makes him look like a female;
- the lack of hair on the body and face;
- a small penis size, not exceeding five centimeters;
- hypoplasia scrotum of a lack of folding and thereon a pigment;
- pale skin and mucous membranes.
Such symptoms are accompanied by disease to emerge in adult males.
For boys manifestation of a pathological condition will be expressed as follows:
- poor erectile function, which is not the norm for this age group;
- weak orgasm with absence of ejaculation;
- loss of libido;
- a change in the scalp when the hair on the head change their character becomes softer and more rare;
- the lack of hair on the body;
- the length of the penis is greater than average rates;
- scrotum looks normal, with the presence of folds thereon and moderate pigmentation.
Methods used in the treatment of hypogonadism
Treatment of hypogonadism in men disease involves the use of hormonal medication, the concentration of which depends on the form of pathology.
So, if the type of disease with hypogonadotropic hypogonadal use a large dose of gonadotropin drugs with testosterone content.
Hypergonadotrophic form cure drugs with a small concentration of hormones.
When choosing a method of treatment, the doctor finds a form of pathology, as well as the age when the patient first felt the symptoms of the disease. Adults spend correction of the missing and the number of androgen treatment or prevention of impotence. Hypogonadism can not get rid of infertility in congenital form.
As the drugs used for the treatment of male hypogonadism, most of those employed that are capable of encourage greater production of testosterone, moreover, they can be both hormonal and without content hormones:
- Methyltestosterone, available in tablets, orally applied. Is contraindicated in case of malignancy in the prostate gland.
- Clomiphene - assigned in the presence of androgen insufficiency, oligospermia due to the reduction of testosterone to diagnose disorders gonadotropic pituitary function.
- Testosterone propionate injection is fast feedback.
- Fluoxymesterone in the form of tablets with a high content of hormones.
- Oxandrolone - tablets with a high androgenic effect, requiring constant monitoring of cholesterol levels.
- Androderm patch androgen, has several species on the basis of which it is attached to different parts of the body. It allows protect the liver from the negative effects of drugs.
The main objective of therapy is to eliminate the causes of the negative changes in the male reproductive system and the application of preventive measures against sexual development lag.
The patient all this time should be under the supervision of your doctor - urologist or an endocrinologist. In the treatment of some forms of male hypogonadism is caused by a hormonal imbalance, estrogen inhibitors are used in the form of Tamoxifen, or Klosilbegita Klomifentsitrat.
Some of the current situation include surgery, as the only method able to help with the lack of severity of the genital glands of male. As such, using testicular transplantation, surgery penis plastics.
Servicing is
On treatment outcome hypogonadal men greatly influenced by the form definition of the disease, its causes and timing of therapy.
To this end, it provides for the following studies:
- held generalization anamnesis with complaints against them;
- using X-ray examined state sella with the definition of its size and the possibility of a tumor in the pituitary gland or BPH;
- during spermogrammy diagnosed with azoospermia absence of sperm in the ejaculate or scanty amount;
- is mandatory blood test for hormones;
- urinalysis ketosteroids.
Results of the study reveal lower levels of testosterone, one of the important indicators, indicating the presence of hypogonadism. Levels of gonadotropins in the case of primary hypogonadism always elevated, the secondary - will be in the normal range or slightly elevated.
elimination of pathology
When the men of problems with conception it is assigned the passage of semen. For this it is necessary to abandon stand for 4-7 days before the procedure, contraindications in this period will visit bath and receive drugs.
For more reliable results it is recommended to repeat the study two weeks after the first analysis. Remedy azoospermia depend on the cause, povlokshey such changes in a man's body. Inflammation, provoked problems are eliminated by using anti-inflammatory drugs, the treatment of which can last from three to nine months.
When hypogonadism when hormonal levels will inevitably lead to azoospermia, the patient undergoes a cure gonadotropins, which will normalize hormone levels.
osteoporosis risk
One of the complications, which inevitably results in hypogonadal men, no matter it is a congenital or acquired in nature, it is osteoporosis. The main cause of such disorders in the bone condition in men is androgenic anabolic action.
The first signs of osteoporosis in men is usually seen in the development of primary hypogonadism, but in rare cases it is not ruled out in the secondary the nature of the disease, caused Kallman's syndrome and diseases and trauma acquired is the hypothalamic-pituitary head portion brain.
The probability of such pathological changes in bone condition occurs when the age weakening of the functions of the parts of the brain. To monitor the state of the bone tissue of patients with the presence of hypogonadism recommended preventive survey is radiography and densitometry.
In identifying the symptoms of changes in bone status is assigned to hormone replacement therapy. The optimal dose of the drug with the content of androgens, used to eliminate osteoporosis in men with hypogonadism has not been established. Typically, enough of one intramuscular injection of 200 mg testosterone exerting prolonged action.
Treatment with replacement therapy is carried out for life, and if monitoring of the bone showed no increase in its density, use other methods of treatment.
The effectiveness of the treatment of male hypogonadism
Persons who have this disease, you need to understand that hypogonadism is not completely cured, but treatment is only carried out contributes to its transition into chronic stage at which are in prolonged remission not manifest severe symptoms.
To achieve such a result is possible only with the timely detection of the disease, that is, at a time when the testicles have not completely lost their functions, although they temporarily and do not perform. In that case, if the patient was a complete testicular atrophy, their functionality is not possible to restore.
See also:Extender for penis enlargement - reviews of doctors and buyers
The essence of the treatment of hypogonadism in men is replacement therapy with drugs the means by which manages to increase the blood levels of testosterone, and if necessary - to reduce the number of estrogen.
On how atrophied male gonads depends on the concentration of the drug and the time limits within which you must use replacement therapy.
Formulations of hormone replacement therapy with synthetic testosterone analog content is not applicable for prostate and in the treatment of malignancies. Hormones are a contraindication for the whole period until it is eliminated by the underlying disease.
It is unacceptable to resort to self serious disease such as the drug and its dose assigns only a physician based on the individual patient.
Therapy with hormones is a direct interference with the complex system of the body. It does not always end well, because there is likely a large number of side effects from excessive libido to an over amount of body fat.
The role of traditional medicine attraction hypogonadism
Hypogonadism is a fairly serious pathology, when the male body is undergoing significant changes in the condition of sexual glands secretion and in its external appearance. To rectify the situation and lead to normal among the recipes of traditional medicine in this situation is impossible, however, to provide some help, they still can.
The primary purpose of these treatments is to increase the number of certain types of hormones in the body of a man:
- To complete the work gonads must be a sufficient number of gonadotropin in the blood, as this hormone is responsible for the regulation of their operation. In order to maintain the physiological functions of the doctors are advised to take extracts from medicinal plants, capable of exerting such an effect. First of all, this applies to devyasilu, wormwood, Vitex sacred. With the help of these plants can contribute to the normalization of hormonal levels and increase the effectiveness of the course of treatment drugs.
- No less important for patients with an inadequate gonadal function has sufficient testosterone levels. Help raise the level of tincture of ginseng, Eleutherococcus, Calamus, and such conventional plants and products used in everyday life, like garlic, celery leaves, organic coffee, mummy.
- In addition to increasing the levels of these hormones, it is equally important to reduce the amount produced by the hormone prolactin. For this purpose are used plants such as peony, leaf Potentilla goose and licorice root.
Independently proceed to any treatment, regardless of whether the drugs or useful plants to be applied, this disease is not allowed. Even if approved by a specialist if the treatment of the patient felt deterioration of health, it is necessary to stop the means of reception.
The result of the treatment
The result of treatment depends largely on the ability of the body of man and of the timely replacement therapy started. Often these drugs with hormone levels, men are forced to take life. Correctly spent treatment is usually favorable, but it will not bring full recovery.
Slight correction of a dose of testosterone a man will feel confident in their ability to meet the needs for sex and will feel the pleasure of sexual intimacy.
Many men at medical forums to share their views on the results of treatment.
In connection with this increased their desire to realization not only in their careers but also in their personal lives. Due to hormonal stability men are able to have a family, children, and feel accomplished and complete.
A source: https://uromens.ru/zabolevaniya/gipogonadizm-u-muzhchin
Male hypogonadism: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
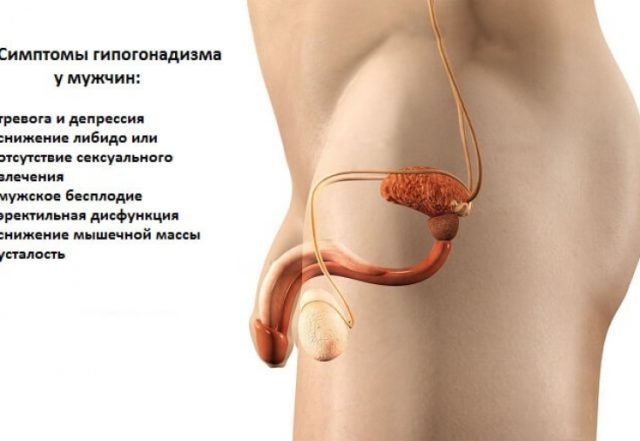
Hypogonadism - pathology associated with testicular failure and impaired production of male sex hormones - testosterone. It is associated with up to 30% of cases of male infertility.
forms of hypogonadism
Primary, or hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Infertility caused by the fact that the anterior pituitary gonadotropins share incorrectly generates - hormones that affect the male reproductive glands. Because of this disrupted the testicles, and, in particular, the synthesis of testosterone and other male hormones that affect the production of sperm.
Secondary or hypergonadotropic hypogonadism due to changes in testicular testicular tissue. They either do not produce testosterone or produce it in insufficient quantities.
normogonadotropic hypogonadism associated with normal output of gonadotropin hormones, but the testosterone level is reduced. It is most commonly associated with the age of the man. Scientists from Massachusetts have found that men's testosterone levels begin to decline by 2-3% per year from 30-35 years.
According to the Russian Ministry of Health Endocrinology Center, age hypogonadism occurs in 15% of men aged 30 to 40 years, 25% of men between 40 and 50 years of age and 40% of men older than 50 years. Also, this form of hypogonadism occurs in every second man obese.
The causes of hypogonadism in men
hypogonadism causes may be congenital pathology - the complete absence of testicles undescended or in the scrotum. The most spread genetic cause of hypogonadism is Klinefelter's syndrome, which occurs every 500th boy. In this case, there may be compacted testicles, long legs and high waist.
Kallmann syndrome is associated with a defect in the production of hormones by the hypothalamus, occurs ten times less. hypogonadism also accompanied by rare genetic diseases - syndrome Bardet-Biedl and Prader-Willi.
More common acquired hypogonadism. It provokes:
- Injuries genitals, testicular torsion;
- Orchitis, epididymitis and other inflammatory processes in the scrotum;
- Surgical intervention;
- Tumors of the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus;
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy;
- Exposure to toxins;
- Hormone deficiency;
- Infectious diseases.
Symptoms of hypogonadism in men
As testosterone affects the muscle and bone mass and the distribution of adipose tissue, the symptoms associated with abnormalities in these parameters. In addition, the manifestation of disease depends on the age at which the disease emerged. Before puberty is high-pitched voice, disproportionate growth, the postponement of fat in the buttocks and hips, pale skin.
Symptoms in case of hypogonadism after puberty are:
- The lack of hair on the face;
- Small member (5 cm);
- Weak potency;
- Immature prostate;
- Obesity;
- Inelastic skin.
Diagnosis of hypogonadism in men
The doctor-andrologist with suspected infertility examines the genitals, inquiring about the presence of injuries, operations in a patient learns about hereditary diseases relatives. He also appoints the semen analysis. The results can reveal a violation of the structure of sperm.
If you suspect that hypogonadism is measured testosterone levels and gonadotropins in blood. When the concentration of the primary form of male hormones is lowered, the secondary - enhanced. Also, your doctor may prescribe a CT scan or MRI of the pituitary.
treatment of hypogonadism in men
Treatment depends on the clinical form and expressed violations. To get rid of some factors can be enough tablets for the other - an operation is needed.
After curing the underlying disease, the therapy reduces to normalize the level of testosterone in the blood - 12-33 nmol / l. To a blood test for testosterone was accurate, it is recommended not to eat, do not smoke and do not engage in sports before serum surrender. For greater reliability of the blood is better to pass several times - on different days in the same time in different clinics.
If the results of the analysis showed abnormalities, treatment basis is hormone replacement therapy. Course drugs prescribed individually.
A source: http://xn--90agcboqvgr.net/article/muzhskoj-gipogonadizm-prichiny-simptomy-i-lechenie/
Hypogonadism in men: what is it and why there

hypogonadism syndrome in males is termed "androgen deficiency" and "testicular failure."
It is a complex clinical and laboratory symptoms that arise due to a deficiency in the male male sex hormones. Can it both because of a disease of the testes, and as a result of a number of other reasons.
Read more about them, and about the symptoms, diagnosis and principles of treatment of this disease, you will learn from this article.
Types of hypogonadism in men
Depending on the level of destruction of isolated hypogonadism:
- primary or hypergonadotrophic (directly pathology arises from the gonads - the testes; pituitary gonadotropins level thus increased);
- secondary, or hypogonadotropic (caused by disruption of the structure and function of the pituitary or hypothalamus; concentration of gonadotropin in the blood is reduced);
- normogonadotropic (pituitary disorders associated with, accompanied by a high content in blood prolactin levels, normal - gonadotropins);
- associated with reduced sensitivity of the target organs to male sex hormones.
Depending on the age of the patient, which developed hypogonadism, it is divided into:
- embryonic (violations occur already in utero);
- prepubertal (aged 0 to 12 years);
- postpubertatnom (disease occurs in people older than 12 years).
According to the causal factors:
- congenital;
- acquired;
- idiopathic (if you can not identify the cause).
Causes and mechanism of development
Primary congenital hypogonadism occurs when:
- true Klinefelter syndrome (blood level of testosterone is reduced by half);
- anorchia (pathology of the testes, their complete absence);
- Turner's syndrome.
Primary acquired hypogonadism is caused by:
- testicular injury;
- radiation or chemotherapy due to cancer of the body;
- defeat testicular toxic substances of a different kind;
- untimely (late) the treatment of cryptorchidism;
- false Klinefelter syndrome (pathology have sets of chromosomes, and there is a lack of function of the cells that produce testosterone).
By innate secondary hypogonadism result:
- Kallman's syndrome (syndrome delay sexual development);
- reproductive syndrome (capable of fertilization) eunuch (occurs due to lack of blood luteinizing hormone);
- a number of genetic diseases associated with impaired blood levels of sex hormones (pituitary dwarfism, congenital panhypopituitarism and others).
The reasons for the same are acquired secondary hypogonadism:
Hypogonadism associated with androgen insensitivity target organs occurs when the deficit the body of female sex hormones (estrogens) or certain enzymes, as well as a result of disease receptors.
When hypergonadotropic hypogonadism pathological process is localized directly in the cells of the testes. In this connection breaks their ability to produce hormones, androgens, whose concentration in the blood, therefore, reduced.
See also:The causes of painful urination in men
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism is not fraught with damage of testicular tissue. It arises as a result of the defeat of the hypothalamic-pituitary region of the brain.
the hypothalamus and / or pituitary broken, blood levels of gonadotropin-releasing hormone produced by cells of the data structures is reduced or they are non-existent.
And the number of these hormones depends on testicular function directly - the amount produced by them androgens (gonadotropin stimulation in the absence of the testes is also absent, no sex hormones secreted).
When hypogonadism associated with end-organ resistance to androgens in the blood levels and gonadotropins, and in fact the male sex hormones are in the normal range. However, the functions do not perform androgens, because due to the pathology of receptors to target organs do not fall.
Another pathogenetic mechanism in hypogonadism in men is to increase the blood levels of a protein-binding globulin, or rather its varieties, linking sex hormones.
Thus biologically active testosterone is reduced, which results in symptoms of hypogonadism.
Such a condition leads one irreversible physiological processes - aging, as well as pathological - cirrhosis and hyperestrogenemia.
Clinical manifestations
Hypogonadism symptomatology varies on the age at which the pathology debut. So…
Symptoms of hypogonadism in men
Prepubertal hypogonadism is characterized by such symptoms:
- eunuchoid appearance (short body in combination with long limbs);
- if the blood concentration of growth hormone in the normal range - high growth if its level is insufficient - low growth, ie dwarfism;
- underdeveloped muscles;
- increase in the size of breast (gynaecomastia true);
- distribution of subcutaneous fat on the female type (with a maximum in the abdomen, buttocks and thighs);
- tall as a woman's voice;
- lack of hair in the armpits and pubic area;
- short (up to 5 cm) the penis;
- underdeveloped scrotum (without folding, pigmented, atonic);
- lack of sexual desire (it is called a syndrome unawakened libido);
- pale skin and visible mucous.
For the post-pubertal hypogonadism is characterized by:
- weakening, slowing erections (and spontaneous, and adequate);
- weakening of orgasm or no;
- absence of ejaculation;
- a sharp decline in libido;
- hair is thin, soft head;
- reduction of body hair on the face, in the armpits and groin, back, chest and so on;
- pale skin;
- penis is 9 cm or more in length;
- scrotum moderately pigmented, with a normal folding, atonic;
- palpable testes flabby, soft.
principles of diagnosis
Diagnostic algorithm is simple. The definitive diagnosis is based on the physician's assessment of the patient's complaints and anamnesis (history) his disease and life, objective status, taking into account the results of laboratory and instrumental methods research.
Anamnesis
There are important the following data:
- whether normal genitalia at birth;
- whether the operation on the genitals or the brain;
- whether the injury of these areas of the body;
- dynamics of sexual attraction (perhaps it was normal, and after any event reduced or absent; or vice versa - is not initially);
- nature of erections (and during sexual intercourse, and spontaneous);
- existence ejaculation;
- especially orgasm.
In order to evaluate the symptoms of hypogonadism leading many experts use special questionnaires, which fills the patient, and on the basis of the data the doctor makes the preliminary findings of his disease.
Evaluation objective status
The patient is measured height, waist circumference and body weight. These parameters are important in order to determine, on the female or male pattern formed by the patient's body, whether it corresponds to his age.
Also examine the state of the musculoskeletal system, breast (finding out whether gynecomastia), skin. Evaluate the nature of hair distribution, the structure of the external genitalia, testicular volume.
Methods of laboratory diagnostics
Determining the level of male sex hormones in the blood can help diagnose correctly.
Significant in the diagnosis of hypogonadism are those laboratory parameters:
- levels of total and free testosterone;
- concentration binding globulin androgens;
- content of gonadotrophic hormones (FSH and LH);
- prolactin;
- semen analysis.
Of course, the first 4 indicators measured in the serum.
diagnostics
Persons who have doctor suspects hypogonadism, conduct a pelvic ultrasound, but not through the front the abdominal wall, and with the use of an endorectal coil (ie, the study is carried out through direct intestine). This is necessary in order to get the most clear image on the monitor, such a study is more informative.
If you suspect a lesion of the hypothalamic-pituitary system to the patient is shown carrying out magnetic resonance imaging of the region of the brain.
diagnostic algorithm
So, if the patient has typical complaints after careful anamnesis (with emphasis on the causal factors of hypogonadism) and detection above clinical symptoms of this disease in the first place the doctor will prescribe to the patient analysis of the concentration of total testosterone in serum blood. If he is less than 12 nmol / L, will require more research in blood LH, follicle-stimulating hormone and prolactin. Depending on the results obtained and it will be determined hypogonadism form individual patient.
If the total testosterone level is more than 12 nmol / L, the next study will be to determine a blood globulin, androgen binding, and the free biologically active testosterone.
Based on these data the doctor will make one of two conclusions: either there is hypogonadism, or it is still there (in It designates the latter case the patient analysis of gonadotropins and prolactin level, whereupon appreciate embodiment hypogonadism).
Treatment
Treatment of this disease in men pursuing these goals:
- restore the concentration of androgen in the blood (this will result in the elimination of symptoms of hypogonadism);
- restore a man's ability to conceive a child.
In order to normalize the levels of male sex hormones in the blood, the patient is prescribed hormone replacement therapy with androgens. Patients receiving this treatment are subject to dynamic observation urologist: young persons - 1 once a year older - every 3-6 months. The survey includes:
- determining the concentration of free testosterone in the blood;
- determining therein the hemoglobin level, the hematocrit (This study necessary, since androgens increase the activity of bone marrow stem cells);
- cholesterol, lipoprotein cholesterol, ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase;
- men older than 40 years - the determination of blood concentrations of prostate-specific antigen;
- also in men older than 40 years - DRE (through the rectum) examination of the prostate gland.
In hypogonadotropic hypogonadism may be used drugs stimulating therapy. These include a hCG, which is administered intramuscularly, selecting the dosage for each individual patient depending upon the weight of his body. This drug stimulates production of androgens of testicular cells (of course, provided that their function is preserved).
With regard to the recovery of sperm's ability to fertilize, patients with hypogonadism hypergonadotropic it is very doubtful.
If there is a form of hypogonadotropic disease if testicular cells that synthesize the sperm is not damaged, the patient is prescribed gonadotropin preparations (luteinizing and / or follicle stimulating hormone Pregnil) that promote recovery and fertility.
Apply them long course - up to six months. Dose picked individually, depending on the serum levels of testosterone and semen analysis results.
In hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, the cause of which is a pathological process in hypothalamic-pituitary, to restore the ability of the drug is used to fertilize gonadodelin. It stimulates the pituitary gonadotropins. Assign it in the pulsed mode - specific dose administered every 1.5-2 hours.
In combination with medication the patient is a restorative therapy, healthy lifestyle, respect for work and rest, good nutrition and physiotherapy.
In some cases, you can not do without the intervention of the surgeon. Displacement operation varies depending on the pathology.
When the surgeon cryptorchidism task is to lower the testicle in the scrotum, in the absence of testicles - testicular implants synthetic (but it is carried out only for cosmetic purposes, to functions such interference will not affect reproductive apparatus), with hypoplasia of the penis - and so phalloplasty Further.
conclusion
Hypogonadism in men - it is a symptom that occurs as a result of deficiency in the blood of male sex hormones - androgens, either because of the insensitivity of the target organs them. Diseases that are associated with this pathology, many.
And they can be associated with both the egg and from the brain (namely - with the hypothalamic-pituitary system) are congenital or develop in the course of a lifetime. The main symptoms - changes in the reproductive system, infertility.
In the diagnosis of the main role is played by laboratory methods: evaluation of blood serum concentration total and free testosterone, gonadotropins, prolactin, and binding globulin sex hormones.
Based on these studies, as well as pelvic ultrasound and MRI of the hypothalamus and pituitary most cases, the doctor can not determine the final diagnosis and the patient appropriate treatment.
The latter usually includes hormones (androgens, gonadotropin, etc.), and in some cases require surgery (e.g., for the purpose of tumor removal).
The prognosis of hypogonadism in men varies depending on the initial pathology: in some cases it is possible restore and appearance, and the patient's fertility, while others - the ability to fertilize and not returns.
Prevention of this condition is to prevent effects on the causal factors, as well as in the careful attention to their health. After all, almost any disease is diagnosed at an early stage, it is much easier to remove, and it does not lead to serious health problems, including to hypogonadism.
To which the doctor ask
Treating the cause of hypogonadism is engaged endocrinologist. Additional aid may have andrologist and sexologist. For realization of reproductive function must often be treated by a reproductive system. If the cause of the disease is in the pituitary lesion is conducted neurosurgical operation.
Urologist tell of hypogonadism in men:
A source: https://myfamilydoctor.ru/gipogonadizm-u-muzhchin-chto-eto-i-pochemu-voznikaet/